What’s Really New with NewSQL?
引言
这篇文章是讨论新出现的被称之为NewSQL的数据库系统。数据库继SQL,NoSQL之后,一个新的发展方向。这篇文中给出了关于NewSQL的分类的讨论,还分析了现在NewSQL系统存在的技术挑战。Paper中将这些数据分为了三类,1. 全新的创建的型的数据库架构,2. 在支持的一些系统使用中间件实现的系统,3. 云计算厂商提供database-as-a-service产品,它们也是基于新的架构。
New Architectures
这类数据是指全新开发的使用多种新技术的数据库产品。代表作就是Google的Spanner。这些系统的几个特点:基于发分布式的架构,都是为分布式环境设计的,资源是shared-nothing的,有专门的组件用于支持分布式的并发控制,容错和复制,还有分布式查询技术;此类数据库的优点就是能够系统能够为多结点执行的进行专门的优化,比如为分布式环境优化的查询优化器。
这些DBMS的存储一般都是自己管理的(Google的Spanner是个例外,它的数据是保存在Google的分布式文件系统CFS上面的),这就因为这些系统不是使用现在的一些组件如HDFS,这样它们要自己负责管理这些资源。这样带来的还是就是它们可以实现将查询发送到数据那里,而不是将数据带到查询这里来。这样就显著的减少了数据传输的数量。 自己管理存储带来的另外一个好处就是可以实现更加精心设计的复制方法,通常这个可以是的系统获得更加好的性能。一些“SQL on Hadoop” 的系统直接利用的是例如Hbase之类的现有的一些东西,在这些系统的基础之上实现事务,这里Paper不将它们归类于NewSQL。
Managing their own storage also enables a DBMS to employ more sophisticated replication schemes than what is possible with the block-based replication scheme used in HDFS. In general, it allows these DBMSs to achieve better performance than other systems that are layered on top of other existing technologies; examples of this include the “SQL on Hadoop” systems like Trafodion and Splice Machine that provide transactions on top of Hbase. As such, we believe that such systems should not be considered NewSQL.
基于全新架构的DBMS的缺点就是数据库用户对这类系统的稳定性可靠性之类的存在一定的担心。另外就是与之前系统的不兼容,一些数据库如Clustrix和MemSQL,则通过兼容MySQL的wire protocol来避免这个问题。代表产品:
Clustrix , CockroachDB, Google Spanner, H-Store, HyPer, MemSQL, NuoDB, SAP HANA, VoltDB.
Transparent Sharding Middleware
这类指的是用于分片的数据库中间件,它们可以将一个数据拆分到多个数据库实例上面运行。这个与上个世纪啊90年代的数据联合技术不同,1. 它每个结点都运行相同的DBMS,2. 每个结点只有整个数据的一部分,3. 不能单独范围or更新。其核心的组件是查询路由、事务协调、数据位置管理、复制和跨结点分区。这类系统每个结点上一般会有一个填充层,代表中间价和本地的DBMS进行交互,执行查找并返回结果。这些中间件给使用者呈现的是一个理解上的数据库,而不同对原来的DBMS系统进行修改。
这类系统的优点在与可以保持对原来的应用程序的兼容性,整体上来说,实现这类系统的难度比前面的全新的架构要简单很多。虽然这里系统可以让数据库拓展到对个结点之上,但是每个结点上面运行的还是传统的DBMS,这样就不能利用现在的很多一些专门为现在环境的优化。比如不能很好的利用现在多核的CPU和充足的内存。代表产品:
AgilData Scalable Cluster 2, MariaDB MaxScale, ScaleArc, ScaleBase3.
Database-as-a-Service
这类系统随着云计算而兴起,这类数据库的管理、配置、调优、复制和备份等都是由DBaaS完成的。用户只要付钱就行。
As in most aspects of cloud computing, the largest companies are the major players in the DBaaS field due to the economies of scale. But almost all of the DBaaSs just provide a managed instance of a traditional, single-node DBMS.
这些产品很多时候还是使用的是传统的数据。但是也有一些是新数据库架构的产品,比如Amazon的Aurora。代表产品:
Amazon Aurora, ClearDB.
最新技术
这里是Paper中讨论的这些系统使用的一些关键的新的技术,有一个总结性的表格:
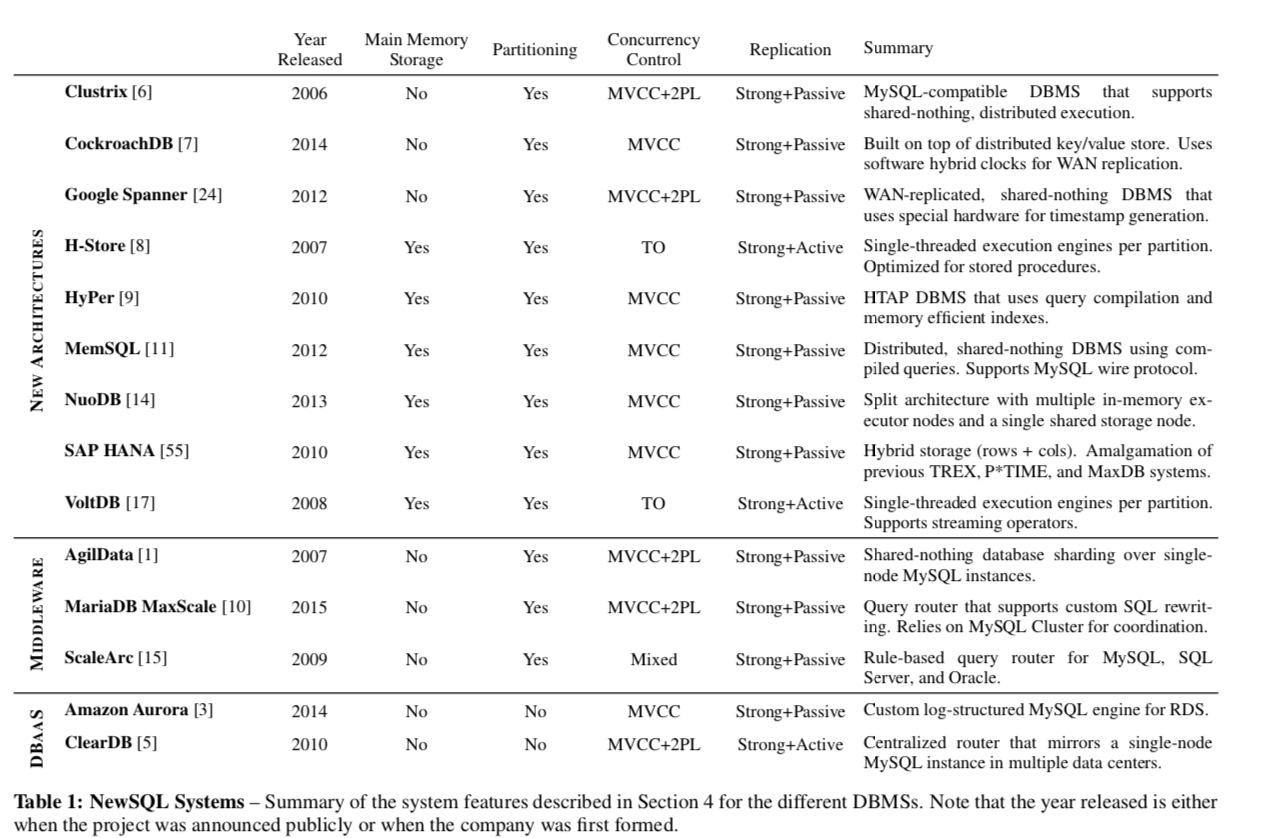
Main Memory Storage
这类系统最大的特点就是数据保存在内存中,系统的各个方面比如并发控制、数据存储等等方面都为内存专门做了一话,代表系统是Hyper、HStore等。关于在内存数据上面的存储管理、并发控制、事务和持久化、备份等等这里近些年由不少的研究,可以参看相关的论文。这里将数据都保存在内存中的系统未来容纳比内存更加大的数据,它们可以实现在必要的时候将一部分数据驱逐到磁盘上面取,这里的工作方式和传统数据buffer pool的方式不同。一个例子就是Anti-Caching架构的HStore。
Partitioning / Sharding & Concurrency Control
分布式数据库为了横向拓展都采用了分片的方式。这样就要求数据能在多个分区上面执行查询操作,并将这些数据合并之后返回。另外的一个技术就是将相关的数据能够放在同一个结点之上,这样可以避免很多跨结点操作的开销,提高系统的性能。 此外,这类系统的结点数量要求是支持可以变化的,因为总是会有机器故障之类的发生,另外就是随着数据的增长需要添加新的结点。这样也就意味着分片也得是可以变化的,并支持一些在线迁移or复制的功能。并发控制在数据库中一直是一个很核心的功能,对于这些新设计的NewSQL,很多都避免使用2PL之类的方式。较多使用的是MVCC的方式。也有的系统将其结合到一起,比如Google的Spanner。对于使用中间件的系统,一吧都继承的低层使用的数据库的方式,
All of the middleware and DBaaS services inherit the con- currency control scheme of their underlying DBMS architec- ture; since most of them use MySQL, this makes them 2PL with MVCC systems.
虽然这些并发控制的机制在新的系统之上会有一些区别,但是没有什么很多的区别,基本的原理没有发生很大的变化,
In general, we find that there is nothing significantly new about the core concurrency control schemes in NewSQL systems other than laudable engineering to make these algorithms work well in the context of modern hardware and distributed operating environments.
Secondary Indexes
次级索引的一个最重要的问题就是如何分片。前面说过,很多NewSQL的数据都是分片保存在不同的结点之上的,而这些数据分片几乎都是按照主键来的,这也是最自然的方式。但是如何在这些按主键分片的数据上面构建次级索引呢?在分布式的数据中,这里的问题关键是2个:
- 在哪里保存这些次级索引;
- 如何维持这些索引;
对于使用中间件的系统在协调器和分片结点都可以保存次级索引,
In a system with a centralized coordinator, like with sharding middleware, secondary indexes can reside on both the coordinator node and the shard nodes. The advantage of this approach is that there is only a single version of the index in the entire system, and thus it is easier to maintain.
对于新架构的系统则都是非中心化、分片的。系统中的每个节点都只存储索引的一部分。这里的分区的索引和一个结点拥有全部索引一个权衡就是,前者的查询可能需要跨多个节点来查找所需要的内容, 但如一个事务更新了索引, 它就只需要修改一个节点结点上的索引数据。在一个结点有全部索引数据的方法中, 这里刚好是相反的。这里也有的系统使用了一种两层的结构,
An example of a decentralized secondary index that mixes both of these concepts is in Clustrix. The DBMS first maintains a replicated, coarse-grained (i.e., range-based) index at each node that maps values to partitions. This mapping allows the DBMS to route queries to the appropriate node using an attribute that is not the table’s partitioning attribute. These queries will then access a second partitioned index at that node that maps exact values to tuples.
Replication & Crash Recovery
复制时实现高可用的一个最基本的方式,复制的方法遇到的一个最重要的问题就是一致性的问题,这里面的内容很多。具体了解还是参看相关的论文or结合一些实例来看,
The first is how the DBMS enforces data consistency across nodes. In a strongly consistent DBMS, a transaction’s writes must be acknowledged and installed at all replicas before that transaction is considered committed (i.e., durable).
...
which has additional overhead and can lead to stalls if a node fails or if there is a network partition/delay. This is why NoSQL systems opt for a weakly consistent model (also called eventual consistency) where not all replicas have to acknowledge a modification before the DBMS notifies the application that the write succeeded.
除了一致性的问题,另外的一个问题就是如何复制这里数据,这里常用的时两种方式,一种叫做active-active,就是每一个副本上面都只想系统的请求,可以理解为这里复制的都是数据执行的命令;另外一种方式是active- passive,这些请求只在一个结点上面处理,在处理之后将数据复制到其它的副本上面。大部分的系统使用费的第二种方式。其中一个重要的原因就是保证命令执行的顺序是一个很复杂的问题(有的以系统的顺序执行也会得到不同的结果,比如使用了now()函数之类的命令,不同的结点命令执行的时间几乎是不可能同时的,这样now()返回的数据在不同的副本上面就会不一样)
Most NewSQL DBMSs implement this second approach because they use a non-deterministic concurrency control scheme. This means that they cannot send queries to replicas as they arrive on the master because they may get executed in a different order on the replicas and the state of the databases will diverge at each replica. This is because their execution order depends on several factors, including network delays, cache stalls, and clock skew.
系统数据recovery的基本方法就是WAL。在分布式的NewSQL中,这个比单结点的数据要复杂不少。使用中间件的价格一般主要依赖于低层使用的DBMS,并添加了如leader election之类的东西。使用新架构的NewSQL则利用一些如Paxos算法之类的。
总结
这篇文章只是总一个大体上谈了NewSQL的分类,和它们相关的技术。作为一个大概的了解还是很不错的,
More long term, we believe that there will be a convergence of features in the four classes of systems that we discussed here:
(1) the older DBMSs from the 1980-1990s,
(2) the OLAP data warehouses from the 2000s,
(3) the NoSQL DBMSs from the 2000s, and
(4) the NewSQL DBMSs from the 2010s.
We expect that all of the key systems in these groups will support some form of the relational model and SQL (if they do not already), as well as both OLTP operations and OLAP queries together like HTAP DBMSs. When this occurs, such labels will be meaningless.
参考
- What’s Really New with NewSQL? SIGMOD Record, June 2016 (Vol. 45, No. 2).
