Windows Azure Storage: A Highly Available Cloud Storage Service with Strong Consistency
引言
Windows Azure Storage是微软的分布式存储系统。与其它公司的一些存储系统不同,WAS一个特点就是提供了多样化的抽象,支持Blob、Table和Queue的抽象。
In WAS, data is stored durably using both local and geographic replication to facilitate disaster recovery. Currently, WAS storage comes in the form of Blobs (files), Tables (structured storage), and Queues (message delivery). In this paper, we describe the WAS architecture, global namespace, and data model, as well as its resource provisioning, load balancing, and replication systems.
基本架构
WAS主要由两部分组成,一是Location Service,二是Storage Stamp。
- Storage Stamp由N(一般为10 - 20个)个机柜的存储结点组成,是一个独立的容错的单元。这里的一个设计目标是保持设备的高的利用率,这个目标的值为70%,避免超过80%,保持一定的富余处理特殊的情况。当一个Storage Stamp达到了超过了这样的利用率之后,使用inter-stamp的复制的方式来降低单个stamp上面的利用率。
- Location Service (LS),LS管理所有的Stamp。这里用户访问的入口使用的是URL的方式。LS负责更新DNS里面的信息。LS自身也使用异地复制的方式来保持一个高的可用性。
为了异地容错,这里WAS会将数据保存在3个不同地理区域。当一个请求一个新的账户时,LS会选择一个地理位置上比较靠近的数据中心内的一个stamp最为primary的stamp,然后LS保存这些相关的元数据,并通知stamp相关信息。之后更新DNS的信息,
The LS then updates DNS to allow requests to now route from the name https://AccountName.service.core.windows.net/ to that storage stamp’s virtual IP (VIP, an IP address the storage stamp exposes for external traffic).
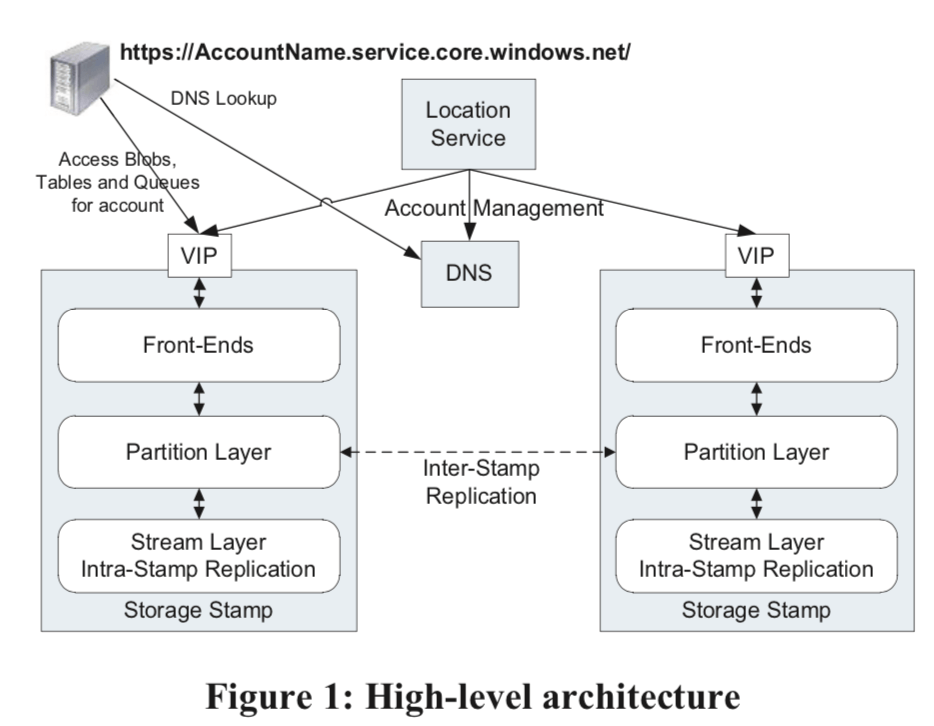
WAS由三层组成:
-
Stream Layer,提供时间的的数据存储和数据复制,这一层负责的是在一个stamp之内的。这里可以看作是一个stamp之内的文件系统。
The stream layer can be thought of as a distributed file system layer within a stamp. It understands files, called “streams” (which are ordered lists of large storage chunks called “extents”), how to store them, how to replicate them, etc., but it does not understand higher level object constructs or their semantics. -
Partition Layer,提供数据抽象,WAS支持的三种的数据抽象由它来实现,依赖于Stream Layer。Partition Layer提供的数据复制是stmap之间的复制,
The partition layer is built for (a) managing and understanding higher level data abstractions (Blob, Table, Queue), (b) providing a scalable object namespace, (c) providing transaction ordering and strong consistency for objects, (d) storing object data on top of the stream layer, and (e) caching object data to reduce disk I/O. -
Front-End (FE) layer,这一层相对来说比较简单。是一个访问资源的代理。接收client的请求,然后请求Partition Layer完成之间的操作,然后返回结果给client。
关于WAS的复制也是在Stream Layer和Partition Layer里面的:
- Intra-Stamp Replication (stream layer),这里保证数据在一个stamp之内的持久化。其复制操作是同步的。这里会将数据跨结点和fault domains来保持数据的可用性。由于这里是同步的复制,且在client写请求的关键路径上面,这里只有在复制成功之后才可以给client返回成功的信息,所以这里实现低延时的操作很关键。
- Inter-Stamp Replication (partition layer),这里的复制是stmap之间的异步的复制。复制操作在后台完成,不在client写请求的关键路径之上。这里的复制是对象级别的复制,与此对应的Intra-Stamp的复制则是复制数据block。
Stream Layer
Stream Layer为Partition Layer提供类似文件相同的API,但是知识类似。其文件操作和很多的分布式存储系统一样,也是append-only的。
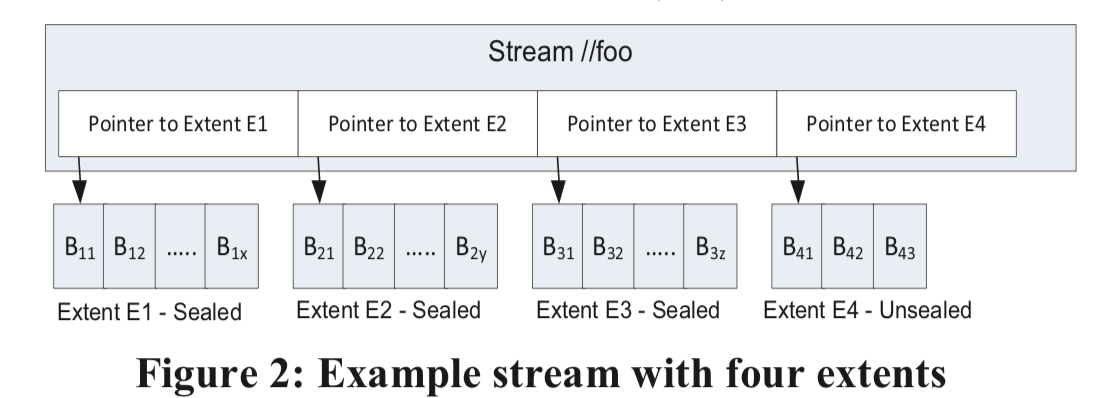
... which contains (pointers to) four extents (E1, E2, E3, and E4). Each extent contains a set of blocks that were appended to it. E1, E2 and E3 are sealed extents. It means that they can no longer be appended to; only the last extent in a stream (E4) can be appended to. If an application reads the data of the stream from beginning to end, it would get the block contents of the extents in the order of E1, E2, E3 and E4.
这里一个熟悉的stram由extent组成,这些extent按照一定的规则排序好。一个extent则是若干数了的block组成。
- Block是数据读取写入的最基本的单元。Block的大小会设置一个上限(默认是4MB),但并不代表Block的大小都是相等的。数据校验也是在Block上的。
- Extent是Stream Layer中复制的单元,默认在一个Stamp里面复制三份。每一个extent被保存为一个NTFS上面的文件。Extent的目标大小文1GB,保存小文件的时候会在一个Exent保存若干个,而对于超大型的blob,则会被拆分为对个Extent来保存,这里拆分的工作在Partition Layer完成,由它复制保存这个blob和具体存储的一些信息。
- Streams,它是一个排序的保存extent位置信息的list。每个Stream会有一个有层级的命名空间。对于Partition Layer来说,一个Stream就是一个巨大的文件。一个Stream里面只有只有最后一个extent可以进行添加操作,其余的都是不可变的。
Stream Layer具体还有个更加复杂的架构,它有Stream Manager (SM)和Extent Node (EN)两个主要部分组成。
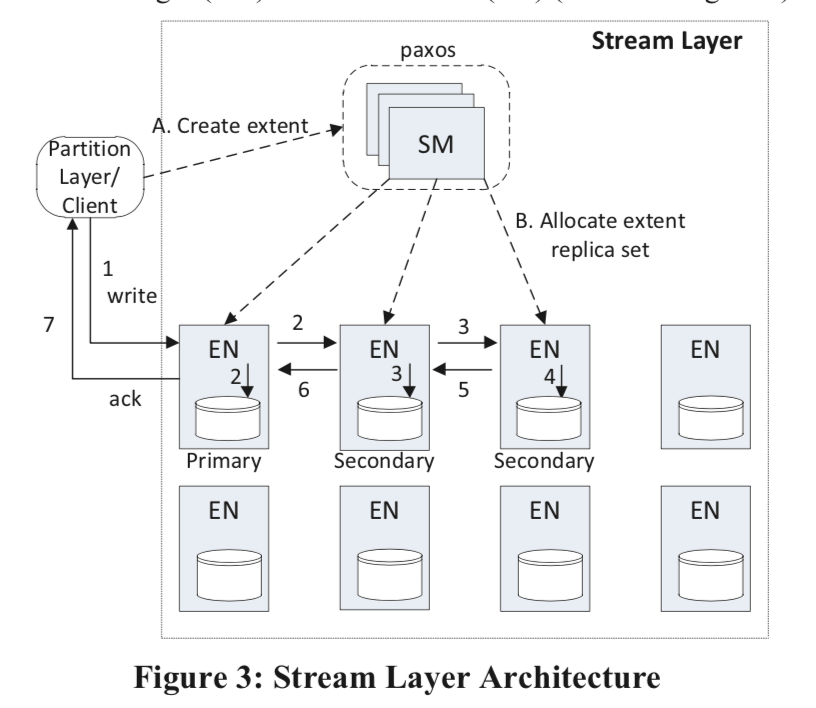
-
Stream Manager是一个Paxos集群。它负责下面的一些任务:
The SM is responsible for (a) maintaining the stream namespace and state of all active streams and extents, (b) monitoring the health of the ENs, (c) creating and assigning extents to ENs, (d) performing the lazy re-replication of extent replicas that are lost due to hardware failures or unavailability, (e) garbage collecting extents that are no longer pointed to by any stream, and (f) scheduling the erasure coding of extent data according to stream policy.它使用定期轮询ENs的方式来获取extent是的最新的信息。如果发现由于故障等的原因导致来一个extent的副本的数量低于预期,会重新添加副本,这里和很多的分布式存储的相同类型。而Extent保存的位置有其随机地挑选不同容错区域。 Stream Manager知道的信息层面只是Extent层面的,也就是说它不知道Block的信息。从上面的图中可以看出,clien写请求的时候,append block不需要Stream Manager的参与。这里和GFS一个类似的地方就是Stream Manager得信息也是保存在内存里面的,
Since the stream and extent state is only tracked within a single stamp, the amount of state can be kept small enough to fit in the SM’s memory. The only client of the stream layer is the partition layer, and the partition layer and stream layer are co-designed so that they will not use more than 50 million extents and no more than 100,000 streams for a single storage stamp given our current stamp sizes. -
Extent Nodes (EN),EN复制保存Stream Manager指定的Extent的副本。它只知道Extents和Blocks的信息,对Stream并不知情。EN将Extent保存为一个文件,除了保存Block和其的chucksum之外,还保存了一个Exent Offset到Block和文件位置的映射关系,一个EN可以知道它自己保存的Exents和Blocks之外,还知道一个Extent的副本的信息。ENs之间的复制是通过复制append的Block来完成的。
添加Block的时候支持一次性原子地添加多个Block。这里和GFS一样会有重复记录得问题,如果一个Client一个请求添加的操作失败的时候,重复该请求,这个时候就可能导致重复的数据Block存在,这里需要应用(这里就是Partition Layer)能够处理这样的情况。这里重复请求或者seal一个Extent的时候,会以commit-length最小的为准。
Stream Layer Intra-Stamp Replication
为了保持一个强一致性,这里Stream Layer提供如下的保证:
1. Once a record is appended and acknowledged back to the client, any later reads of that record from any replica will see the same data (the data is immutable).
2. Once an extent is sealed, any reads from any sealed replica will always see the same contents of the extent.
在一个Stream被创建的时候,SM会为这个Stream分配三个EN来保存第一个Extent,一个primary和两个secondary。这些信息会被返回给Client。Client的请求总是有primary来完成,primary负责向secondary添加数据,当都返回成功时,才认为添加成功。每一次添加操作的时候,primary要负责完成下面的事情:
- 决定添加到的Extent的offset,
- 对并发的请求进行排序;
- 将数据append到选择好的offset的后面;
- 所以的append操作都返回成功之后才给Client返回成功;
As appends commit in order for a replica, the last append position is considered to be the current commit length of the replica. We ensure that the bits are the same between all replicas by the fact that the primary EN for an extent never changes, ...
当一个Extent增长到一定的大小的时候,就需要对去进行sealing操作。这个是在ENs里面完成的。SM会首先询问三个数据副本这个Extent的长度。当发现长度不等的时候会选择最小的长度做为sealing的长度。这样做并不会导致数据丢失,因为primary只会在都保存成功的时候才返回成功,
Once the sealing is done, the commit length of the extent will never be changed. If an EN was not reachable by the SM during the sealing process but later becomes reachable, the SM will force the EN to synchronize the given extent to the chosen commit length. This ensures that once an extent is sealed, all its available replicas (the ones the SM can eventually reach) are bitwise identical.
这里关于这里Paper中还有一些读取模式和优化的讨论。
Partition Layer
Partition Layer则是在Stream Layer的基础上实现其它的功能,主要负责的任务如下:
(a) data model for the different types of objects stored,
(b) logic and semantics to process the different types of objects,
(c) massively scalable namespace for the objects,
(d) load balancing to access objects across the available partition servers, and
(e) transaction ordering and strong consistency for access to objects.
在这里的一个重要的内部结构就是Object Table (OT),可能是一个数PB级别的一个巨大的表。这么大的表是必须分区保存的。OT会被动态地划分为RangePartition。Partition Map Table 负责保存RangePartitions到partition server得映射关系,用于路由Front End的请求。架构图:
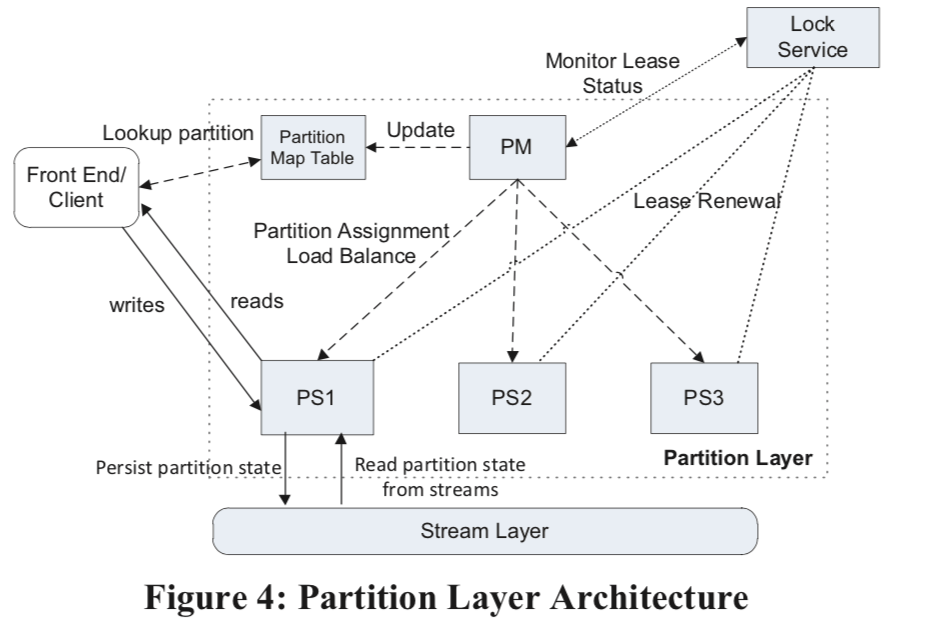
-
Partition Manager (PM),负责将Object Tables划分为RangePartitions,在交给Partition Server保存。这些信息会被PM保存到Partition Map Table中。PM会保证每一个RangePartition同一时刻只会被分配到一个PS,这里就要利用到Lock Service,不同的RangePartition之间是不会有重叠的。这里还负责处理负载均衡的问题。
-
Partition Server (PS) ,复制处理PM分配的RangePartitions上面的请求。这里的数据都交给Stream Layer保存。
maintains a memory cache of the partition state for efficiency. The system guarantees that no two partition servers can serve the same RangePartition at the same time by using leases with the Lock Service. This allows the PS to provide strong consistency and ordering of concurrent transactions to objects for a RangePartition it is serving. A PS can concurrently serve multiple RangePartitions from different OTs. -
Lock Service,这个是个类似于Chubby的系统,PM的领导选举和PS的服务租约都需要用到这个lock service。这里做的方式也和使用Chubby的没有很大的不同。从上面的图中看,这里是处理Partition Layer之外的,是一个单独的lock service。
RangePartition也是使用了LSM-tree来持久化保存数据,每一个RangePartition又一组的Stream组成:Metadata Stream,Commit Log Stream,Row Data Stream,Blob Data Stream。内存中的Memtable功能就是LSM-tree中的Memtable,保存最近更新的一些信息。此外还使用Index Cache来Cache index的数据,Row Data Cache缓存的就是行数据。 当一个写入请求到达 RangePartition得时候,操作的信息会先被append到Commit Log 中,然后被添加到Memtable里面。这里时候就可以返回client成功的信息了。当Memtable或者Commit Log Stream达到一定的大小的时候,Memtable就会被持久化保存到row data stream中,这个时候Commit Log Stream也就可以移除了。这里也就相当于一个checkpoint,为了减少checkpo的数量,PS会定期地合并它们。
评估
这里详细的信息参看[1].
参考
- Windows Azure Storage: A Highly Available Cloud Storage Service with Strong Consistency, SOSP’11.
