PNUTS and Cassandra
引言
PNUTS是雅虎开发的一个类似的Amazon Dynamo的系统,不同的Dynamo的是,PNUTS提供了更加多样化的一致性的支持,这个系统是非开源的。而Cassandra是facebook主导开发的一个类似的系统。
数据模型
Cassandra和PNUTS之间的数据模型是很相似的,类似于Bigtable的表格的特点。在这样的一种模型上面,抽象为类似传统数据库一样的table,每个table可以由若干的指定类似的列。由于Cassandra和PNUTS本质上还是key-value的系统,它们进行删除更新等的操作的时候还是只能根据primary key来处理。下面是Cassandra的主要的接口:
• insert(table,key,rowMutation)
• get(table,key,columnName)
• delete(table,key,columnName)
columnName can refer to a specific column within a column family, a column family, a super column family, or a column within a super column.
一致性模型
PNUTS和Cassandra在一致性的一个相同点就是只支持在单行上面的事务,这点和Bigtable也相同的。 雅虎在它的应用中认为仅仅就是简单的最终一致的系统不能满足一些的要求,
PNUTS provides a consistency model that is between the two extremes of general serializability and eventual consistency. Our model stems from our earlier observation that web applications typically manipulate one record at a time, while different records may have activity with different geographic locality.
PNUTS这里的一致性模型是基于per-record timeline consistency,即一个记录上面的更新的操作都是以相同的顺序应用到所有的副本上面的。实现这种模型的基本的方式就是指定副本中的一个为Master。对于一条记录的Master根据workload自动调整。一条记录会携带一个sequence number,在每一次更新操作的时候就会递增,
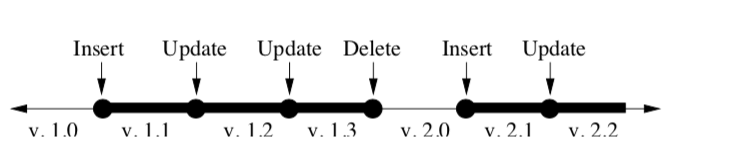
如上面的图所示,这个 sequence number是由两个部分组成的,一个是添加删除操作导致的generation的变化,一个是更新操作导致的version的变化。这里只会保存一个version。在此的基础之上有以下的一致性的支持:
-
Read-any,返回任何一个稳定版本的记录,这个记录不会保证是最新的;
-
Read-critical(required version),读取一个数据的要求就是他的版本号不能比指定的旧;
-
Read-latest,读取一条记录的最新版本,这里的延时要明显大于读取任意版本的;
-
Write,直接更新一条记录;
-
Test-and-set-write(required version),只有在一条记录的版本是指定的时候才能进行更新操作。这个在实现单行事务的时候很有用,
This call can be used to implement transactions that first read a record, and then do a write to the record based on the read, e.g., incrementing the value of a counter. The test-and-set write ensures that two such concurrent increment transactions are properly serialized. ... Of course, if the need arises, our API can be packaged into the traditional BEGIN TRANSACTION and COMMIT for single-row transactions, at the cost of losing expressiveness.
为了低的延时,PNUTS使用的是异步地在副本上面应用更新的方式,这里使用了雅虎自己的message broker,一个publish/subscribe的系统。上面的提到的一致性的模型的实现也基本就是基于这个系统。PNUTS这个的Master是在record级别上面的,也就是说不同的记录可能是不同的master,这样有利于提高系统的性能和吞吐量。而且写操作在雅虎的实践中,这条记录的Master和操作的发起者有85%左右的都是在同一个数据中心。然后,对于非Master的副本,使用的就是雅虎的pub/sub系统来处理,这里会保证操作的顺序是按照写操作提交的顺序来的。这里的在一体记录上面的更新不一定就等直接请求这条记录的Master,也可以直接请求一个非Master副本,不过这个副本必须将这个操作转发给Master,这样来保证操作顺序的要求。对于一条记录的Master的信息,保存在这条记录的元数据中,
Each record maintains, in a hidden metadata field, the identity of the current master. If a storage unit receives a set() request, it first reads the record to determine if it is the master, and if not, what replica to forward the request to. The mastership of a record can mi- grate between replicas.
这里的Master是会根据系统运行的状态变化的。为了保证在primary key上面的约束条件,一个key的添加操作必须发送给同一个存储结点。对于同时的添加操作,就由这个存储结点来决定那一个操作成功。为了实现这个也是指定一个tablet的副本为tablet master,将这些操作发送给这个副本。这里的master和记录基本的Master不一定是相同的。
Cassandra
对于Cassandra的一致性模型,在Cassandra的论文[2]没有仔细讨论,不过在其它的一些资料中有说明[3]。在Cassandra中也是支持不同的一致性基本(当然也都是弱一致性的)。
基本架构
在PNUTS中,数据可以按照字典顺心和Hash两种方式来分布。Table的数据被水平切分为tablet,这些tablets被保存到若干的服务器上面,这一个服务器上面可能保存数千的tablets。当然同一个tablet在一个服务器上面只会被保存一份。一般的tablet大小到MB到小几GB的级别。为了负载平衡,tablet的分布可以被动态地调整。
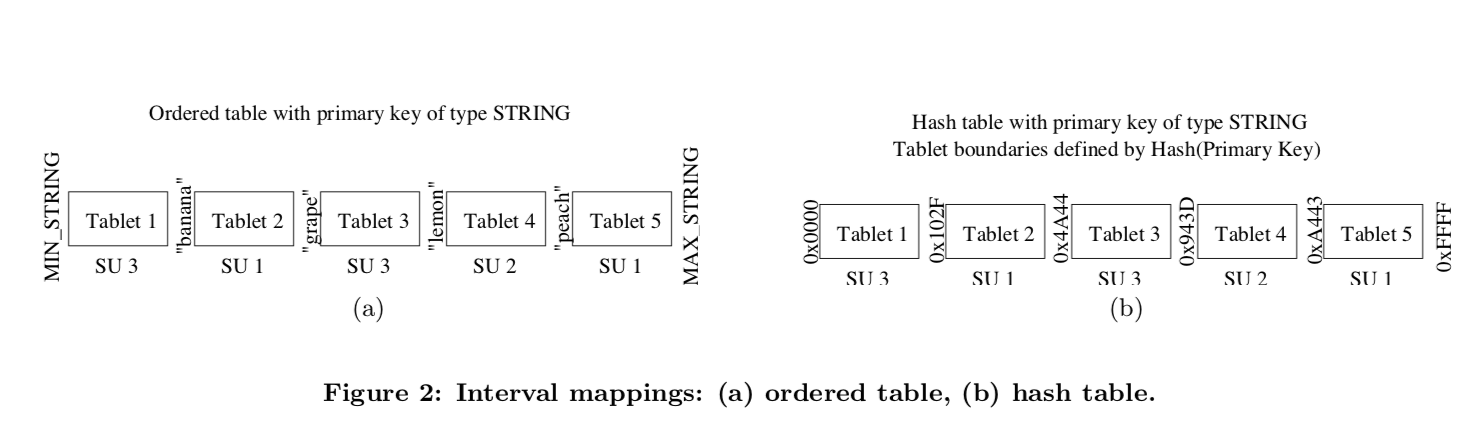
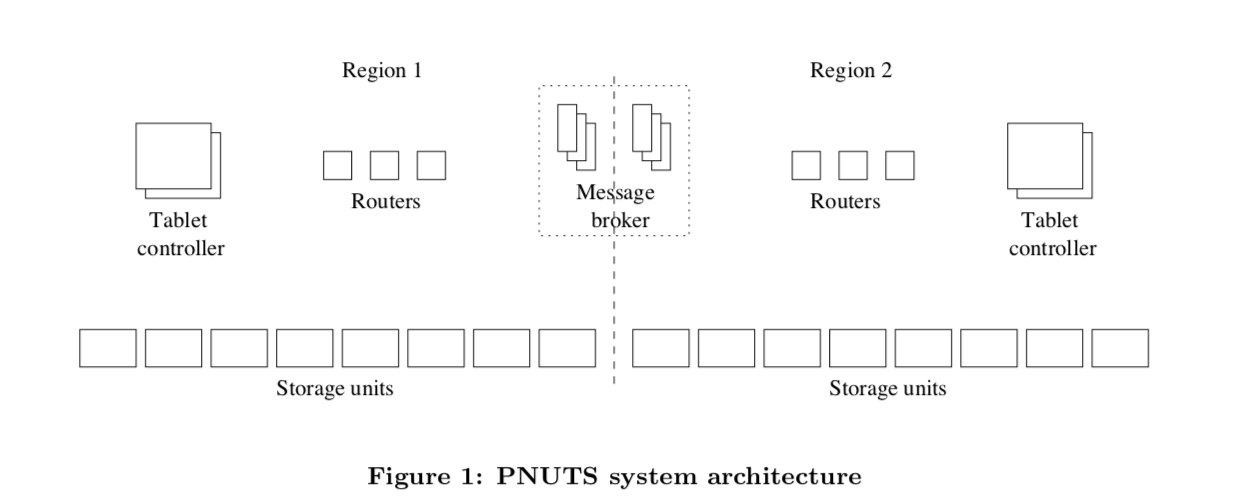
下面的图大概表示了PNUTS的架构。这里主要是3个足迹,一个存储单元负责保存数据,负责处理set get之类的请求。一个写的操作在提交之前会被先写入到message broker中。这里的storage unit可以使用雅虎自己实现的一种hash table,也可以只用MySQL,
The storage unit can use any physical storage layer that is appropriate. For hash tables, our implementation uses a UNIX filesystem-based hash table implemented originally for Yahoo!’s user database. For ordered tables, we use MySQL with InnoDB because it stores records ordered by primary key. Schema flexibility is provided for both storage engines by storing records as parsed JSON objects.
为了知道一条记录被保存在哪一个storage unit上面,这里使用的就是router。对于sorted的存储方式,这里就使用primary的分区方式找到对应的区间。对于Hash的存储方式,使用的使用hash分区。这些那一个storage unit保存哪些tablet的信息只是被缓存在routers的内存中(这样操作的时候就可以获得很好的性能)。真正拥有这些数据的是tablet controller,这些tablet的分裂和移动也都是tablet controller决定的。这里Massage Broker就是前面已经提到的过的pub/sub系统。
与PNUTS的分区方式不同,Cassandra使用的方式更加像Dynamo的方式,使用的是基于一致性hash的方式。在Dynamo中,一个物理的结点会对应多个虚拟上的环的位置。而在Cassandra中,为了实现更加好的负载均衡,使用的方式是分析结点负载来决定的方法,
The basic consistent hashing algorithm presents some challenges. First, the random position assignment of each node on the ring leads to non-uniform data and load distribution. Second, the basic algorithm is oblivious to the heterogeneity in the performance of nodes. Typically there exist two ways to address this issue: One is for nodes to get assigned to multiple positions in the circle (like in Dynamo), and the second is to analyze load information on the ring and have lightly loaded nodes move on the ring to alleviate heavily loaded nodes. Cassandra opts for the latter as it makes the design and implementation very tractable and helps to make very deterministic choices about load balancing.
Cassandra的写入操作的过程与PNUTS的相差比较大,
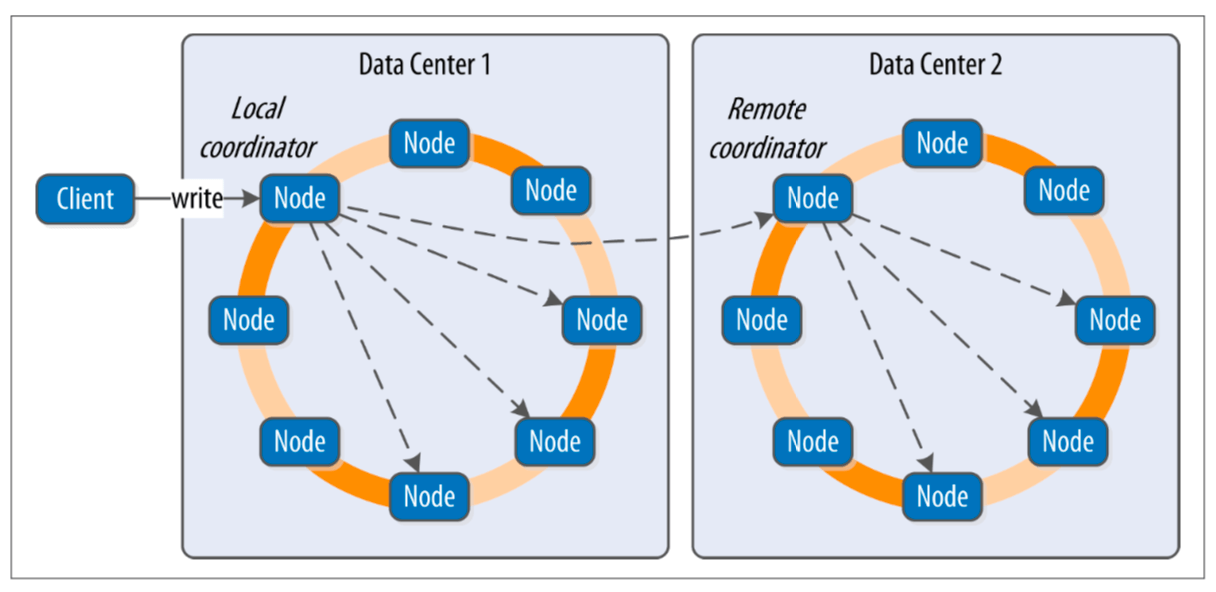
(上面图片来自[3])
客户端将写操作的请求发送给对于key的coordinator结点,这个结点在接受到这个请求之后,如果发现存在满足一致性要求的副本的数量,就同时地给这些副本发送写操作的请求。那些在这个时间内不能正常工作的结点在恢复之后会从其它的结点新的数据。如果如上面的如所示,副本跨越来不止一个的数据中心,另外的数据中心的写操作是发送给另外的数据中心里面的coordinator完成的。
评估
参看论文[1,2]。
参考
- PNUTS: Yahoo!’s Hosted Data Serving Platform, VLDB ‘08.
- Cassandra - A Decentralized Structured Storage System.
- Cassandra: The Definitive Guide
