Amazon Aurora: Design Considerations for High Throughput Cloud-Native Relational Databases
引言
Aurora是Amazon的分布式数据库,为云环境设计,这篇Paper发表在SIGMOD2017上,从整体上介绍了Amazon Aurora。Aurora有很多有意思的创新的地方。这篇文章中主要讨论了三个问题:
1. How to reason about durability at cloud scale and how to design quorum systems that are resilient to correlated failures. (Section 2).
2. How to leverage smart storage by offloading the lower quarter of a traditional database to this tier. (Section 3).
3. How to eliminate multi-phase synchronization, crash recovery and checkpointing in distributed storage (Section 4).
可拓展和可用性存储
可拓展和可用性使用副本是一个最常用的办法,在这里Aurora也不例外。之前在Amazon中有使用过的基于Quorum的协议也被用用在Aurora这里。在Aurora中,数据会被默认保存为6份,分布在3个不同的AZ(Availability Zone),写入使用6/4的Quorum协议,即写入的时候有4个副本返回成功就代表成功,读区使用3/6,3 + 4 > 6。这里不是常见的复制3份基于以下的考虑是因为Aurora认为三副本的设置无法容忍一些同时出现的故障,
hese failures may be spread independently across nodes in each of AZ A, B and C. However, the failure of AZ C, due to a fire, roof failure, flood, etc, will break quorum for any of the replicas that concurrently have failures in AZ A or AZ B. At that point, in a 2/3 read quorum model, we will have lost two copies and will be unable to determine if the third is up to date. In other words, while the individual failures of replicas in each of the AZs are uncorrelated, the failure of an AZ is a correlated failure of all disks and nodes in that AZ.
使用了这样的副本机制之后,Aurora可以做到:1. 一整个AZ加上另外一结点的故障不会导致数据的丢失,也不会影响到读取的可用性,2.任意2个节点or 一整个AZ的故障不会影响到写入操作。
Segmented Storage
为了出现故障时候能影响到更加少的数据和更快的恢复,Aurora将数据分成段来管理,每一个段的大小为10GB,每6个构成一个Protection Groups (PGs) ,目前支持最大的存储空间为64TB。低层是用的Amazon EC2 的存储。
These are each replicated 6 ways into Protection Groups (PGs) so that each PG consists of six 10GB segments, organized across three AZs, with two segments in each AZ. A storage volume is a concatenated set of PGs, physically implemented using a large fleet of storage nodes that are provisioned as virtual hosts with attached SSDs using Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2). The PGs that constitute a volume are allocated as the volume grows.
在10Gpbs的网络喜爱,Aurora可以做到一个数据段的故障在10s就恢复,所以只有在10s遇到2个及以上的数据段故障的时候才会影响到可用性。
The Log is Database
Aurora中最核心的一个概念就是The Log is Database了。在一般的MySQL写数据会写入多次,如LOG,数据Page,还有就是Double Write和BinLog等带来的写入,这样加起来就远远超过了数据原来的大小。这个在多副本的情况下变得更加严重(这个写放大的问题在很多的存储系统中都存在),下面的一个图就是表示出了MySQL写入的数据:
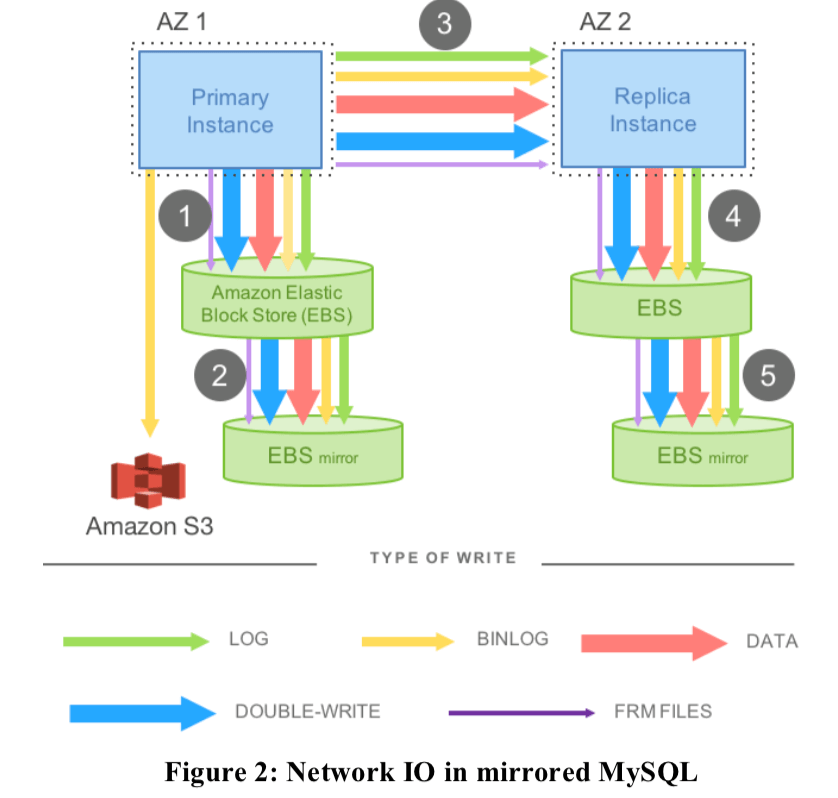
FRM: finally the metadata (FRM) files,这个的数据量比较小。而未来解决这个问题,在Aurora中,把大部分的东西都取消了,只需要写log即可。下面是一个实例图:
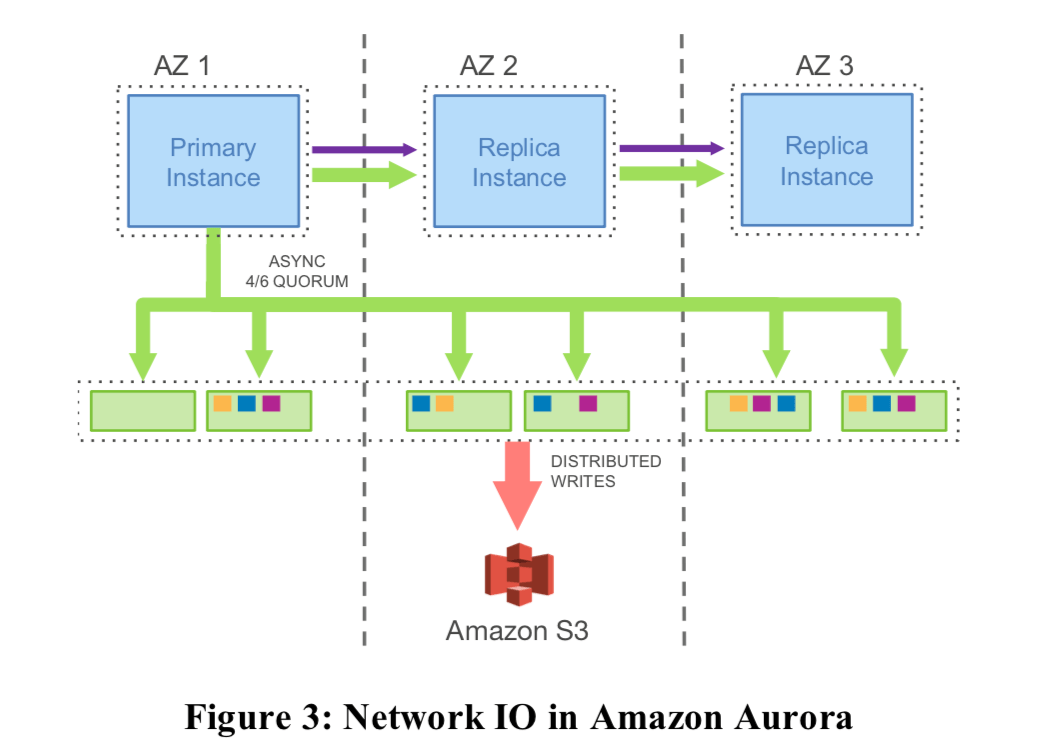
在数据库的redo log中,是包含了全部的数据信息的。也就是说只要有了redo log,就使用这个恢复出数据page来。在读取page的时候,如果这个page不是最新的,就需要存储层是用redo log构造出新的page来。
No pages are ever written from the database tier, not for background writes, not for checkpointing, and not for cache eviction. Instead, the log applicator is pushed to the storage tier where it can be used to generate database pages in background or on demand.
这里从redo log中恢复出数据page来的工作在存储层完成,这个工作是运行在后台异步完成的。这种方式显著地减少了网络通信的流量。在传统的数据中,在Crash之后重启需要从最近的checkpoint开始将redo log里面的记录进行重放。而在Auroara中,这一些都不是有数据库计算部分完成的,它也就不需要做这些工作,所以在Auroara中,Crash之后的恢复就是简单的重启即可。
存储层设计要点
存储的最重要的设计原则就是尽量减少前台的请求的响应时间,这里大部分的工作都是在后台完成的。在存储节点上面,有着不同的任务,Aurora根据目前系统额负载情况将CPU分配给哪些人物,比如在负载比较高的时候,就减少旧版本数据的回收之类的工作。下面的图表示了Aurora的数据流动:
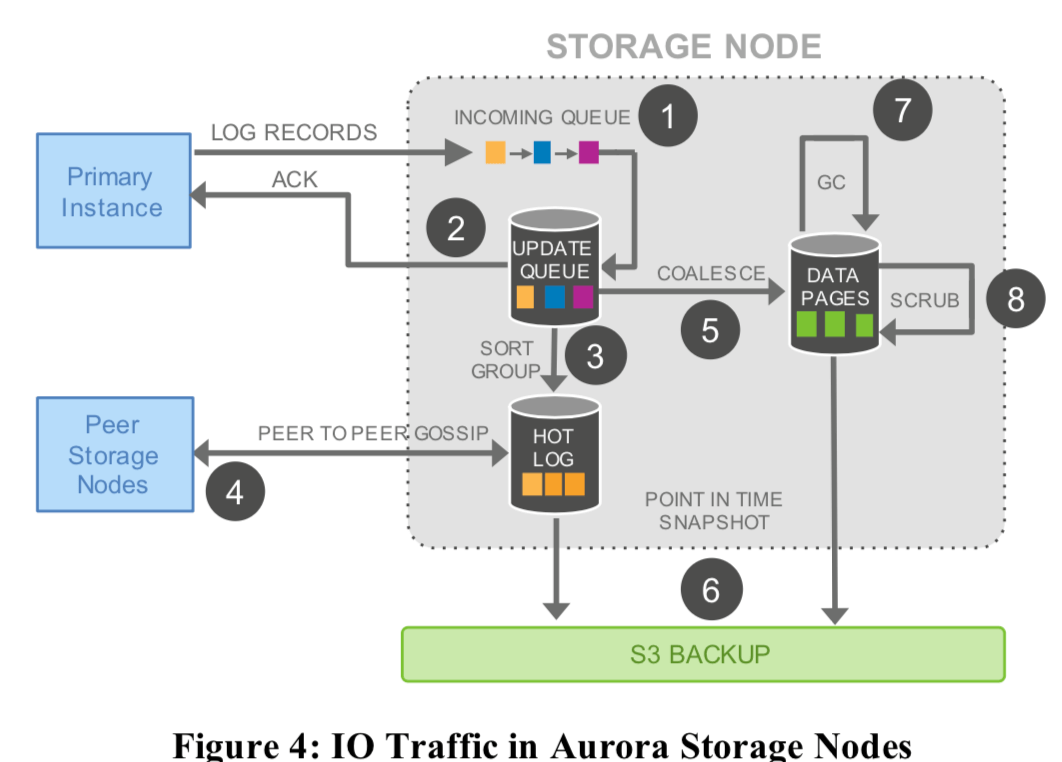
步骤:
- 存储结点在接受到日志记录之后在其添加到内存中的队列中;
- 在持久化这个log之后,回复数据实例,表示工作已经完成;
- 组织好日志,因为这里Aurora的工作方式,这里可能有些redo log是不全的,这里要去确认;
- 如果这里发现了缺失的log,使用基于gossip协议的方法从其它的存储结点获取缺失的log;
- 将这些redo log转化为数据page;
- 周期性地将log和数据page备份到S3;
- 周期性地回收旧的无用的数据;
- 周期性地对数据进行CRC校验;
这里只有第1 2步是串行同步处理的,其余都是异步处理的。
The Log Marches Forward
这里讨论的就是log的一致性的问题。
几个关键的概念
Aurora不使用2PC之类的提交协议,而是利用了数据库redo log中的LSN来解决一致性的问题。ARIES风格的WAL每一个redo log record都由一个单调递增的LSN标示。由于这里使用的Qurom协议,这样有些结点可能会缺失一部分的数据,这里使用gossip协议补充完整,在读取时需要访问日志完整的结点。如何发现这些缺失的日志呢?在结点出现异常的时候如何决定某些事务是应该提交还是回滚呢?这里先Aurora中几个关键的概念的解释:
- Volume Complete LSN(VCL),这里是存储层可以保证可以提供的redo log的最大的LSN。在恢复的过程中,大于这个VCL的redo log都需要被截断(也就是丢弃了);
- Consistency Point LSNs(CPLs),在MySQL之类的数据中,一个事务可能会产生多条的redo log,也就是说一个完整的事务log可能是一组的日志,而前面说到的VCL可能就处于一组日志的中间,这个事务的信息在这里就是不完整的;
- 所以这里又定义了the Volume Durable LSN(VDL),是已经持久化的COLs中LSN最大的,这里很显然满足VDL <= VCL。所以这里大于VDL的日志都需要被截断;
The database can, however, further constrain a subset of points that are allowable for truncation by tagging log records and identifying them as CPLs or Consistency Point LSNs. We therefore define VDL or the Volume Durable LSN as the highest CPL that is smaller than or equal to VCL and truncate all log records with LSN greater than the VDL. For example, even if we have the complete data up to LSN 1007, the database may have declared that only 900, 1000, and 1100 are CPLs, in which case, we must truncate at 1000. We are complete to 1007, but only durable to 1000.
正常情况下的操作
-
写入,正常情况下,数据库向存储层发送redo log,在达到了指定的Quorum之后标志为持久化。在一个事务的所有redo log都持久化之后,就可以推进VDL。由于在任意的时刻都有可能存在大量的正在执行的事务,每一个事务产生各自的log。未来避免过量的log没有被标记为持久化,这里定义了一个LSN Allocation Limit (LAL)(默认为10m),表示了目前的LSN和VDL不能超过的最大的差值。
这里还有一个问题就是Aurora是按段来保存数据的,这样就有可以一个段里面只有一个事务的部分的日志。这里Aurora这每一条log中保存了前一条log的链接信息。这里有引入了另外的一个概念就是Segment Complete LSN(SCL)代表了完整日志的点,通过这个发现缺失的log,使用gossip从其它结点补全,补全之后可以将其向前推进。
-
提交,Aurora中提交的操作是异步的。一个客户端提交操作的时候,每一个事务Aurora保存一个代表了这个事务的commit LSN。工作线程将这个提交的任务挂载在一个等待提交完成的list上。当VDL大于一个事务的commit LSN之后,就代表了这个事务已经成功提交完毕,这个时候就可以回复客户端。这样的好处就是工作线程可以在提交的时候继续工作,提高了性能。
-
读取,这里Aurora的一个特点就是buffer pool里面的数据page在缺失的时候会从存储层读区,但是这些page从来不会写入到存储层,在不需要的时候就是直接丢弃。emmmm,这里论文的描述很模糊,好像也存在一些矛盾的地方。这里Aurora只说了要保存一个结点上面的数据page必须是新的数据(这里要处理的一个问题就是这个数据在一个结点被修改了,这个数据page的副本可能在其它结点的buffer pool里面)。这里Aurora通过使用前面的VDL就可以不使用read quorum。这里通过读取完整VDL的结点就可以保证得到最新的数据,
The database can then select a storage node that is complete with respect to the read point, knowing that it will therefore receive an up to date version. A page that is returned by the storage node must be consistent with the expected semantics of a mini-transaction (MTR) in the database. Since the database directly manages feeding log records to storage nodes and tracking progress (i.e., the SCL of each segment), it normally knows which segment is capable of satisfying a read (the segments whose SCL is greater than the read-point) and thus can issue a read request directly to a segment that has sufficient data.这里还有几个概念就是Minimum Read Point LSN 和Protection Group Min Read Point LSN (PGMRPL),分别代表了副本会读取的最小的LSN和整个的最小的会读取的LSN,这样就可以用来回收旧的不会再使用的数据。
-
复制,在Aurora中,一个写结点可以最多带15个读结点,它们挂在在一个共享的存储上。这样,添加读区副本就可以不增加存储开销。这里写入结点的日志既发给存储层,有发给读结点。在读结点上,如果发现一个redo log对应的数据page不在buffer pool中,表示这个时候不需要对自己buffer pool里面的数据page进行更新,这个时候直接丢弃就可以了。如果存在,则要进行更新操作。这里的操作是异步的,不会影响到写结点。为了保证准确性,这里必须满足两点:1. 回放的日志的LSN <= VDL,这个是很显然的,未来避免回复之后没有被成功提交的数据;2. 这里必须原子性的回放mini-transaction的日志,保证看到的是一致的数据库。
The replica obeys the following two important rules while applying log records: (a) the only log records that will be applied are those whose LSN is less than or equal to the VDL, and (b) the log records that are part of a single mini-transaction are applied atomically in the replica's cache to ensure that the replica sees a consistent view of all database objects. In practice, each replica typically lags behind the writer by a short interval (20 ms or less).
Recovery
这里来比较一下Aurora的恢复机制和ARIES风格的WAL之间的区别。在后者中redo log、undo log以及checkpoint是几个核心的概念,在Aurora中,没有了checkpoint,因为它的redo log是一直在回放的,这些在存储层解决了。所以在恢复的时候第一步就是使用read quorum读取其它节点上面的redo log,更新VDL,
Once the database has established a read quorum for every PG it can recalculate the VDL above which data is truncated by generating a truncation range that annuls every log record after the new VDL, up to and including an end LSN which the database can prove is at least as high as the highest possible outstanding log record that could ever have been seen.
在Aurora中,没有提交事务的undo recovery的工作可以在online进行。
Put it All Together
下面的图就表示了Aurora的整体的架构:
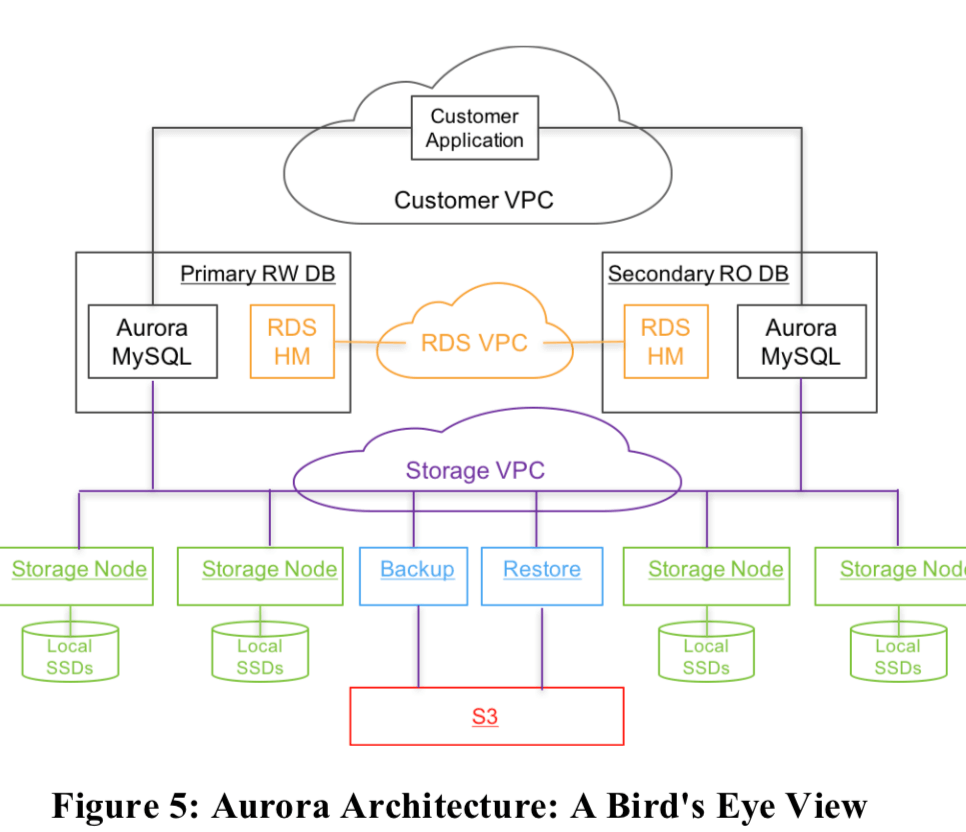
这里对MySQL进行了不少的修改(具体可参考论文[1]),计算和存储分离的架构。使用 Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS)作为控制面(control plane),RDS在每一个结点上面部署了一个agent叫做HM(Host Manager (HM)),负责监控实例的健康状况,决定是否异常,需要被替换。每一个数据实例有一个写入结点和0到多个读取的结点组成,跨AZ部署,
For security, we isolate the communication between the database, applications and storage. In practice, each database instance can communicate on three Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) networks: the customer VPC through which customer applications interact with the engine, the RDS VPC through which the database engine and control plane interact with each other, and the Storage VPC through which the database interacts with storage services.
存储服务是基于EC2,至少跨越了3个AZs。存储结点负责管理本地的SSD,并和存储引擎交互已经其它存储结点交换。备份使用的S3。此外这里还使用了DynamoDB来保存一些元数据,
The storage control plane uses the Amazon DynamoDB database service for persistent storage of cluster and storage volume configuration, volume metadata, and a detailed description of data backed up to S3.
评估
具体的信息可以参考论文[1].
参考
- Amazon Aurora: Design Considerations for High Throughput Cloud-Native Relational Databases, SIGMOD 2017.
