f4: Facebook’s Warm BLOB Storage System
F4使用设计和Haystack一起使用,来降低成本的对象存储系统,一个基本的出发点就是Haystack中保存的对象(比如图片)在刚刚一开始用户传上去的时候使用频繁,不久之后使用率就会大大降低。Haystack 3-备份的形式好处在于性能良好,缺点在与成本比较高。F4使用了Reed-Solomon编码在实现高可靠的同时将副本的数量降下来。
Overview
F4的数据都是从Haystack转移过来的,所以对于F4来说,它不需要insert的操作。F4只支持read和delete操作。通过10 + 4的所罗门编码blocks,每一个block的size为1GB:
The block-size for encoding is chosen to be a large value—typically 1 GB—for two reasons. First, it decreases the number of BLOBs that span multiple blocks and thus require multiple I/O operations to read. Second, it reduces the amount of per-block metadata that f4 needs to maintain.
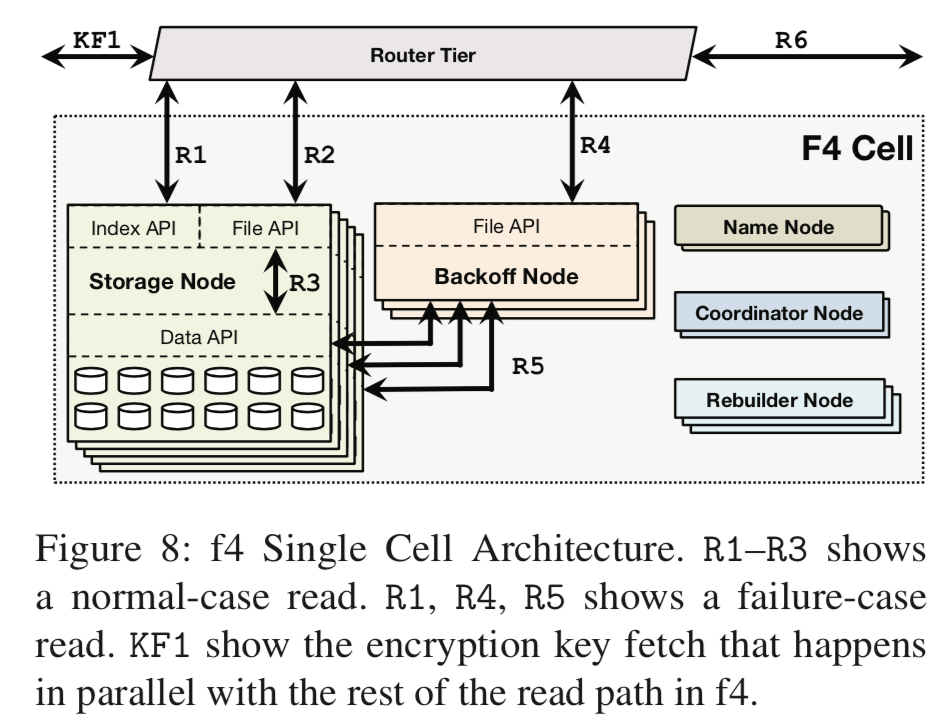
### 基本结构
Name Node
保存data block和parity block(所罗门编码生成的block)和storage node直接的映射关系,通过primary- backup来容错。
Storage Nodes
保存实际的索引和数据块:
...Index API. It stores the index—BLOB to data file, offset, and length—file on disk and loads them into custom data structures in memory. It also loads the location-map for each volume that maps offsets in data files to the physically-stored data blocks. Index files and location maps are pinned in memory to avoid disk seeks.
...
The Data API provides data access to the data and parity blocks the node stores. Normal-case reads are redirected to the appropriate storage node (R2) that then reads the BLOB directly from its enclosing data block (R3). Failure-case reads use the Data API to read companion and parity blocks needed to reconstruct the BLOB on a backoff node.
Backoff Nodes
负责在故障的情况下进行online reconstruction操作,是一个CPU密集的操作。
Each backoff node exposes a File API that receives reads from the router tier after a normal-case read fails (R4). The read request has already been mapped to a data file, offset, and length by a primary volume-server. The backoff volume-server sends reads of that length from the equivalent offsets from all n − 1 companion blocks and k parity blocks for the unavailable block (R5). Once it receives n responses it decodes them to reconstruct the requested BLOB.
Rebuilder Nodes
作为Backoff Nodes的补充,在故障的情况下恢复数据。
Rebuilder nodes are storage-less, CPU-heavy nodes that handle failure detec- tion and background reconstruction of data blocks. Each rebuilder node detects failure through probing and re- ports the failure to a coordinator node. It rebuilds blocks by fetching n companion or parity blocks from the failed block’s strip and decoding them.
Coordinator Nodes
类似一个管理者的功能,主要是调度block rebuilding等的任务。
A cell requires many maintenance task, such as scheduling block rebuilding and ensuring that the current data layout minimizes the chances of data unavailability. Coordinator nodes are storage-less, CPU-heavy nodes that handle these cell-wide tasks.
Fault Tolerance
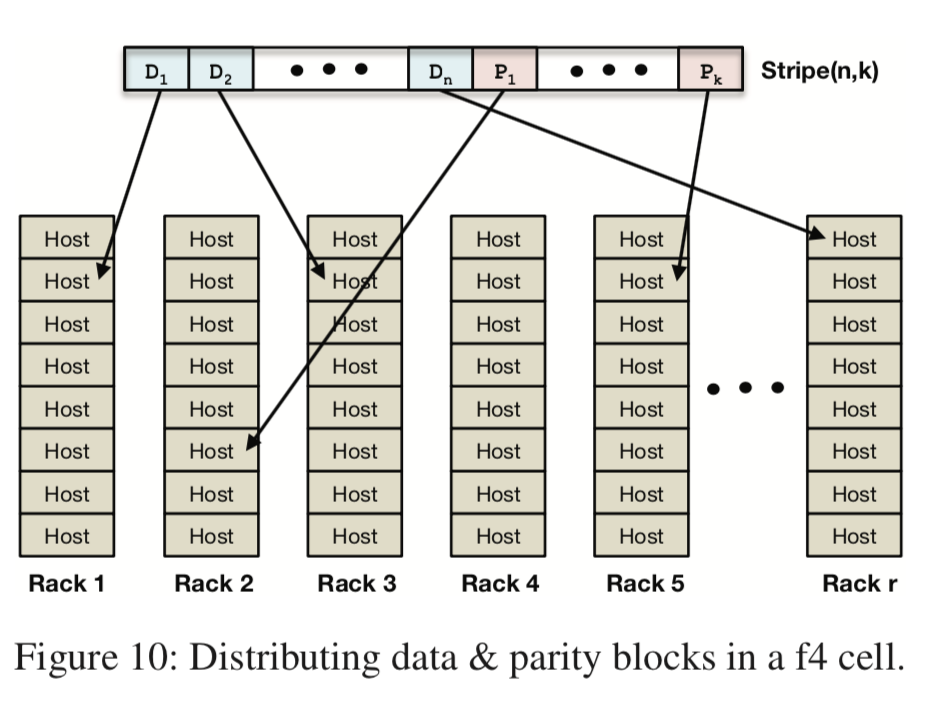
F4 单个cell可以磁盘,主机,机柜基本的错误,其次通过跨机房复制来容忍整个数据中心故障。 此外,F4对于block的分布是设计原则是尽可能的将相关数据的不同的block发布在不同的机柜里面。
Our current implementation initially lays out blocks making a best-effort to put each on a different rack. The placement balancer process detects and corrects any rare violations that place a stripe’s blocks on the same rack.
看法
对于这样的一个系统来说,单单看论文感觉挺无趣的。这样的分布式系统的难点也在与实现它,虽然看起来类型的系统总体都差不多。F4不用考了更新操作,也不用考了一致性之类的问题,自然看起来也简单了很多。
参考
- f4: Facebook’s Warm BLOB Storage System, OSDI 2014.
- Finding a needle in Haystack: Facebook’s photo storage, OSDI 2010.
