Log-structured Memory for DRAM-based Storage
引言
Log-structured的文件系统是很有名的一类文件系统了,其Log-structured设计的主要目的就是讲写入转化为顺序写来提高性能。而这篇文章在Main-Memory的存储系统是讨论了Log-structured的内存分配,主要目的是提高内存利用率,此外就是提高性能。这个是RAMCloud系统的一部分。
动机
通用的使用malloc(or类似方式)的内存管理方式的一个缺点就是低的内存利用率:
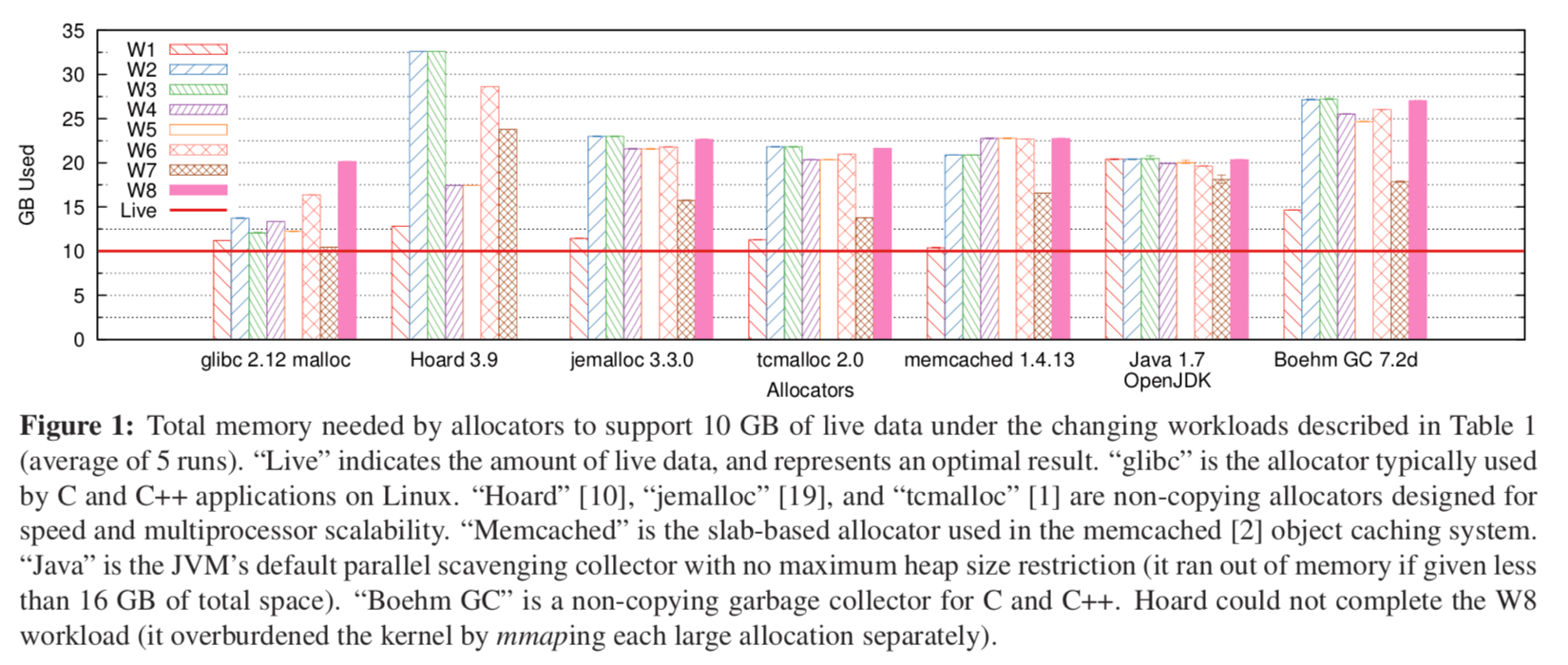
从这个图标来看,各个的利用率都很不好看。
基本设计
在看这里之前需要对Log-Structured File System有些了家,如果没有,可以看看论文[2]。这里的allocator时为RAMCloud设计的,这里就可以把它看作是一个Key-Value Service。基本情况如下:
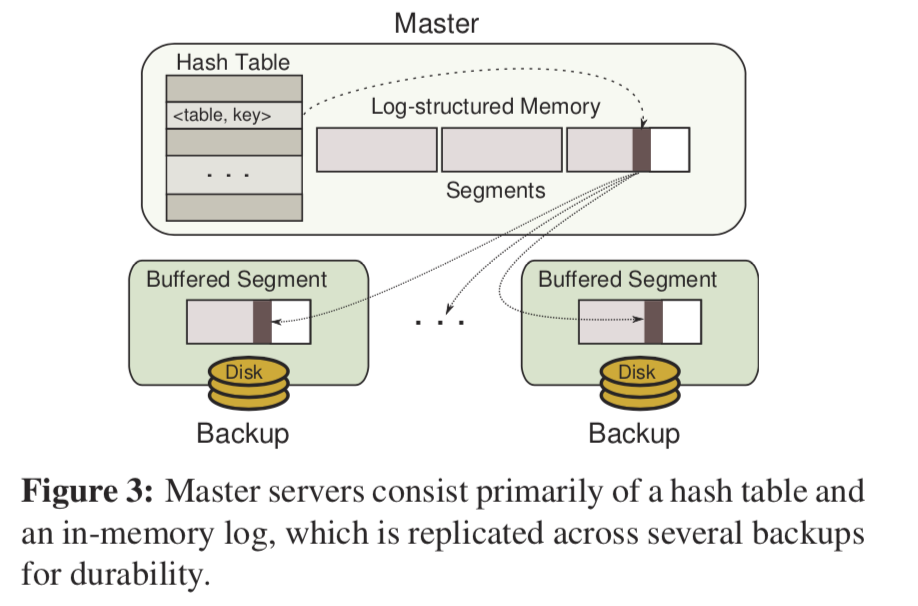
LFS中log包含了很多额外的索引的信息,为的是方便读取。由于DRAM的特点以及这个allocator不会存在文件系统那样的结构,所以log的结构上会简单很多。每一个object必须包含了以下的数据(paper中还讨论了很多关于从持久化的存储中recovery的内容,这里只关注这个内存分配器的设计,RAMCloud关于recovery有另外的论文):
- the table identifier,2. key, and 3. version number for the object in addition to its value 。
每个segment包含了整个log的信息摘要。删除一个object时候,是在log的后面添加一个tombstone记录,tombstone 包含了 table identifier, key,和 被删除object的version number。
Tombstones have proven to be a mixed blessing in RAMCloud: they provide a simple mechanism to prevent object resurrection, but they introduce additional prob- lems of their own. One problem is tombstone garbage collection. Tombstones must eventually be removed from the log, but this is only safe if the corresponding objects have been cleaned (so they will never be seen during crash recovery). To enable tombstone deletion, each tombstone includes the identifier of the segment containing the obsolete object. When the cleaner encounters a tombstone in the log, it checks the segment referenced in the tombstone. If that segment is no longer part of the log, then it must have been cleaned, so the old object no longer exists and the tombstone can be deleted. If the segment still exists in the log, then the tombstone must be preserved.
Two-level Cleaning
这里把内存分配出去比较简单,难点在于回收操作。 所以这里关于分配的就直接忽略了。回收操作这里就会遇到这样一些问题:
- 越高的内存利用率意味着越高的回收成本,因为利用率越高,segment里面活着的object越多,每次回收操作能得到的效果越差。这给系统造成了很大的成本。
- 另外一个与RAMCloud自己的特点有关,RAMCloud内存中的数据最终会被备份到持久化的存储单元上的。二在磁盘上做这些操作的成本更加高。
RAMCloud这里使用Two-level的清理方式,将磁盘和内存上的回收彼此分离。第1层的回收称为segment compaction ,只在内存中操作,讲原来的segment里面的存活的object拷贝到新的segment,回收原来的空间。第2层成为combined cleaning ,同时在内存和磁盘中操作。
Seglets
Seglets时是为了解决回收之后segment大小不相同的问题(在segment大小固定的情况下)。将segment拆分为seglet,每一个seglet为固定的64K大小。segment是一个seglet的集合,不在是固定的。
Parallel Cleaning
这里主要是要解决回收缓存中的contention的问题:
There are three points of contention between cleaner threads and service threads handling read and write requests. First, both cleaner and service threads need to add data at the head of the log. Second, the threads may conflict in updates to the hash table. Third, the cleaner must not free segments that are still in use by service threads. These issues and their solutions are discussed in the subsections below.
- cleaner线程和service线程同时使用log的问题;
- 同时更新hash table问题;
- 应该什么时候回收segment;
对于第1个问题,解决办法是cleaner和servic的线程使用不同的log segment;第2个问题就是直接使用lock了。对与第3个问题,实际上和现在的一些同步方法例如RCU,hard pointer之类的方法要解决的问题是相同的RAMCloud使用的方式当最近的请求都处理完成后就可以回收了。此外关于处理磁盘上备份的内容和deadlock避免的问题可以参考原论文。这里的重点就是如何回收内存吧。
评估
Log-structured的内存分配方式在RAMCloud中可以实现80 - 90%的内存利用率。利用率高是最吸引人的地方吧。
• RAMCloud supports memory utilizations of 80-90% without significant loss in performance.
• At high memory utilizations, two-level cleaning im- proves client throughput up to 6x over a single-level approach.
• Log-structured memory also makes sense for other DRAM-based storage systems, such as memcached.
参考
- Log-structured Memory for DRAM-based Storage. FAST 2014.
- The Design and Implementation of a Log-Structured File System, TOCS 1992.
