SLIK: Scalable Low-Latency Indexes for a Key-Value Store
引言
前面看过的Log-structured Memory for DRAM-based Storage是RAMCloud关于内存管理的部分,SLIK的RAMCloud中关于Key-Value的部分。SLIK最大的几个特点:
- multi-key-value store,这个事与一般的KVS最大的不同的一个地方,一般的系统都是一个key对应一个value,这个SLIK实现了类似次级索引的功能。Value和很多的KVS一样,都是当作一个bytes的对象而已;
- SLIK的索引和对象事分开的,而不是保存在一起;
- 由于分布式的方式能带来可拓展性的同时也带来的一致性的问题,这里SLIK可以保证对客户端可见的一致性。它使用了一种创新的轻量级的方式来更新索引。
- SLIK可以将耗时的操作放在后台运行,而不会影响到系统的正常运行;
- SLIK的次级索引使用的是Btree,使用映射到主键hash值的方法保持了Btree节点的紧凑性,这里就可能导致hash冲突的问题,如何解决这个问题之后会提到。
... the resulting system provides extremely low latency indexing and is highly scalable:
• SLIK performs index lookups in 11–13μs, which is only 2x the base latency of non-indexed reads.
• SLIK performs durable updates of indexed objects in 30–36 μs, which is also about 2x the base latency of non-indexed durable updates.
• The throughput of an index increases linearly as it is partitioned among more and more servers.
• SLIK’s latency is 5–90x lower than H-Store,a state-of-the-art in-memory database.
基本架构
未了支持多个索引,SLIK使用的是一种multi-key-value的格式来保存数据,一个数据由一个变长的value和若干个变长的key组成,在SLIK中,Value都是当作一个blob对象,不做任何其它意思的解释。SLIK将第一个key当作是primary key,其它的都是secondary key。secondary key不要求是唯一的,每一个secondary key会对应一个索引。SLIK的一个设计目标就是可以拓展到大规模的机器集群上面,所以分区是不可避免的。索引也会被分区未indexlets,这些保存在不同的机器之上,
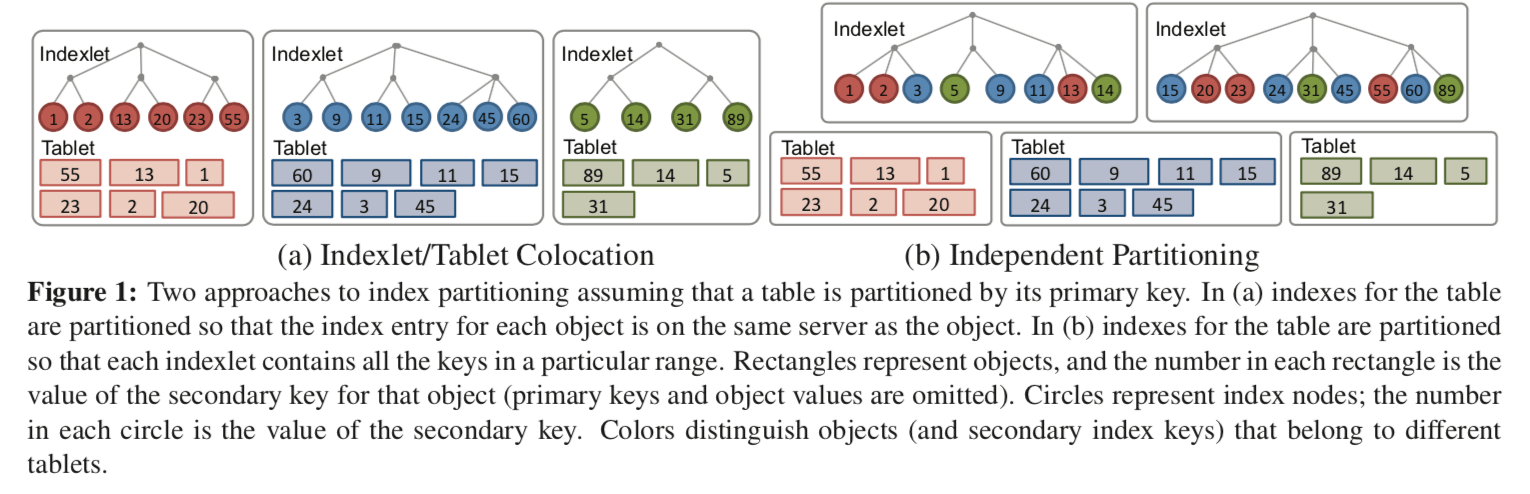
这里SLIK要处理的一个问题就是如何组成索引和数据,上面的图上表示了两种类型的分区的方法:
-
Colocation Approach,就是将索引的分区和数据的分区放在一起,一个分区内的数据会在这个分区内组织对应的索引结构。这种方式也是现在的很多的系统常用的一种方法,比如H-Store,Cassandra的。
We call this Colocation Approach, in which each server stores a table partition (or tablet) plus one indexlet for each of that table’s indexes. The indexlet stores only index entries for the tablet on the same server.这种方法的优点是在数据规模比较小的时候可以提供更加小的延时,因为索引和数据保存在一个结点之上,就可以避免在查找了索引之后,然后根据索引去其它的结点获取数据。缺点就是随着机器数量的增长,它的性能会下降非常明显。因为SLIK是支持多个索引的,因为找根据一个(非primary)的索引查找的时候,它是可能在任意的数据分区里面的,所以它的查找方式得是并发向所有的分区请求,这样的话机器数量的增长对它的性能影响非常大。
-
Independent Partitioning,第二种方式就是数据和索引是分开的,这样话查找操作是分为两步:查找数据对应的索引的分区,然后根据索引的信息去获取实际的数据,
In the first step, the client issues an RPC to the server holding the relevant indexlet. This can typically be processed entirely by a single index server. If the queried range spans multiple indexlets, then each of the corresponding servers is contacted. This RPC returns information to identify the matching objects. The client then contacts the relevant data servers to retrieve these objects.
这种方法的优点就是可拓展性更加好,缺点就是在一些情况下会增加延时。
- 这里还有第三种方式,在其它的一些系统上采用,基本思路就是使用第二种方法的同时,但是将一部分或者所有的数据每一个索引都复制一份。之中方法的缺点就是增加大量的内存使用(这样的话添加的操作也会变得更加复杂了),优点就是既满足查找低延时的同时又提供了很好的拓展性。这种方法SLIK这里没用使用。
正常操作下的一致性
由于SLIK是将对象和索引分开的,这样的话如何解决索引和数据之间的一致性的问题就是SLIK必须要考虑的。这里的一些系统是发送了一致性,允许出现索引和对应数据的不一致可以简化系统、提高性能。也有一些系统使用了复杂的方式来实现这些操作是原子的,不过这个会提高系统的复杂性和可能降低系统的可拓展性。SLIK这里可以保证以下两个特点:
- 一个对象保护次级索引,那么一个索引参考能够返回这个对象;
- 如果一个对象进程索引查找被返回,那么这个对象包含了在这个指定范围内的key。
为了实现这些特点,SLIK使用了叫做ordered write approach的方式,
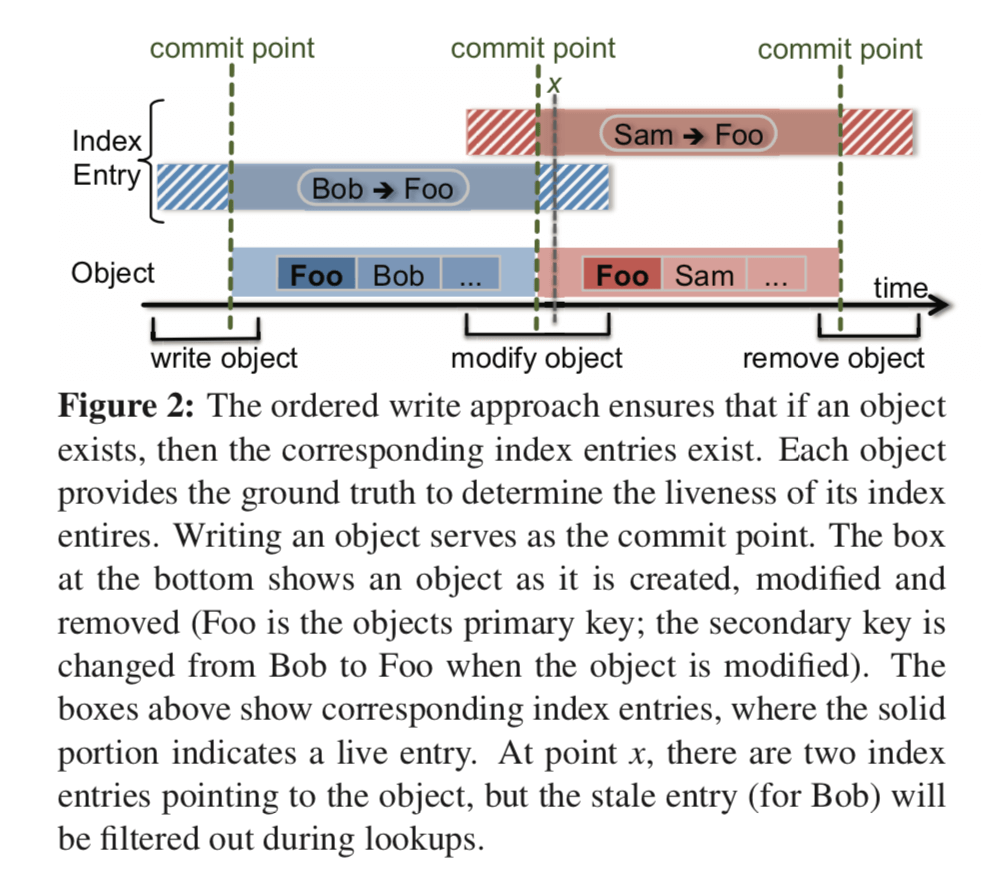
上面这个图比较清晰的表示出了这个机制的基本的思路:index entry存在的生命周期要长于对象存在的生命周期。SLIK对于添加一个对象是,是先添加对象对于的索引项,然后在添加对象本身。在需要的时候还要去删除旧的索引项。
Specifically, when a data server receives a write request, it first issues requests (to the server(s) with relevant indexlets) for creating index entries corresponding to each of the secondary keys in the new object’s data. Then it writes the object and replicates it durably. Finally, it asynchronously issues requests (again, to the server(s) with relevant indexlets) for removing old index entries, if this was an overwrite. This means that if an object exists, then the index entries corresponding to it are guaranteed to exist – thus ensuring the first of the two consistency properties.
这样就可以满足性质中的第1条,但是不能满足第2条。查找操作还是有可能返回一个没有添加的对象,这里解决这个问题的方式是在客户端解决,客户端的库在使用次级索引查找到primary key的hash只之后,回去见检查这个对象是否正的存在。这样SLIK就可以实现上述的2条性质。在内部是存在不一致的,但是在客户端的时候将这个不一致隐藏了起来。
API
SLIK通过的API处理常见的Key-Value的get put之类的API之外,还有API为索引的操作提供了支持:
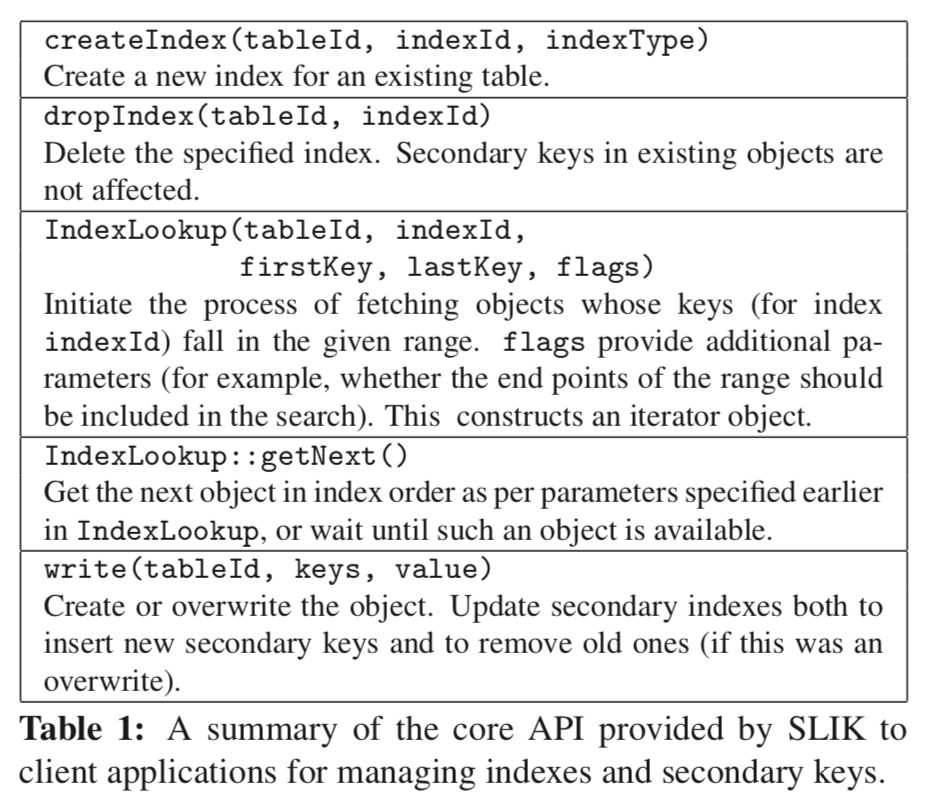
索引存储和持久化
这里主要讨论两个问题,先来看看前面说的使用映射到主键hash值的方法保持了Btree节点的紧凑性,不需要保存primary key,这里就可能导致hash冲突的问题。出现冲突的情况后,就可能导致出现返回额外的数据,这里会有额外的consistency algorithm解决,这里应该就是客户端处理这类情况。
It may occasionally select extra objects, but these extra objects get pruned out as a by-product of the consistency algorithm.
另外一个问题就是如何将索引持久化,SLIK的索引数据是一直保存在内存中的,数据当然也就是保存在内存中的,数据RAMCloud会有额外的机制进行持久化。对应索引的持久化,一种方法就是是用对象数据本身来重建这些index。RAMCloud中的一个设计目标就是在奔溃后能在几秒内就恢复,但是这种重建的方法是不能满足这个要求的,重建的话在大量的数据的时候可能花费相当上的时间。所以这个SLIK只能使用另外的一种方式,就是将这些索引的数据也持久化,索引数据会被备份带其它服务器上面去,在奔溃的时候会痛RAMCloud的快速恢复机制来恢复。这雨这部分的具体如何实现在几秒内就恢复这些数据,RAMCloud有另外的一篇论文,可以参考[2]。当然这种方式存在不少的缺点,这里是不得已而为之,主要的缺点就是持久化这些索引数据的行为会增加添加和更新操作的成本,
Second, the backup approach requires an object to be written durably during each index update, whereas the rebuild approach would not require this step. This durable write affects the performance of index updates.
Carsh后的一致性
这里主要讨论了两个地方的crash的问题,一个就是server的carsh如何处理,一个是client的cash如何处理。client的crash处理起来相对来说简单不少,SLIK能够保证client的crash不会对系统的执行操作影响。不过这里的server的crash要处理2个问题:
-
在添加了索引之后添加数据对象之前系统崩溃了,或者是在删除了数据对象之后,还没有来得及删除索引数据之前,这个时候就会多出来无效的索引。这里使用的垃圾回收的办法。后台会有专门的任务来扫描这些索引,如果发现了无效的索引就会将其移除。
If the object does not exist, the data server sends an entryRemove request to the index server. If the table partition corresponding to an entry is being recovered, the collector simply skips that entry: it will be removed during the next scan. -
另外一个可能导致的不一致的地方就是删除or添加操作的时候索引结构的内部的不一致性,由于SLIK使用的是Btree的结构来保存这些信息,这样的话添加or删除的操作就可能导致树结构的更改,这里SLIK的解决方式是使用log-structured memory 或者 transaction log,
In order to maintain the consistency of the index across server crashes, multi-object updates must occur atomically. SLIK uses a multi-object update mechanism implemented using the log-structured memory or transaction log of the underlying key-value store. This ensures that after a crash, either all or none of the updates will be visible.
大规模的操作
这里主要讨论的是如何处理索引创建和索引分裂和迁移的问题。对应索引的创建,为了不影响系统的正常运行,SLIK这里使用的是后台创建的方法,只有在索引创建成功之后才会被使用,这个过程不会锁表。
To populate the new index with entries corresponding to the objects already in the underlying table, client- level code scans this table, reading each object and then rewriting it. Before rewriting the object, the client can restructure the object if the schema has changed. The act of rewriting the object creates an entry in the new index corresponding to this object.
一个分区的索引在增长到一定程度的时候就需要将其分裂,后者迁移到另外的地方。这里SLIK还是要保证在操作的过程中不会影响到系统的运行,使用的方法就是类似于虚拟机迁移的方法,在迁移的时候记录变化,然后将这些变化也传输过来,这里只有在复制最后的变化是才需要锁,
SLIK keeps track of the mutations that have occured since the copying started (in a log), and transfers these over as well. A lock is then required only for a short duration of time, while copying over the last mutation.
评估
具体信息这里可以参考论文[1]
参考
- SLIK: Scalable Low-Latency Indexes for a Key-Value Store, ATC ’16.
- Fast Crash Recovery in RAMCloud, SOSP ‘11.
