From ARIES to MARS: Transaction Support for Next-Generation Solid State Drives
引言
WAL是数据库等系统的设计中一个很核心的一个部分。之前的WAL机制如ARIES都是为HHD设计的。对于现在越来越快的SSD和出现的非易失性内存,如何优化原来的WAL设计,更好的利用新的硬件,这篇Paper就是讨论了这个问题。
This paper presents a novel WAL scheme, called Modified ARIES Redesigned for SSDs (MARS), optimized for NVM-based storage. The design of MARS reflects an examination of ARIES, a popular WAL-based recovery algorithm for databases, in the context of these new memories. MARS provides the same high-level features for implementing efficient and robust transactions as ARIES, but without any of the disk-based design decisions ARIES incorporates.
基本思路
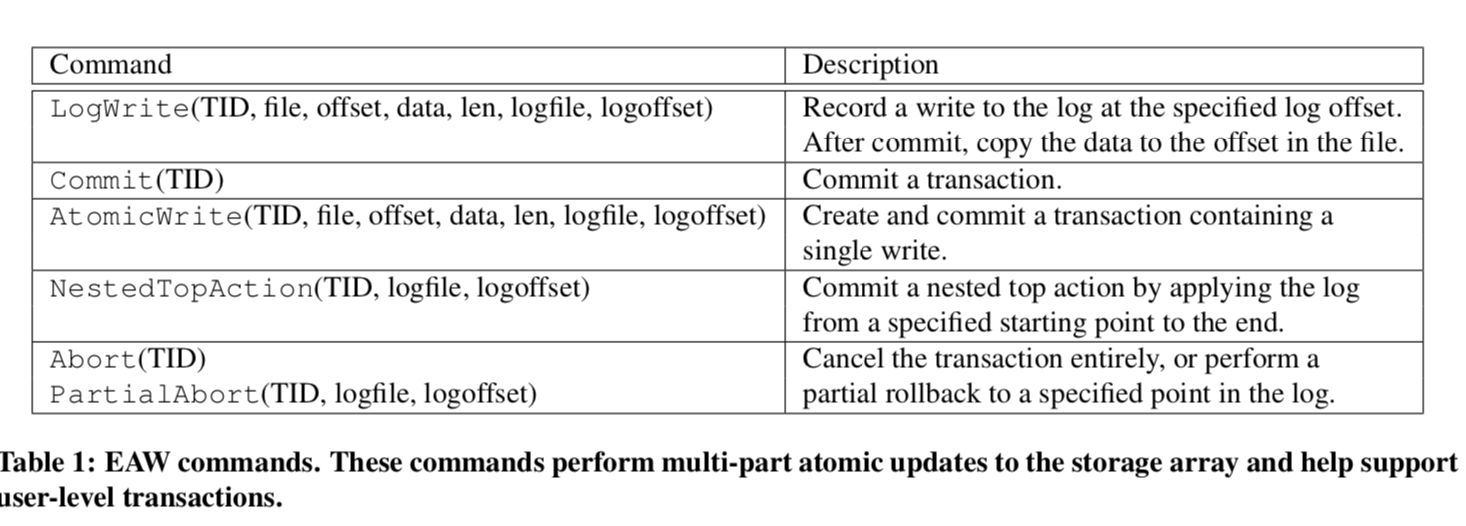
EAW
editable atomic writes (EAW)时MARS中一个很核心的对象,它有一组redo log项组成,每项里面包含一个对象。此外,这个log最大的不同在与可以被修改。
Once committed, the SSD hardware copies the final values from the log to their target locations, and the copy is guaranteed to succeed even in the presence of power or host system failures. EAWs make implementing ARIES-style transactions simpler and faster, giving rise to MARS. EAWs are also a useful building block for other applications that must provide strong consistency guarantees.
atomic意味着对这些项的更改是原子的,不仅仅如此,EAW还支持对多个位置的原子修改。这里只讨论来EAW的基本特性,在后面会讨论它具体时怎么实现的,EAW基本接口:
Deconstructing ARIES
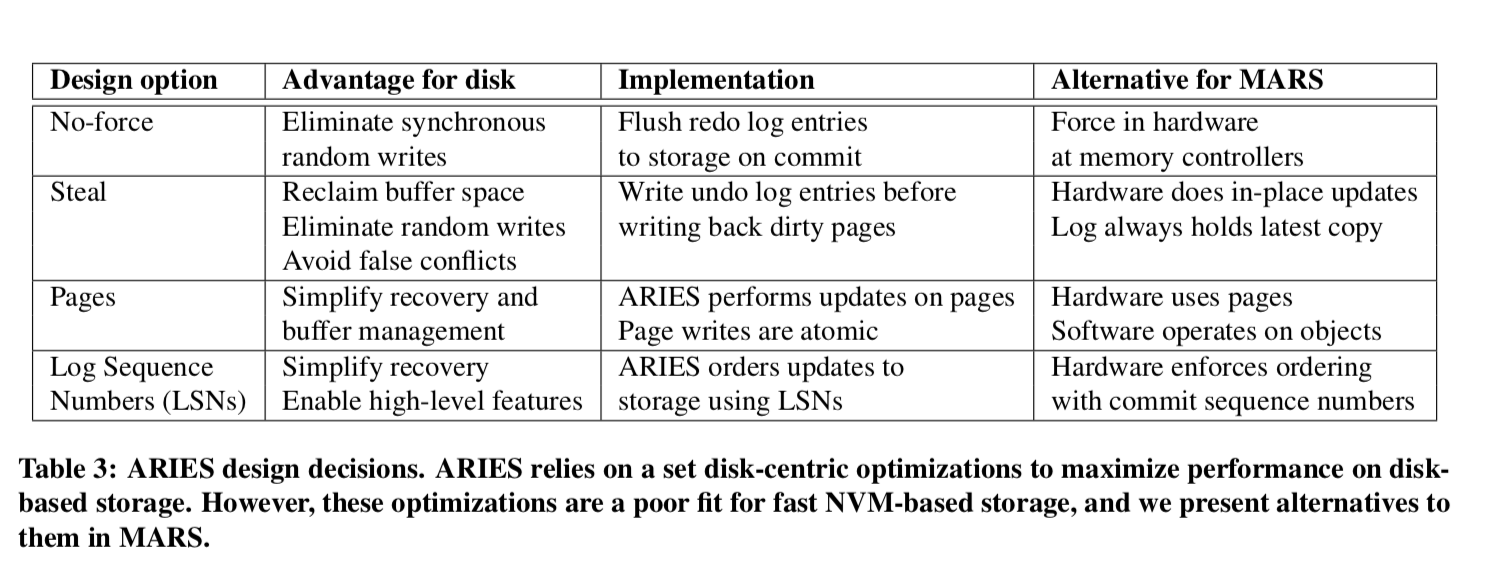
说MARS之前,先来回顾一下ARIES的几个最明显的特点:
- 事务提交之前先在Log中持久化相关的数据;
- ‘No-Force’ policy,由于有了Log,也就不需要立即就将更新之后的page持久化;
- ‘Steal’ policy,没有提交的事务更新的pages也能写入到磁盘上面(这个是为了支持”很大”的事务),因为有undo log,这也是可以恢复的;
- 使用LSN (Log Sequence Numbers)来保证标记log,page是基本的管理单位;
Building MARS
MARS在3个主要的地方不同于ARIES,首先它依赖于存储设备,通过EAW的操作,在提交的时候应用redo log;第二,没有undo log,不过通过EAW保留来undo log能带来的好处;第三,没有transactional pages,直接操作对象。
Updatable Log
上面提到,MARS的log时可以修改的,这里是通过软件和硬件的共同配合来实现的,具体的细节在实现这一章。
MARS uses LogWrite operations for transactional updates to objects (e.g., rows of a table) in the database. This provides several advantages. Since LogWrite does not update the data in-place, the changes are not visible to other transactions until commit. This makes it easy for the database to implement isolation. MARS also uses Commit to efficiently apply the log.
Force
ARIES不行强制将立即就将更新之后的page持久化,只是考虑到HHD的特点,避免随机写操作。但是对应随机写性能很好的NVM来说,这个随机写可以接受。所以MARS是强制的,
No-Steal
由于在MARS的log中总是保证数据的最新持久化版本,数据只有在Commit的时候才会被更新,所以undo log是没有必要的,所以也就没有什么steal了。
Instead of writing uncommitted data to disk at its target location, MARS writes the uncommitted data directly to the redo log entry corresponding to the LogWrite for that location. When the system issues a Commit for the transaction, the SSD will write the updated data into place.
byte-addressable
EAW提供了byte-addressable的接口。ARIES中的LSN和Page都是为顺序写磁盘的方式设计的,这里就没有这个必要的。这里的很多工作都交给了EAW了完成:
Instead of an append- only log, EAWs provide a log that can be read and written throughout the life of a transaction. This means that undo logging is unnecessary because data will never be written back in-place before a transaction commits. Also, EAWs implement ordering and recovery in the storage array itself, eliminating the need for application-visible LSNs.
Implementation
实现上需要软件和硬件相互配合,这也可能是其的一个缺点。
TODO
Results
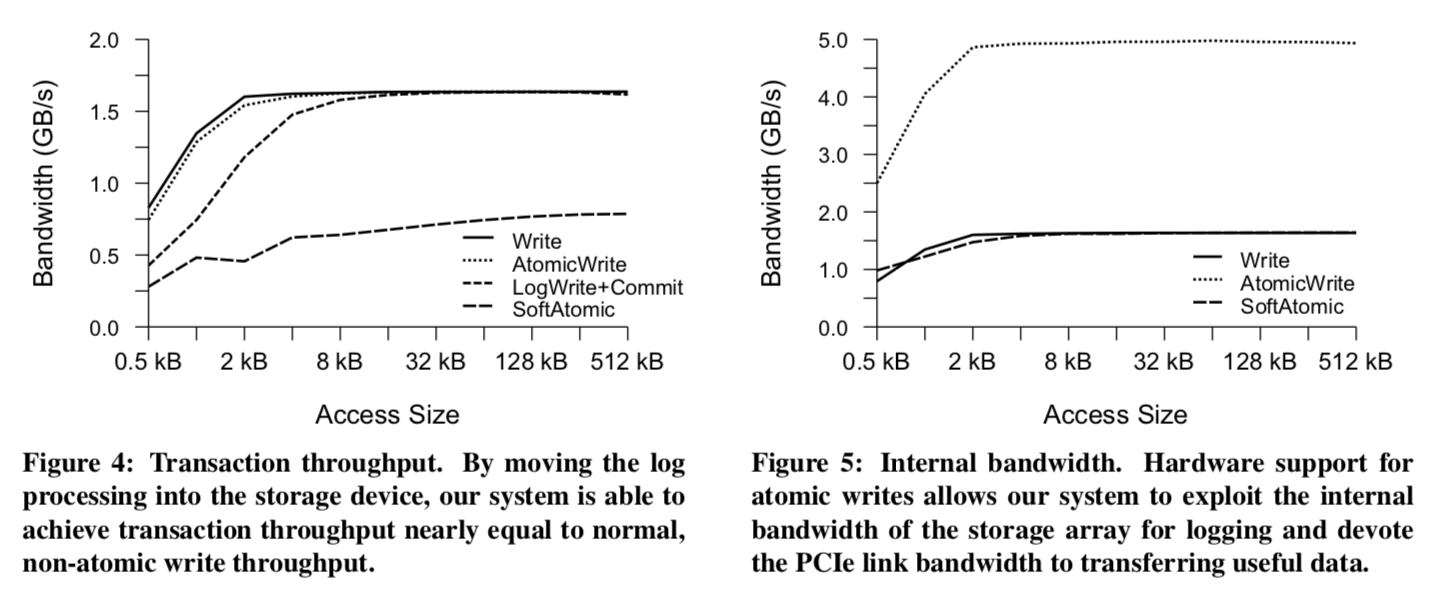
We have implemented EAWs and MARS in a next-generation SSD to demonstrate that the overhead of EAWs is minimal compared to normal writes, and that they pro- vide large speedups for transactional updates to hash tables, B+trees, and large graphs. In addition, MARS outperforms ARIES by up to 3.7× while reducing software complexity.
参考
- From ARIES to MARS: Transaction Support for Next-Generation, Solid-State Drives, SOSP 2013.
- https://blog.acolyer.org/2016/01/20/from-aries-to-mars/, the moring paper.
