NOVA: A Log-structured File System for Hybrid Volatile/Non-volatile Main Memories
引言
NOVA是一个利用NVMs加速的Log-structured文件系统。在传统的Log-structured文件系统上面NOVA使用了1. 每一个inode维持一个log来提高并发度;2. 将文件的数据保存在log之外来减小log的体积和加快GC,
. Experimental results show that in write-intensive workloads, NOVA provides 22% to 216× throughput improvement compared to state-of-the-art file systems, and 3.1× to 13.5× improvement compared to file systems that provide equally strong data consistency guarantees.
基本设计
在NOVA的实现中,以下的几个观点对设计产生了比较大的影响:1. 在NVMM上面实现原子更新比较容易,但是实现有效的查找比较麻烦;2. 由于NVVM随机访问的成本比较低,有一些随机访问页关系不大;3. 使用当个的log不适应NVVM的环境。基于上面的一些考虑,NOVA基于下面的一些设计原则:
-
Keep logs in NVMM and indexes in DRAM,NOVA将文件数据和log保存到NVVM中,相关的索引保存在内存中;
-
Give each inode its own log,每一个inode对应一个log,随意增加了不少的随机访问,但是在NVVM上关系关系不大。好处就是能提高并性度;
-
Use logging and lightweight journaling for complex atomic updates,对于设计到单个inode操作,一般使用原子的log操作即可,对于跨越多个inode的操作,比如一些文件夹的操作,NOVA使用了日志的方式;
-
Implement the log as a singly linked list,使用4KB的Page保存Log,这些Page组织为Linked List的形式;
-
Do not log file data,NOVA不会log数据,对于数据使用COW的方式,
Using copy-on-write for file data is useful for several reasons. First, it results in a shorter log, accelerating the recovery process. Second, it makes garbage collection simpler and more efficient, ... Third, reclaiming stale pages and allocating new data pages are both easy, ... Fourth, since it can reclaim stale data pages immediately,
实现
数据结构和空间管理
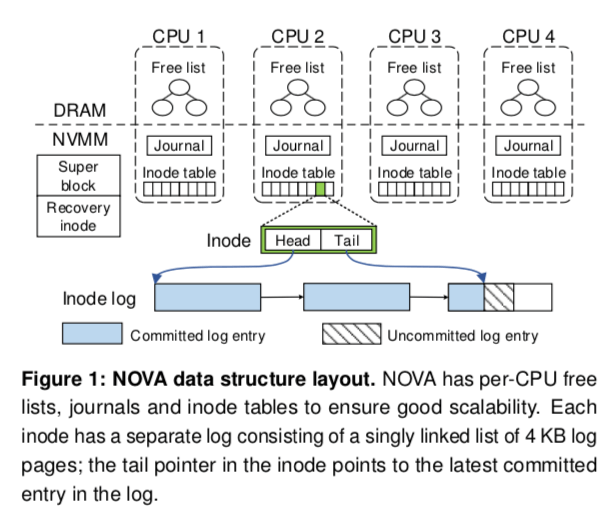
NOVA一个大概的结构如下图所示。NOVA主要分为4个部分,Super Block + Recovery inode、inode tables、journals和 log/data Pages。NOVA这里的一个优化inode table、journal和free page列表都是每一个CPU核心一个,降低了处理的时候的冲突。
-
Super Block,和一般文件系统一样,Super Block保存的一些文件系统全局的信息;Recovery inode包含了一些用于加快故障恢复的信息;
-
inode tables保存的当然就是inode;有2MB的一个inode数组组成的列表,使用inode号就能定位inode的位置。每一个inode保护一个指向log头和尾的指针,是4KB大小的页组成的列表。NOVA可以通过扫描这个log的列表构建内存中的数据结构;
-
journals(日志)提供对文件夹操作的原子性;是一个4KB大小的循环缓冲区。为了协调在多个inode上面的更新操作,NOVA会使用到journal(日志),
To coordinate updates that across multiple in- odes, NOVA first appends log entries to each log, and then starts a transaction by appending all the affected log tails to the current CPU’s journal enqueue, and updates the enqueue pointer. After propagating the updates to the target log tails,NOVA通过使得一个journal的<enqueue, dequeue>指针对相等来提交日志。举一个例子:对一个文件的创建,NOVA会首先在日志中记录目录log的tail以及新的inode的valid bit,在故障恢复的时候通过回滚<enqueue, dequeue>之间来撤销操作。
-
log/data Pages保存的就是log和数据了。在NVVM空间管理的时候,空间会被划分为pool,每个CPU分配一个。在内存中保存一个空闲列表,当前CPU的pool里面没有可用的空间时,会从一个公共的pool里面分配。这里的分配方式有些像一些内存分配器的方式。
NOVA一些操作的实现
NOVA实现了快速的对元数据、数据和mmap的原子性操作,主要基于几种类型的操作:
-
64bit原子更新,现在的处理器一般都支持64bit数值的原子更新,及时在NVVM上面也可以;
-
Logging,用于记录单个inode上面的操作,比如 write, msync 和 chmod。这个log是独立的,如前面讲的;
-
轻量级的 journaling,主要用于设计到多个的inode的操作,主要有关于目录的操作,
At any time, the data in any NOVA journal are small—no more than 64 bytes: The most complex POSIX rename operation involves up to four inodes, and NOVA only needs 16 bytes to journal each inode: 8 bytes for the address of the log tail pointer and 8 bytes for the value. -
强制写入顺序,NOVA要求下面的顺序:1. 提交数据和log的写入在更新log tail之前;2. 提交journal数据在传播更新操作之前;3. 提交一个新版本的数据page在回收一个旧版本之前。一段示意的伪代码,
new_tail = append_to_log(inode->tail, entry); // writes back the log entry cachelines clwb(inode->tail, entry->length); sfence(); // orders subsequent PCOMMIT PCOMMIT(); // commits entry to NVMM sfence(); inode->tail = new_tail;
一些操作
-
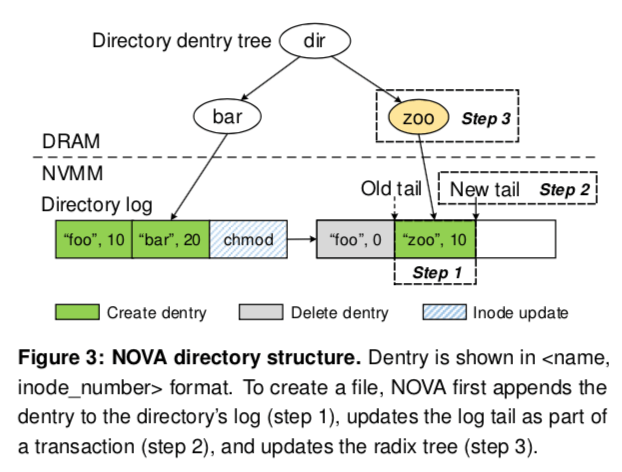
目录操作,如前面所言,目录操作很多时候设计到多个inode的更新。NOVA使用了日志的方式。另外,为了加快查找,NOVA在内存中保存了对于每一个目录的radix tree,
... NOVA keeps a radix tree in DRAM for each directory inode. The key is the hash value of the dentry name, and each leaf node points to the corresponding dentry in the log. The radix tree makes search efficient even for large directories.
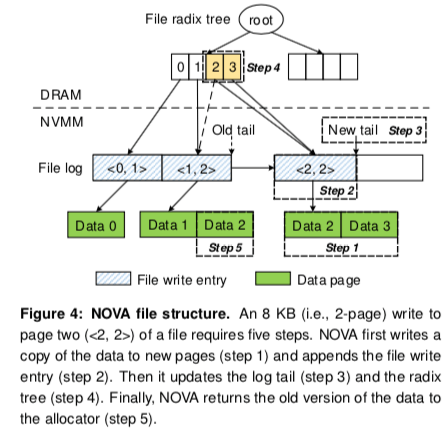
- 文件操作,与一般的log-structured的文件系统不同,NOVA在每一个inode的log中只会记录元数据的更改,对数据页的更改使用COW的方式。与目录一样,NOVA对数据也在内存中维持了一个radix tree。
-
mmap操作,NVVM是支持内存寻址的,mmap的实现也可以在一般的文件系统的实现上面有所改进。 DAX-mmap方法是就是一种直接操作NVVM的方式。但是其一缺点就是只支持64bit的原子操作。NOVA另外提供一种atomic-mmap的方式,它使用拷贝Page副本然后在写会的操作实现更大范围的原子操作,
NOVA allocates replica pages from NVMM, copies the file data to the replica pages, and then maps the replicas into the address space. When the application calls msync on the replica pages, NOVA handles it as a write request described in the previous section, uses movntq operation to copy the data from replica pages to data pages directly, and commits the changes atomically.这种方式的优点就是更强的一致性的保证,但是缺点就是overhead很大。在一些情况下也是有用的。
-
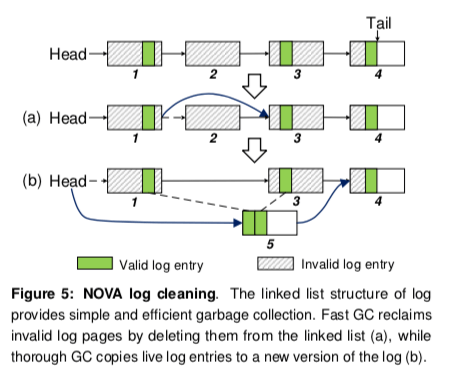
垃圾回收。垃圾回收是Log-structured文件系统中的一个重要的部分。由于NOVA的实现,这部分在NOVA实现是一个简单高效的操作。对于数据页的回收,在这个COW操作数据页的版本变成不是最新的马上就可以回收了。对inode的log回收麻烦一点,主要就在于判断一个log entry是否可以回收,可以回收要满足它不是最后的entry还有满足下面中条件的至少一个,
* A file write entry is dead, if it does not refer to valid data pages. * An inode update that modifies metadata (e.g., mode or mtime) is dead, if a later inode update modifies the same piece of metadata. * A dentry update is dead, if it is marked invalid.NOVA的Fast GC回收这个log里面的数据都已经没用的,如下面的2;Thorough GC是一种拷贝回收的方式,如下面的1,3的回收。
-
关机与恢复,前面讲到了NOVA在内存中保存了大量的类似于索引的结构、free list等的结构,在启动的时候需要通过扫描文件系统的一些结构来构建这些结构。这些结构构建采用了lazy的方式,只有在需要的时候才回去构建。另外在故障恢复的时候,可能还需要恢复分配器等额外的信息,这种情况下分两步进行,
First, NOVA checks each journal and rolls back any uncommitted transactions to restore the file system to a consistent state. Second, NOVA starts a recovery thread on each CPU and scans the inode tables in parallel, performing log scanning for every valid inode in the inode table.
评估
这里详细信息可以参看[1]
参考
- NOVA: A Log-structured File System for Hybrid Volatile/Non-volatile Main Memories, FAST ’16.
