Fast Crash Recovery in RAMCloud
引言
这篇是关于RAMCloud如何快速恢复的Paper,之前已经看过了RAMCloud的内存管理,以及Key-Value系统的实现。这里只会关注如何快速恢复的部分。RAMCloud可以实现在crash之后,将几十GB的数据在1-2内恢复,这个是一个很惊人的数字,
RAMCloud employs randomized techniques to manage the system in a scalable and decentralized fashion. In a 60-node cluster, RAMCloud recovers 35 GB of data from a failed server in 1.6 seconds. Our measurements suggest that the approach will scale to recover larger memory sizes (64 GB or more) in less time with larger clusters.
基本思路
RAMCloud的数据持久化备份子啊磁盘上面的,要向在1-2秒的时间将及时GB的数据一下子恢复到内存里面,这里使用的部分就是利用大规模的资源。可以简单的理解为将数据分散保存在非常多的磁盘上面,如何在恢复的时候并发的读取这些磁盘上面备份的数据,这样就可以实现在极短的时间内将数据取回。比如,同时使用1000个磁盘,这样64GB的数据大概就会被分为64MB的小部分,以现在的HHD大约100- 200MB/s的顺序读取速度,就可以在1s内将这些数据读取到内存里面,然后在将这些数据恢复成所需要的格式,就可以做大在就可以做到恢复 64GB的数据的时间为 1-2s。
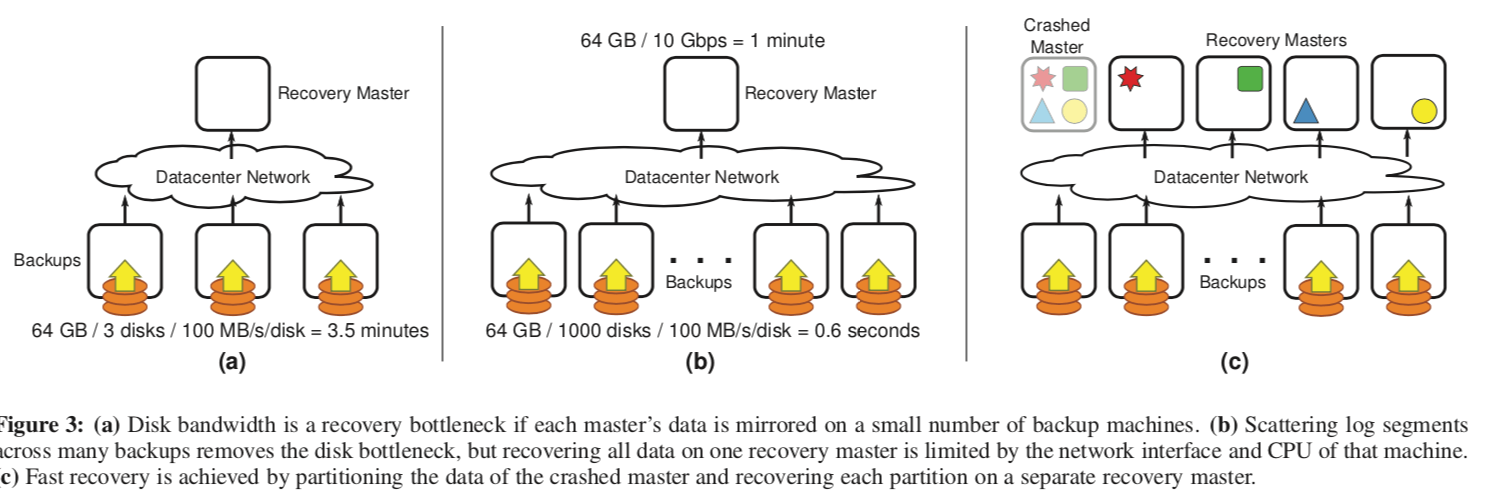
前面说了这个操作的基本原理,但是这里仅仅是使用成百上千的磁盘是不够的,还要其它方面技术的支持。如上面的图所示,图b中使用了1000个的磁盘,但是只有一个单一的Recovery Master,这样恢复的时间既收到网络带宽的限制,又收到单一结点数据处理能力的限制。所以RAMCloud这里使用了多个的Recovery Master。这个时候,数据会被分为大致相等的数据分片,每个数据分片交给一个Recovery Master来处理,100个左右的Recovery Master就可以满足在1-2s内恢复64GB数据的要求。可以说这里的做法就是堆机器解决问题,通过堆硬件资源来解决磁盘、网络和CPU的瓶颈,只要数据分区做得好,能做到这样的效果还是很显然的,
Thus, the overall approach to recovery in RAMCloud is to com-bine the disk bandwidth, network bandwidth, and CPU cycles of thousands of backups and hundreds of recovery masters. The sub- sections below describe how RAMCloud divides its work among all of these resources and how it coordinates the resources to re- cover in 1-2 seconds.
Scattering Log Segments
如何将这些数据分散保存到成百上千的磁盘上面是要解决的第一个问题(这里将其叫做segment),这里要考虑到一下的问题:
- 一个segment的master和backup要分布在不同的机柜之上,避免一个机柜的故障导致这个分片不可用;
- 要考虑到不同的机器的不同的磁盘带宽、网络带宽等的因素;
- 要避免backup过高的负载,因为masters一些操作都是同时进行的;
-
存储服务器可能连续地被添加or移除,这个可能造成semgent的分布不均匀;
在哪里放置一个segment可以使用一个中心的协调者,但是这个的缺点就是可拓展性方面的问题,比如10000个结点(…..可怕)可能在1s之内备份100,000个或者更多的segment,这样的操作强度会给这个协调者很大的压力。这里RAMCloud使用的方法是去中心话的方法,由每一个Master自己决定一个segment应该放在哪一个位置,使用了一种随机话的加上优化调整的方法。它首先会在备份的结点中随机地挑选若干个,然后总这些随机挑选的中间选择最合适的一个。这里要考到的因素包括已经分配给这个备份结点的segment数量,已经这个结点能够提供的各种资源的情况,这里不会选择同一个机柜上面的机器,一个备份结点的负载已经太高的话也会拒绝Master的请求,这样的话Master只能挑选其它的备份结点,
The best backup is the one that can read its share of the master’s segment replicas most quickly from disk during recovery. A backup is rejected if it is in the same rack as the master or any other replica for the current segment. Once a backup has been selected, the master contacts that backup to reserve space for the segment. At this point the backup can reject the request if it is overloaded, in which case the master selects another candidate.
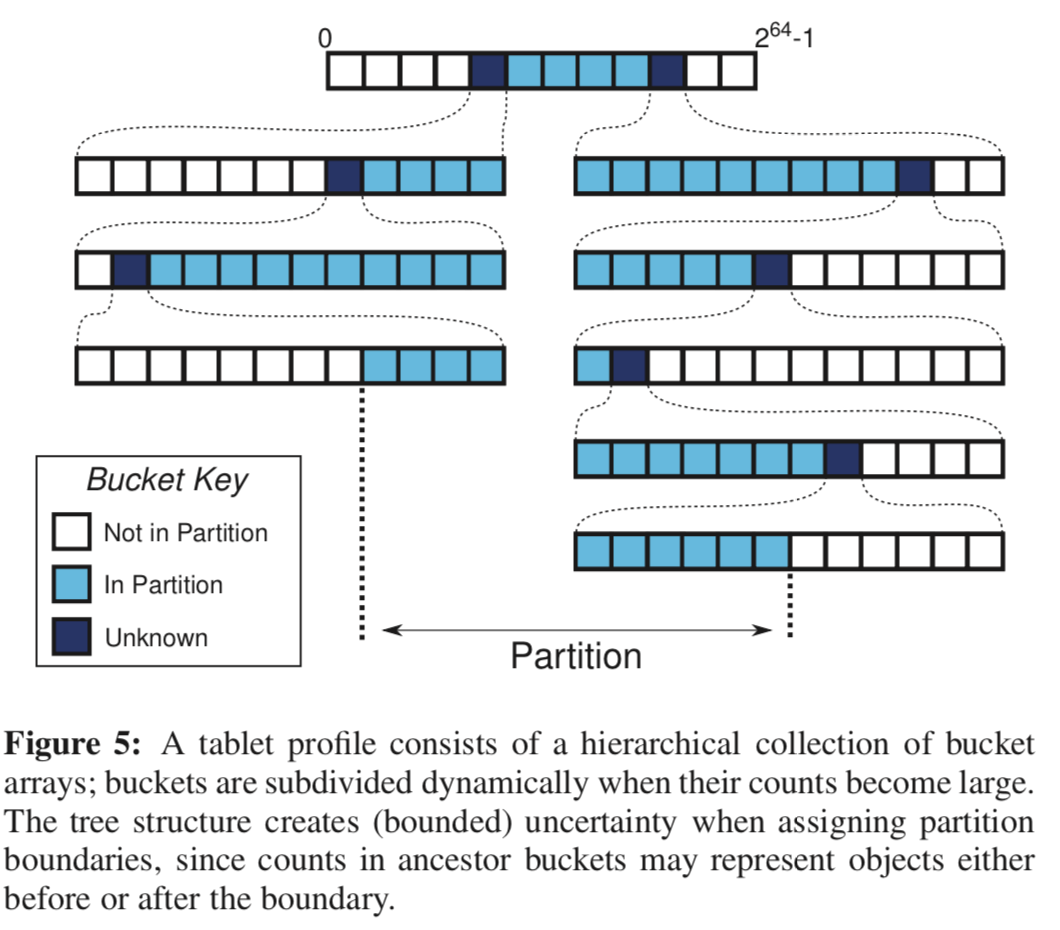
RAMCloud的Masters会挑选其中的一个副本为primary replica,在恢复的时候选择这一个副本,如果这个副本不能使用,就只能使用其它的副本了。 在这里,RAMCloud为提供信息给master立遗嘱使用,这里会保存一些关于资源使用的信息,称之为tablet profiles,
RAMCloud computes wills using tablet profiles. Each tablet pro- file tracks the distribution of resource usage within a single table or tablet in a master. It consists of a collection of buckets, each of which counts the number of log records corresponding to a range of object identifiers, along with the total log space consumed by those records. Tablet profiles are updated as new log records are created and old segments are cleaned, and the master periodically scans its tablet profiles to compute a new will.
关于这里时如何处理的,在论文的3.9节。
Failure Detection
RAMCloud这里使用了两种方法来发现结点的故障:1. 客户端发现这个server无法正常服务的时候,2. 每一个服务器定期地随机给其它的服务器发送ping信息,如果发现不能正常回复,就讲信息报告给coordinator,这个coordinator还要去确认情况,
In either case, server failures are reported to the coordinator. The coordinator verifies the problem by attempting to communicate with the server itself, then initiates recovery if the server does not respond. Timeouts must be relatively short (tens of millisec- onds) so that they don’t significantly delay recovery.
Recovery
在发现了一个服务器的故障之后,就启动恢复的流程,这个过程分为3步:
-
设置,Coordinator查明故障的服务器的segments被备份在哪里,然后挑选recovery masters ,分配数据分片给每一个处理;这一步又要处理3个问题:
-
发现Segment的副本,这里像前面的一些方法一样,也避免了使用了一个中心化的方法,没有保存一个全局的备份服务个segment 之间的映射关系,所以这里只能通过询问所有的备份服务器的方法来发现想要的segment。
-
查明不完整的Logs,查到了想要的副本的位置之后,RAMCloud并不能保证数据都一定是完整的。为了检查数据的完整性,它使用的是Log自身的数据来校验数据的完整性,这里使用了一个
log digest,包含了写入此段时日志中所有段的标识符列表。日志摘要很小,即使在未压缩时也少于1% 存储开销。这里还要处理的一个问题就是可能所有的副本的数据都是不完整的。为了保证日志摘要日志摘要的真确更中,这里使用类似于Copy-On-Write的方式,再有在新的更新并持久化的之后才讲就的置为非活动的。这里RAMCloud如果怎么样都找不到完整的数据信息,那么它就不能恢复这些信息。也就是说,在RAMCloud中,它不能完全地处理crash的问题的。If the active log digest and a replica for each segment cannot be found, then RAMCloud cannot recover the crashed master. In this unlikely case, RAMCloud notifies the operator and waits for backups to return to the cluster with replicas for each of the missing segments. Alternatively, at the operator’s discretion, RAMCloud can continue recovery with loss of data. -
开始恢复,这里主要就是将这些恢复的工作划分,这里划分给谁是由Master它自己决定,在正常操作的时候,它会根据系统的情况,计算出分区能够将恢复的工作平均地分配,这里在这里叫做_遗嘱_,它描述了在自己crash之后应该如果处理它的数据,这个信息会定期的同步到coordinator。在恢复设置的过程中,每个crash master会从coordinator接收到两个信息,一个是log segment的地址信息的list,一个是crash master必须恢复并纳入自己管理的tablets的list。
-
-
Replay,Recovery masters 并行地处理这些数据;大部分的时间是花在这里的,每一个segment要用6步来恢复数据带内存里面,这些步骤的详细信息参考原论文[1],为加快这里的速度,在读取不同的segment和不同的服务器上的操作都是并行的,另外一个就是这里6步的操作时流水线化的,这样就能尽可能地充分利用硬件的资源,
The second dimension is pipelining: all of the six stages listed above proceed in parallel, with a segment as the basic unit of work. While one segment is being read from disk on a backup, another segment is being partitioned by that backup’s CPU, and records from an- other segment are being transferred to a recovery master; similar pipelining occurs on recovery masters.这里另外的一个优化就是如何处理这些segment的顺序,这里时备份服务器先决定读取这些segments的顺序,将这些信息发送给coordinator,之后recovery master就可以获取到这些信息,这样就可以避免recovery master要请求A分段的时候,备份服务器准备好的却是B分段,从而造成流水线的停顿。这里还有停顿可能时由于备份服务器速度太慢造成的,recovery master就并发的请求这些备份服务器。所以这里recovery master重建这些书的时候,顺序是没有任何保障的,这里使用版本好来避免乱序造成的数据错误,这里之后保留最新的数据版本。
-
在处理完成之后,开始为这些数据提供服务,并清理crash服务器占用的资源。在recovery master恢复完成这里的数据之后,就通知coordinator可以将原来的master占用的资源清理了。到了这个时间节点,这些recovery master就可以为client提供相关的服务了。
Consistency
这里的主要的内容不在这篇论文里面,在这篇论文发表之后的另外一篇论文[2], 这里主要有2点:1. 在被怀疑crash的服务器(sick master)的数据被恢复之前,必须停止服务,因为如果时被误以为失败的话,还在提供服务的话,被恢复的数据就不能保证时最新的。2. 保证在恢复操作的时候,只有一个coordinator可以操作集群的配置。
这里coordinator会禁止sick master的备份操作,这样的话sick master就会去联系coordinator。Coordinator在恢复开始时联系备份服务器, 以查找sick master日志中每个段的副本, 包括仍在写入的活动的segment,一旦联系上处理这个segment的备份服务器, 将会拒绝从sick master的备份操作, 并指示masters必须停止服务请求, 直到它已与coordinator联系。
Once a backup with a replica of the active segment has been contacted, it will reject backup opera- tions from the sick master with an indication that the master must stop servicing requests until it has contacted the coordinator. Masters will periodically check in with their backups, so disabling a master’s backup operations will also stop it from servicing read requests by the time recovery completes.
Additional Failure Modes
上面的故障的处理只考虑了单个master情况。另外还有几个的故障类型:
- Backup Failures,当一个备份故障时,RAMCloud会创建一个新的副本来替代这个故障的备份。在coordinator发现某个备份服务器失败的时候,会通知所有的masters,如果某个master发现有数据段保存在来故障的备份的服务器上面,它会从其它的副本恢复这些数据。
- Multiple Failures,这里处理的方式就是单独处理每一个的失败,这里要处理的问题就是备份服务器的primary也故障了,这里就只能使用其它的备份了。
- Cold Start,这里处理的问题就是整个集群断电的故障。这一班的情况下,一个备份服务区在crash之后恢复会丢弃它备份的数据,因为前面已经提到了这个时候它的数据已经被其它的副本替代了。但是这里,它必须先向coordinator请求指示。coordinator会来获取它保存的数据的信息。
评估
这里详细数据可以参考[1]。
参考
- Fast Crash Recovery in RAMCloud, SOSP ‘11.
- Implementing Linearizability at Large Scale and Low Latency, SOSP’15.
