Xen and the Art of Virtualization
引言
这个是一篇很重量级的文章。注意这篇Paper里面的一些描述是在2003年的时候,可能已经不符合现在的情况。这里按照原论文的描述来。
This paper presents Xen, an x86 virtual machine monitor which allows multiple commodity operating systems to share conventional hardware in a safe and resource managed fashion, but without sacrificing either performance or functionality. This is achieved by providing an idealized virtual machine abstraction to which oper- ating systems such as Linux, BSD and Windows XP, can be ported with minimal effort.
基本架构
Xen是一个半虚拟化的解决方案。全虚拟化的方式在当时存在不少的问题,一个原因就是x86缺少虚拟化的支持。比如的Interl的VT-x技术出现在这篇论文发表2,3年之后。为了解决当时这些全虚拟化的存在的问题,这里使用了半虚拟化的方法(paravirtualization),这样的一个要求就是需要修改guest操作系统。Xen有下面的设计原则:
- 虽然Xen需要修改Guest操作系统,但是不要求修改应用,这个是至关重要的;
- 完全支持多任务操作系统;
- 半虚拟化有助于实现隔离的情况下实现高性能;
- 隐藏虚拟化资源带来的影响;
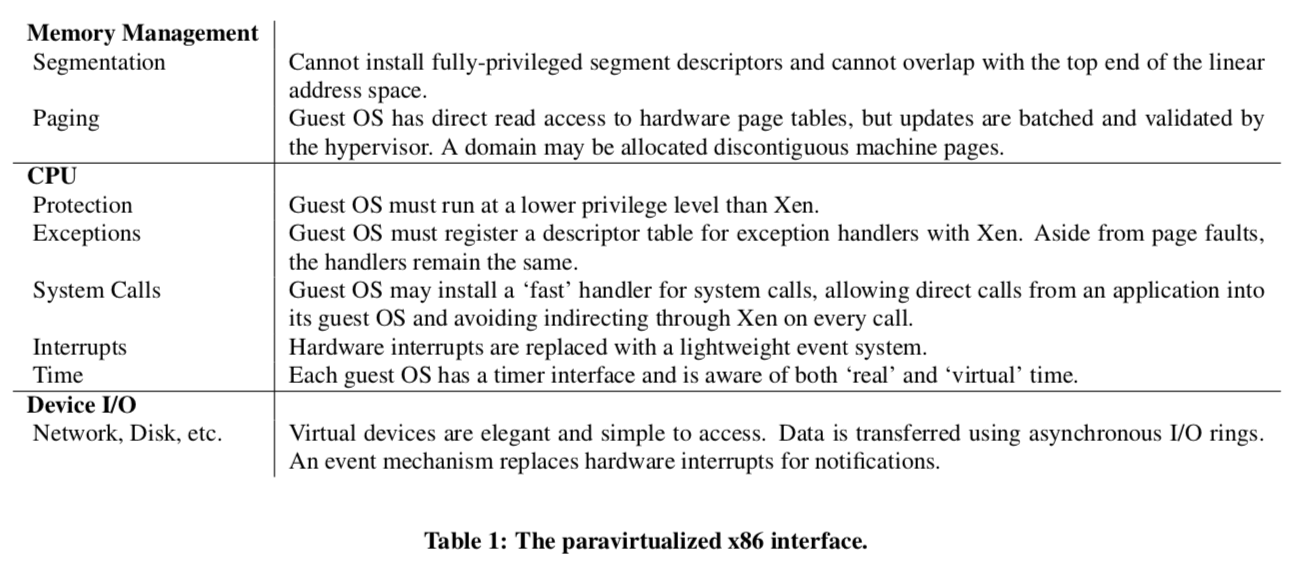
这里将可以在Xen上面运行的OS叫做guest operating system,将运行在Xen上面的操作系统的实例叫做Domain,这里有点像程序和进程的区别。Xen自己叫做hypervisor。下面的表表示了半虚拟化的x86的interface,主要就是三个方面:内存、CPU和Device IO。x86的很多的特点给虚拟化带来了很多麻烦。
-
内存管理,x86不支持软件管理的TLB,同时也缺失标记的一些方法(这里的标记应该是值标记TLB的一项服务于那一个进程的地址空间or globel还是local的一些优化进程切换时TLB性能的一些方法)。Xen使用的方法是1. guest OSes直接负责和管理物理页表,2. Xen保留地址空间最上面的64MB为其所用,避免进入和离开hypervisor得时候需要爱刷新TLB。当一个guest OS需要分配一个新的page的时候,它从自己预留的memory中分配,这里需要向Xen登记。这里时候guest OS必须放弃直接写page-table内存的权限,应为这里的操作需要Xen来验证。增加的overhead可以通过一次处理多个pages来平摊。每一个空间地址上面的64MB是不能被guest OSes使用的,而Xen使用这些内存就可以避免在每次离开or进入hypervisor的时候都需要进行TLB flush。段是x86中一个很无聊的玩意儿,这里也需要处理,
Segmentation is virtualized in a similar way, by validating up- dates to hardware segment descriptor tables. The only restrictions on x86 segment descriptors are: (i) they must have lower privilege than Xen, and (ii) they may not allow any access to the Xen-reserved portion of the address space. -
CPU,这里要处理的一个问题就是特权的问题。guestOS必须允许在比hypervisor低的CPU特权级别上面。这里好在x86是支持4个特权等级的(现在x86有更加好的解决方案,部分在03年的时候还没有出现)。Xen通过修改guestOS的方式让其运行在ring1的级别上面。这样在可以在geustOS不能执行一些特权指令,保证安全性和隔离性。在geustOS需要执行一些特权操作的时候,必须有Xen验证执行。当geusOS尝试直接执行特权指令的时候,CPU会什么都不做or产生错误。一些异常如页缺失、软件trap在x86上面都是比较容易处理虚拟化的。这里使用的也是类型中断向量表的方法。这里另外一个要主要的问题就是guesOS缺失一些特权的问题,比如访问CR2寄存器在处理page fualt的时候是必须的,而处在ring1的guestOS有不能访问。所以需要hypervisor将这些信息拷贝到guestOS的地址空间当中(这里应该也要对geustOS进行修改)。为了提高syscall的性能,Xen使用了fast’ exception handler的方法,以便于不需要ring0也可以直接运行。这些fast’ exception handler必须初始的时候被Xen验证。另外还有一个double faults的问题
if the handler’s code segment is not present or if the handler is not paged into memory then an appropriate fault will be taken when Xen executes the iret instruction which returns to the handler. Xen detects these “double faults” by checking the faulting program counter value: if the address resides within the exception-virtualizing code then the offending guest OS is terminated. -
Device I/O,这里的设计Xen重复利用了半虚拟化的好处理。和全虚拟机的技术相比,它们要完全模拟出虚拟化的硬件,而Xen在这里只需要一种简单的抽象机制。Xen使用共享内核和异步buffer的方式来传输数据,并且Xen可以对这些相关的信息进行验证。Xen使用轻量级的事件传递机制来异步通知一个domain。这个机制通过更新一个bitmap或者是直接调用一个geustOS的制定的一个event handler。
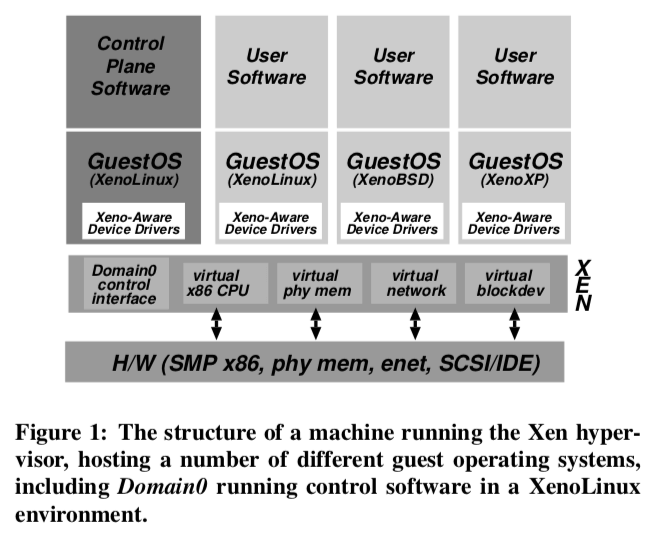
详细的设计
Control Transfer: Hypercalls and Events & Data Transfer: I/O Rings
这里描述的是Domina和Xen之间是如何进行交互的。Doamin使用同步的hypercall方式来请求Xen,这个有点类似于应用程序使用syscall请求kernel。而Xen使用异步的异步的事件机制,事件也有不同的类型,这个有点类似于Unix上面的signal机制。Xen会设置一个pre-domian的bitmap来设置相关的信息,然后相关的回调处理这些事件,
The callback handler is responsible for resetting the set of pending events, and responding to the notifications in an appropriate manner. A domain may explicitly defer event handling by setting a Xen-readable software flag: this is analogous to disabling interrupts on a real processor.
由于Domain和设备之间存在一个Xen,所以这里Domain和IO设备之间的数据传输也必须经过Xen。Xen使用IO rings来处理这个问题。这里就类似于生产者、消费者模型。Domain请求Xen的时候,通过将请求信息放入这个ring然后使用hyercall来请求Xen处理,geustOS会赋予这些请求一个唯一的标识符,这样Xen就可以对这些进行重新排序处理而不会一下到geustOS处理返回的结果;Xen处理完成的时候使用时间通知来通知对应的Domain,Domain可以选择这个事件积累一定的数量之后在通知它,这里就是使用批量的方式来平摊overhead。这样的方式可以看起来并不能适应现在的一些高速网络。
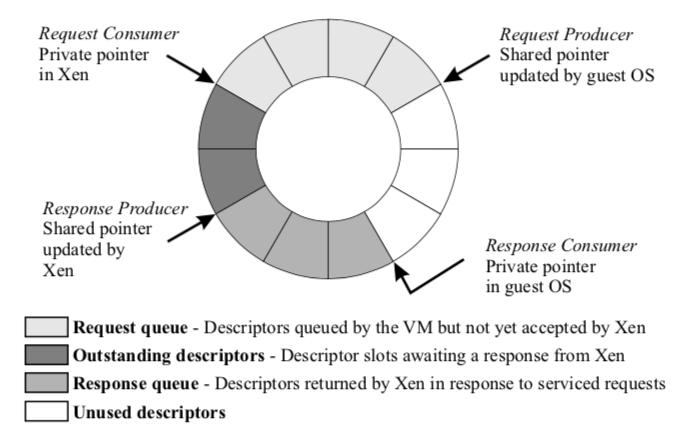
Subsystem Virtualization
这部分将的就是CPU,address space,physical memory,network和disk之类的子系统是如何虚拟化的。
-
CPU scheduling,Xen使用Borrowed Virtual Time (BVT)调度算法对Domain进行调度,这里调度算法的选择低延时是一个重要的考虑因素。
BVT provides low-latency dispatch by using virtual-time warping, a mechanism which temporarily violates ‘ideal’ fair sharing to favor recently-woken domains. However, other scheduling algorithms could be trivially implemented over our generic scheduler abstraction. Per-domain scheduling parameters can be adjusted by management software running in Domain0. -
Time and timers,Xen为guestOS提供real time, virtual time and wall-clock time几个事件的概念。Real time就是现实流失的事件,以从启动开始流失的纳秒计数。Virtual time只在这个geustOS运行的时候就是增加,常用于geustOS中进程的调度,wall-clock time顾名思义,它和real time存在一个对应关系。
-
Virtual address translation,与其它的使用virtual page table的方式不同,为了避免virtual page table带来的性能损失,Xen使用的方法是geustOS可以直接只读的访问物理的page table,只有字啊需要更新这个page table的时候,需要通过hypercall的方式经过Xen来验证、处理,
To aid validation, we associate a type and reference count with each machine page frame. A frame may have any one of the following mutually-exclusive types at any point in time: page directory (PD), page table (PT), local descriptor table (LDT), global descriptor table (GDT), or writable (RW). Note that a guest OS may always create readable mappings to its own page frames, regardless of their current types. A frame may only safely be retasked when its reference count is zero. -
Physical memory,在一个Domain被创建的时候,一些内存会被预留给这个Domain。所以内存是被静态地分给这些Dmmains的。Xen不保证预留给一个Domain的内存在物理上都是连续的,这个问题需要geustOS自己来处理。这些Xen预留给Domain的内存被称为hardware memory,而现在的OS同时自己看到的物理内存是连续的,这里就是需要进行处理一下使得这些内存看起来是连续的physical memory,
Mapping from physical to hardware addresses is entirely the responsibility of the guest OS, which can simply maintain an array indexed by physical page frame number. Xen supports efficient hardware-to-physical mapping by providing a shared translation array that is directly readable by all domains – updates to this array are validated by Xen to ensure that the OS concerned owns the relevant hardware page frames. -
Network,为了处理各给Domain的Network,Xen抽象出virtual firewall-router (VFR),每一个Domain可以有到一个or多个的逻辑上attach到VFR上面的VIFs。VIF类似于一个网卡。
A VIF looks somewhat like a modern network interface card: there are two I/O rings of buffer descrip- tors, one for transmit and one for receive. Each direction also has a list of associated rules of the form (<pattern>, <action>) — if the pattern matches then the associated action is applied.Domain0复制处理上面所说的规则。 guest OS将buffer描述符添加到transmit ring的方式来传输数据包。Xen则拷贝这些描述符和数据包的header,拷贝header是为了执行可能的过滤规则。payload不会被拷贝而使用DMA处理,在数据传输的过程中相关的内存page必须被固定以免被交换。Xen使用简单的RR的方式处理这些数据包。
-
Disk,Xen中,只有Domain0才可以直接访问存储硬件,比如磁盘。其它的Doamin访问必须通过virtual block devices (VBDs)的抽象。而这些VBDs由Domain0来管理,这样简化了Xen的设计。VBD的访问也是通过I/O ring的机制。在Xen中,这些IO请求也是会被重新排序的,所以请求返回的顺序是乱序的,
... On receiving a disk request, Xen inspects the VBD identifier and offset and produces the corresponding sector address and physical device. Permission checks also take place at this time. Zero-copy data transfer takes place using DMA between the disk and pinned memory pages in the requesting domain.
评估
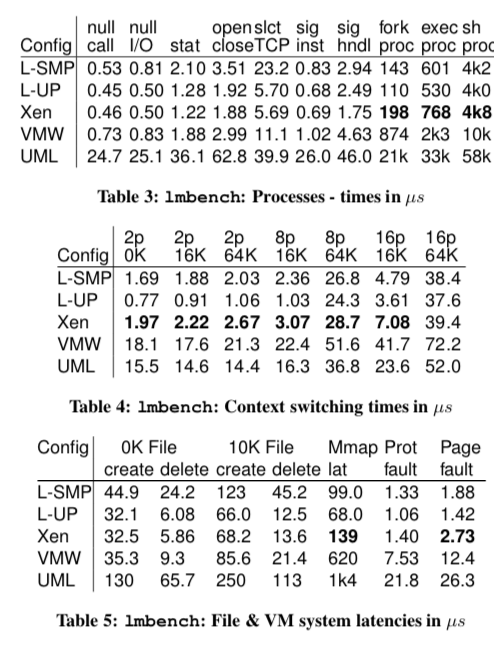
这里的具体数据可以参看[1].
参考
- Xen and the Art of Virtualization, SOSP’03.
