Dune: Safe User-level Access to Privileged CPU Features
引言
做为一个计算机系统的常识,为了保护系统,我们知道,用户进程的权限是很有限的。这样的设计带来一些好处的同时,也屏蔽了一些好处。如java虚拟机,有时候需要控制线程,要经常性地进行GC,这个时候如果能让JVM访问一些kernel feature,就能得到很多好处。Dune的一个基本思想是利用虚拟化,将一些之前只能是kernel feautre的功能暴露给应用,同时保证系统的安全性。一个Dune进程做为一个普通的Linux进程,不够使用VMCALL来进行系统调用。之前有个的一个类似的系统是Exokernel,不过那个更像是一种类型的kernel,而这个是一个内核上的功能。
基本架构
Dune可以看作是一个虚拟化的一个模块,有内核部分和应用库组成:
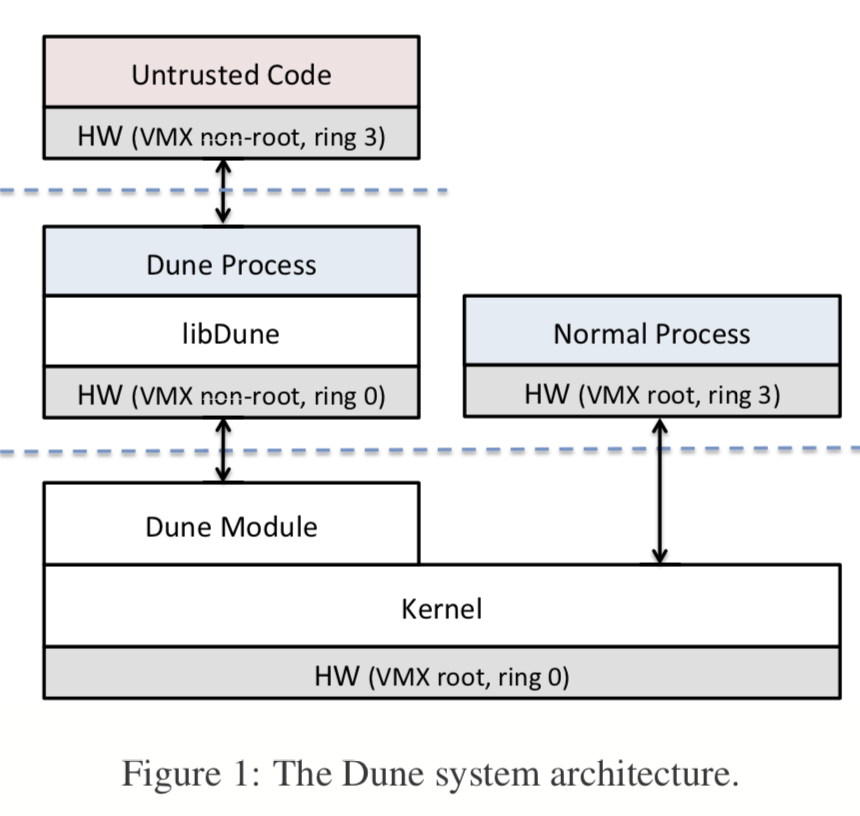
Dune的基本架构如上图所示,在内核中,添加了一个Dune Module,一个Dune Process,运行在VMX non-root的ring0权限下,再在此之上运行平常的代码。应用不必要一开始在Dune中运行,可以在运行。通过对 /dev/dune/ 进行操作进入Dune状态。不过一旦进入,就不能退出。Dune不同于VMM的一些地方:
- Dune不支持运行一个完整的OS;
- 与一般的VMMs不同,Dune使用hypercall调用的是一般的linux syscall;
- 一般的VMM是虚拟完整的硬件,而Dune之暴露硬件的一部分features;
- Dune不需要save和restore所有的state;
- Dune中的内存布局可以是稀疏的,不必想VMMs一样每一个VM都有一个分隔的地址空间。
Memory Management & Exposing Access to Hardware & Preserving OS Interfaces
内存管理Dune的最大的要处理的一个问题,由于Dune想要暴露出来page table,于此同时又要保存一般的内存空间的功能。在上面的图中有一定的体现。
For processes using Dune, a user controlled page table maps guest-virtual addresses to guest-physical. Then the EPT, managed by the kernel, performs an additional translation from guest-physical to host-physical. All memory references made by processes using Dune can only be guest-virtual, allowing for isolation and correctness to be enforced in the EPT while application-specific functionality and optimizations can be applied in the user page table.
为了实现这些功能,Dune还做了很多工作,Paper有较详细的描述。使用VMX的机制是这些变得简单。VMX本身是为虚拟化设计的,提供了访问虚拟化硬件的功能。
Exceptions and privilege modes are implicitly available in VMX non-root mode and do not require any special configuration. On the other hand, virtual memory requires access to the %CR3 register, which can be granted in the VMCS.
同时,用于Dune面向的是进程,它不是一个操作系统,使用它时是以进程为粒度进行控制的。可以理解为一个进程跑在一个单独的Dune环境中。虽然Dune暴露了一些硬件的功能,但是由于一些原因,这个还是做了不少限制。 对于其它的一些比如system calls,Dune是不能允许Dune 进行直接进行的,要必须经过Dune。
Instead, processes must use VMCALL, the hypercall instruction, to make sys- tem calls. The Dune module vectors hypercalls through the kernel’s system call table.
此外,Dune还改变了如Signal之类的处理方式。
Dune completely changes how signal handlers are in- voked. Some signals are obviated by more efficient direct hardware support. For example, hardware page faults largely subsume the role of SIGSEGV. For other signals (e.g., SIGINT), the Dune module injects fake hardware interrupts into the process.
实例
-
沙箱,Dune作为一个Container,将不信任的代码保持在一个安全的环境之后运行,可以通过对syscall做一些新的动作,改变这些call的行为。限制syscall也是linux seccomp的一个功能,这个感觉是一个更加高级的版本。
-
Wedge,一个特权分离的系统,例如一个web服务器中,一个用户的请求在一个隔离的sthread中运行,这样就要求sthread能被快速回收利用,而Dune就充分利用了可以访问一些硬件特性来实现这些功能:
Wedge uses many of Dune’s hardware features. Ring protection is used to enforce system call policies; page tables limit what memory sthreads can access; dirty bits are used to restore memory during sthread recycling; and the tagged TLB is used for fast context switching. -
Garbage Collection,这个我认为是这个3个例子中最有趣的了,假设JVM如果可以直接访问page table,捕获page fault等的一些动作,会是相当的好玩。
其它
Dune更加像一个特殊的Unikernel(这么说也不合适,因为Dune也算不上一个kernel),它只提供虚拟化一些硬件的功能,将很多unikernel要做的工作都将给原来的kernel。与Exokernel想要做的很多东西是相同的,但是Dune比一个Exokernel简单多了。思路非常不错,之后在Dune上的一些研究工作也不少,比如IX,ZygOS等等,这个是一个很好玩的东西。
参考
- Dune: Safe User-level Access to Privileged CPU Features, OSDI 2012.
