Improving Network Connection Locality on Multicore Systems
引言
这个是最近三篇关于Linux 内核网络栈优化文章中的第1篇,后面的两篇会之后加上[2,3]。这篇文章解决Linux中Connection Locality的问题的。提出了一个叫做MegaPipe办法。 问题: 这以幅图就基本说明了目前存在的问题。多个核心共享一些结构导致了冲突的问题。
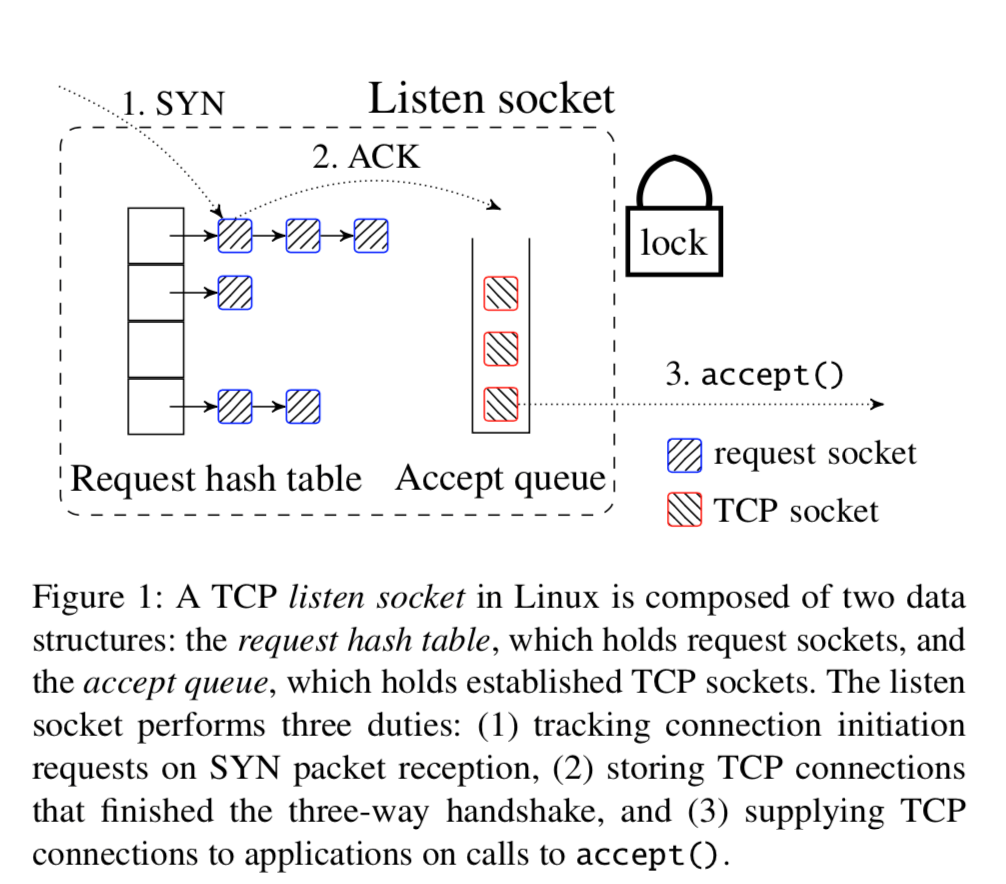
基本思路
基本思路就是将这些共享的结构弄成非共享的。Affinity-Accept 将这些结构变成了每一个核心一份。 第一个要解决的问题就是包路由的问题,这里需要将来自一个连接的包有交给同一个核心。这里通过网卡的功能解决。
The NIC hardware typically hashes each packet’s flow identifier five-tuple (the protocol number, source and destination IP addresses, and source and destination port numbers) and uses the resulting hash value to look up the RX DMA ring where the packet will be placed. Since all packets from a single connection will have the same flow hash values, the NIC will deliver all packets from a single connection into a single DMA ring.
Accept Affinity每个core一个accept queue,应用线程优先在本地的core上的accept queue来处理连接。一个应用线程调用accept的时候,它返回本地的accpet queue上面的已经处理好的连接,如果本地没有,那就将这个线程睡眠。
When new connections arrive, the network stack wakes up any threads waiting on the local core’s accept queue. This allows all connection processing to occur locally.
负载均衡
上面的分区的方式可能导致的一个问题就是负载不均衡的问题。这里的负载不均衡分为两类:这里就不具体讨论细节了。
-
short-term imbalance,可能是一些突发的原因导致的,这里使用的解决方式就是connection stealing,类似于work steaing的功能。
Affinity-Accept’s connection stealing mechanism consists of two parts: the first is the mechanism for stealing a connection from another core, and the second is the logic for determining when stealing should be done, and determining the core from which the connection should be stolen. -
longer-term load imbalance,可能是不均衡的分配导致的,这里的解决方式是 flow group migration 方式解决。
each non-busy core finds the victim core from which it has stolen the largest number of connections, and migrates one flow group from that core to itself (by reprogramming the NIC’s FDir table). In our configuration (4,096 flow groups and 48 cores), stealing one flow group every 100ms was sufficient. Busy cores do not migrate additional flow groups to themselves.
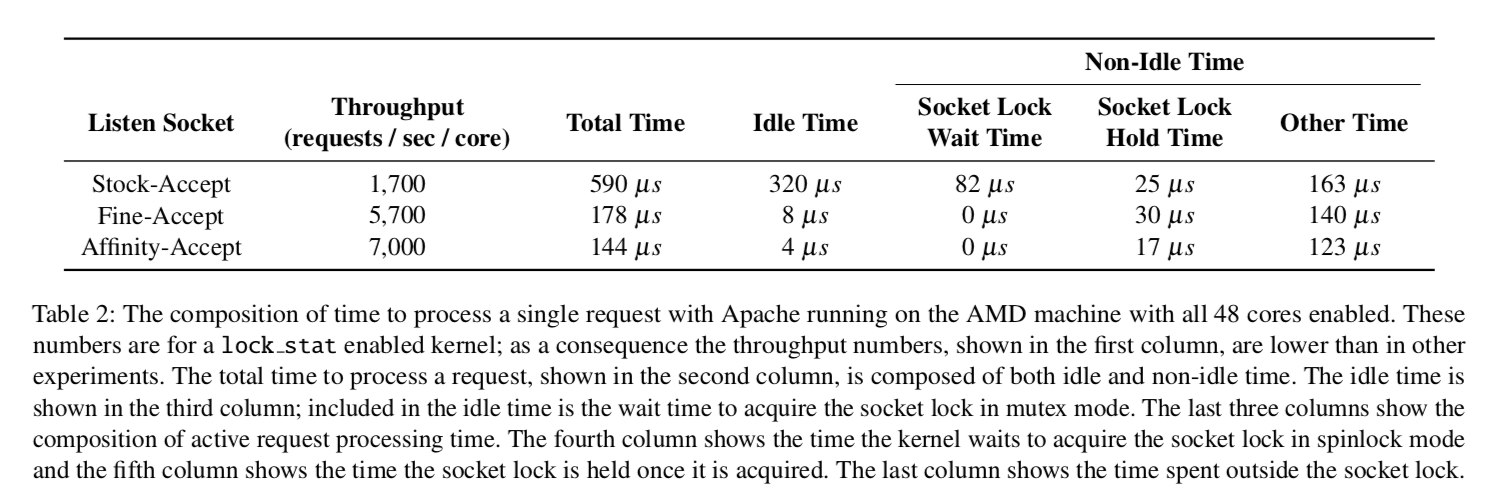
评估
Scalable Kernel TCP Design and Implementation for Short-Lived Connections
引言
这篇Fastsocket的文章是最近的关于Linux网络栈优化的第3篇,出自清华大学和新浪。所以要解决的问题和前面的2个差不多,还是要解决Linux内核网络栈存在的一些可拓展性的问题。和前面的两篇的最大的一个区别就是这篇文章里面讲的Fastsocket被实际使用了。
基本思路
- 将导致竞争的全局结构分区处理;
- 正确处理包以实现主动连接和被动连接的connection locality;
- 解决socket和VFS耦合导致的性能问题,同时保证兼容性。
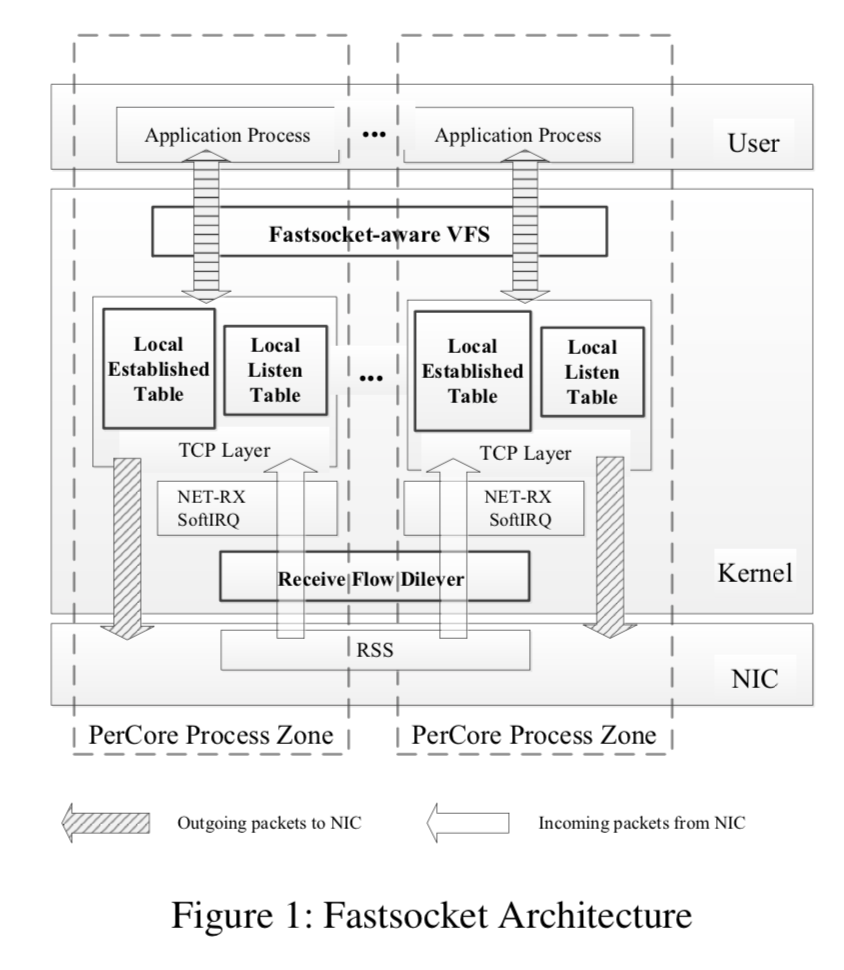
基本的架构图如下:
Local Listen Table
和前面2篇文章的思路一样,这里的做法也是讲listen table之类的共享结构分区处理: 一个进程创建一个listen socket,这个socket对应的 Listen Table是 global listen table。然后这个进程fork出子进程,子进程继承了这个socket,准备好接受新的连接。在fastsocket中,使用local listen() 来告诉内核我想处理的是我绑定的CPU core上面处理的连接。
We refer to the copied listen socket as the local listen socket and the original listen socket as the global listen socket.
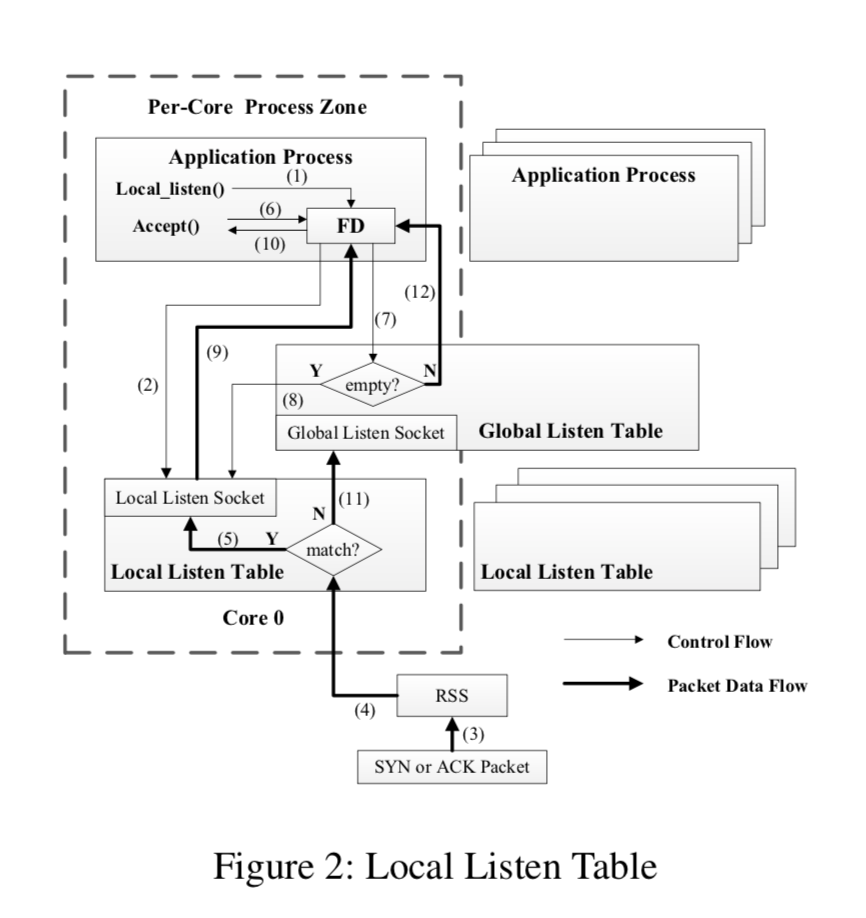
Fastsocket在添加局部化结构的同时,并没将原来的全局结构完全去除,而是两者都同时存在。Kernel优先处理局部上面的操作,对于一些其它特殊的情况,则使用原来的逻辑处理。这样做提高了系统的robustness和兼容性。
In Fastsocket,Figure2 shows,when a SYN packetcannot match a local listen socket in the local listen table, the kernel will set up a new connection with the global listen socket in the global listen table (11). When any application process calls accept() (6), the ready connection in the global listen socket will be found since the accept queue of the global listen socket is checked first (7). The kernel can then accept() the connection from the global listen socket to the applica- tion process, just what the legacy TCP stack does (12).
Local Established Table
Local Established Table是在内核初始化的时候就准备好的。
• Fastsocket allocates a local established table for each CPU core when kernel initializes network stack.
• New established sockets are inserted into the local estab- lished tables.
• In NET RX SoftIRQ , the kernel checks the local estab- lished table to match an established socket for any incoming packet.
Active Connection Locality
前面的两篇文章都没有处理主动连接的问题。Fastsocket使用源端口的hash来做为绑定CPU core的方式。
When the application running on CPU core c attempts to establish an active connection, RFD chooses a port psrc so that c = hash(psrc). Upon receiving a response packet, RFD picks the destination port of the received packet pdst which is the port RFD previously chosen, determines which CPU core should handle the packet by hash(pdst), and steers the packet to the selected CPU core, if this is not the CPU core currently handling the packet.
经过了上面的处理,如何区别主动和被动连接的包呢?这里使用了如下的几种方式:
- 如果收到的包的源端口是小于1024的,就认为是主动去连接而产生的包;
- 如果收到的包的目的端口是小与1024的,就认为是被动连接产生的包;
- 如果上面的包都不符合规则,就查看这个包使用和一个listen socket对应,如果是,则认为是一个被动连接产生的包,否则就是主动连接产生的包。
Fastsocket-aware VFS
这个问题已经被反复提到了,这篇论文中也指出了:
- Sockets are not on disk.
- Directory path is never used to identify socket.
- Avoid Unnecessary Overhead
- Keep Compatibility
由于fastsocket要保证兼容性,所以它不能想MegaPipe一样另外搞一个与VFS不关联的lwsocket。具体怎么做论文中也吗提到,简而言之就是只保留必要的部分.
In short, Fastsocket-aware VFS internally customizes VFS for sockets to improve scalability while externally keeping VFS compatibility for socket applications and system tools.
评估
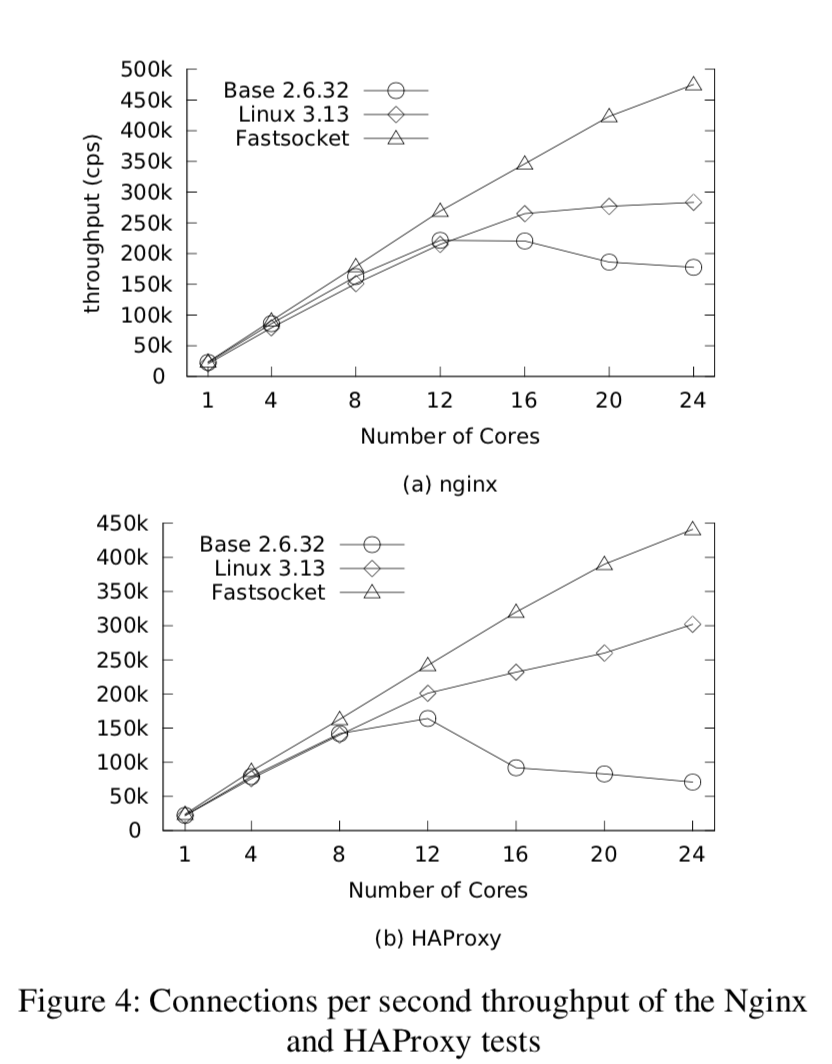
参考
- Improving Network Connection Locality on Multicore Systems, EuroSys’12.
- MegaPipe: A New Programming Interface for Scalable Network I/O, OSDI 2012.
- Scalable Kernel TCP Design and Implementation for Short-Lived Connections, ASPLOS ’16.
