PacketShader: a GPU-Accelerated Software Router
引言
之前在大学的时候问过系里的一位老师有没有使用GPU处理网络数据包和加密处理的研究。但是那位老师说2010年韩国的一个大学做过相关的研究。我想他说的就是这一个了。
Optimizing Packet I/O Engine
文章的主要内容中,先谈的是Packet IO Engine的优化。这里的原来的Linux的网络协议栈存在下面的两个问题:
- 频繁的buffer分配和回收造成不小得overhead;
- 相关的元数据如
skb占用了大量的内存,它保存了各类协议需要的信息,而时间里面很多是很少被用到的。
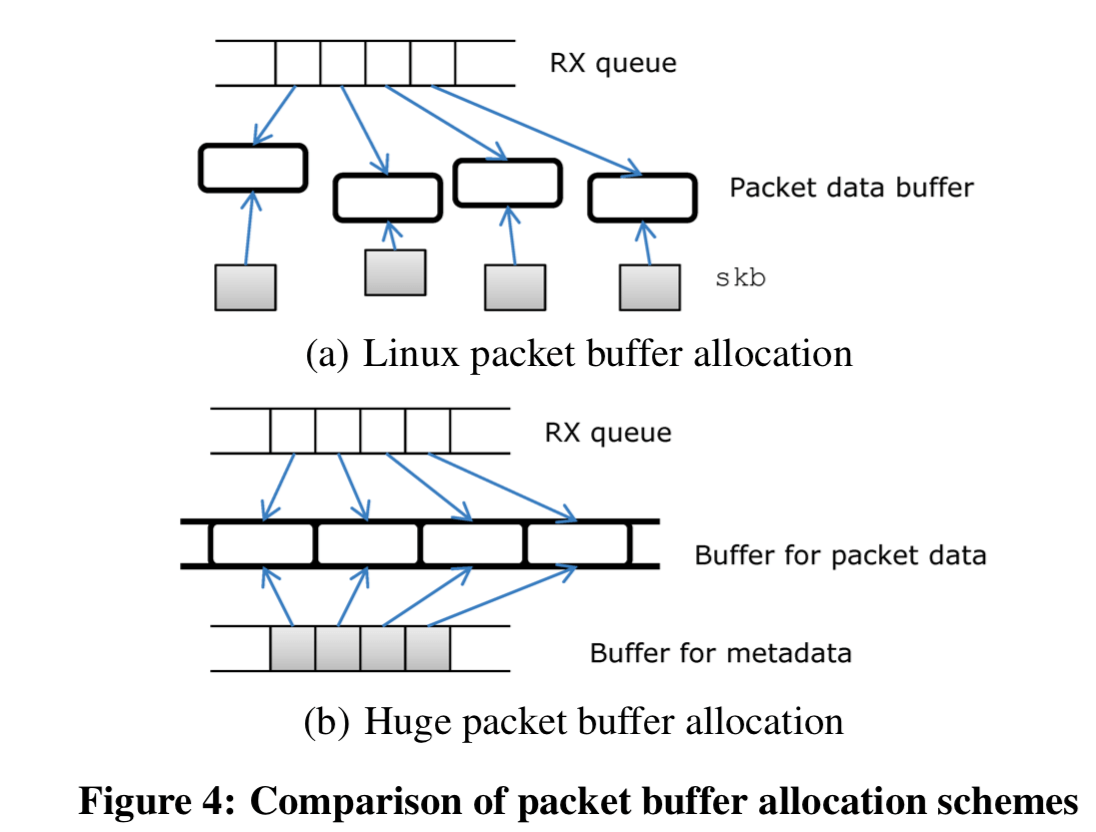
Huge Packet Buffer
这里先优化的就是buffer的问题。这里不在使用动态分配skb的方式,而一次性分配两个大的buffer。一个用来保存元数据,一个用来保存数据packet。一个buffer由固定大小的cell组成,一个cell就对应了一个RX队列中的数据packet。用于保存NIC数据packet的cell的尺寸是2048bytes,可以很好的处理以太网1518bytes的最大的包的尺寸,同时保存1024bytes对齐。这里的cell会被重复利用,而不是allacate和deallcate的方式。这样避免很多的开销,
The cells are reused whenever the circular RX queues wrap up. This scheme effectively eliminates the cost of per-packet buffer allocation. Huge packet buffers also reduce per-packet DMA mapping cost , which translates the host memory address into I/O device memory address so that NICs can access the packet data buffer.
与此同时,skb结构里面的很多的字段是很少用到的。这里的应用是software routers,所以这里就不要的完全删除,这样的结构就是元数据的大小只有8byts,直接就减少了200bytes。
Batch Processing
批量处理也是一个很常用的方法。PacketShader在packet处理的各个步骤都使用了批量处理得方式。这样用以下一些的好处:
(i) in hardware: NICs aggregate multiple packets into a single PCIe transaction for better I/O bandwidth utilization,
(ii) in device driver: the amortized cost of per-packet bookkeeping operations decreases, and
(iii) in applications: processing multiple packets achieves smaller instruction footprint with reduced function call overheads and synchronization operations.
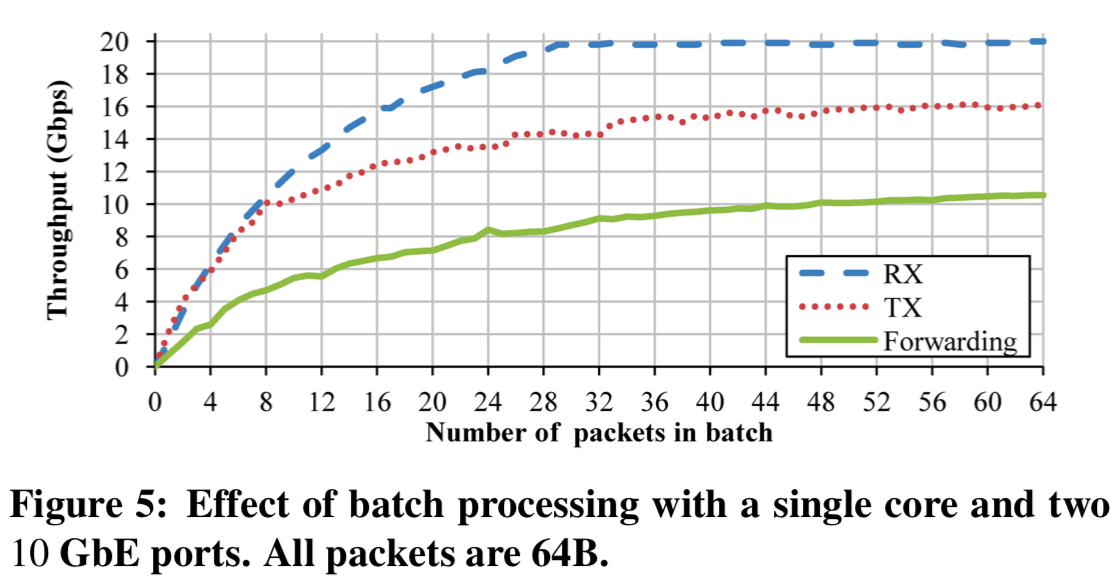
这里将批处理的方式应用的很彻底,从硬件到应用层面都使用了这样的方法。为了充分利用前面的huge packet buffers 。这里的IO Engine使用激进的预取方式,用来消除一些Cache Miss带来得开销。下面的图表示出在一次批量的packet数量在32以下的时候,提升是很明显的,
Multi-core Scalability & NUMA Scalability
这里就是就是一些多核下面的RSS优化,以及缓存的false sharing优化。NUMA主要就是NUMA-aware的一些优化。挺有效,没什么特别的。细节可以参看[1]。这里IO Engine表现出的性能还是很优秀的:
With RX and TX together, the minimal forwarding performance (without IP table lookup) stays above 40 Gbps for all packet sizes. By comparison, RouteBricks forwards 64B packets at 13.3 Gbps or 18.96 Mpps running in kernel mode on a slightly faster machine with dual quad-core 2.83 GHz CPUs. Our server outperforms Route-Bricks by a factor of 3 achieving 41.1 Gbps or 58.4 Mpps for the same packet size even though our experiment is done in user mode.
GPU 加速
基本架构如下:
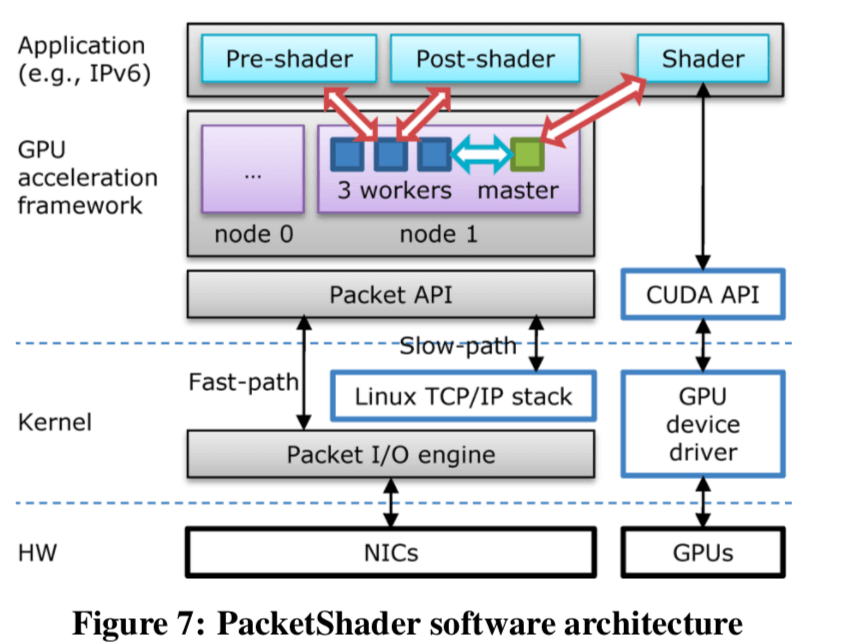
这里要解决的第一个问题就是在CUDA上面,多个CPU线程同时访问同一个GPU的时候,会由于频繁的上下文切换导致性能的下降(写这篇Paper的时候,不清楚现在CUDA是个上面情况了)。这里就是将与GPU交互的工作拆出来,使用一个独立的线程处理。这个线程在这里被叫做Master Thread,其余的工作线程叫做Worker Thread。Worker Thread有什么工作需要用到GPU的,都需要通过Master Thread来代理完成。这里每一个线程都映射到一个CPU corebing设置亲和性。同时,在NUMA的情况下,根据结点进行分区,每个分区的处理都是独立的,
Those workers communicate only with the local master to avoid expensive node-crossing communication. Once a worker thread receives packets, all processing is done by the CPU and the GPU within the same node. The only exception is to forward packets to ports in the other node, but this process is done by DMA, not CPU.
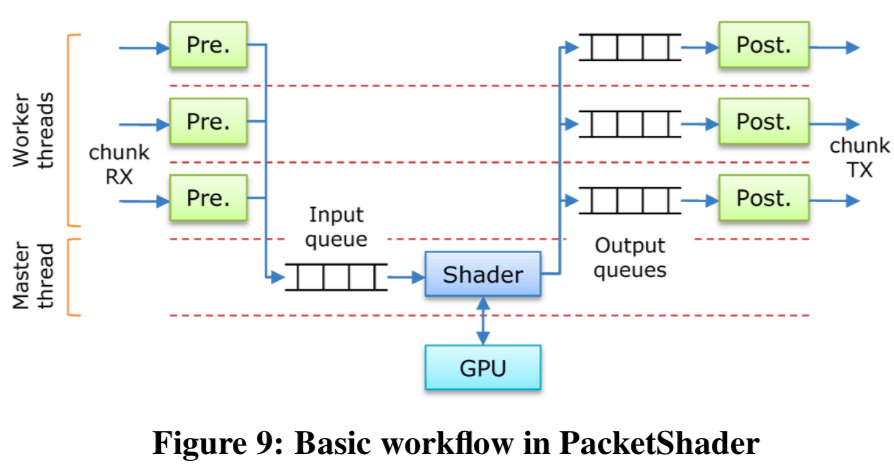
这里的三个重要的callback函数就是pre-shader, shader, and post-shader。这个也就代表来PacketShader的packet处理的三个步骤。这里将一次处理的多个packets叫做一个chunk。Chunk的大小是不固定的,但是会设置上限。 操作步骤如下:
- Pre-shading,Worker Thread一次取一个chunk。去除其中无效的数据包。然后由这个chunk中有效的packets构建一个数据结构,将这个数据结构传递给Master Thread。举个例子,对一个IPv4的数据转发,这里构建的结构就是IP地址的一个数组;
- Shading,Master Thread将这些数据传输到GPU的内存中,启动GPU kernel处理数据,然后取回结构。将其放入output queue,以转发给Worker Thread;
- Post-shading,Worker处理结果,然后将数据包传到对应的端口。
优化方法
-
Chunk Pipelining,Chunk的处理前面提到了被分为几个步骤,这里这些步骤就是流行化的;
-
Gather/Scatter,Master Thread流水线式的多份的输入数据(gatter),然后交给GPU处理之后拆分交付结果到对应的output queue(scatter);
-
Concurrent Copy and Execution,利用GPU的特点,将一些数据传输和计算的时间重叠,
In the meantime, NVIDIA GPUs support copying data between host and device memory while executing a GPU kernel function. This optimization is called “concurrent copy and execution” and is popular for many GPGPU applications [40].
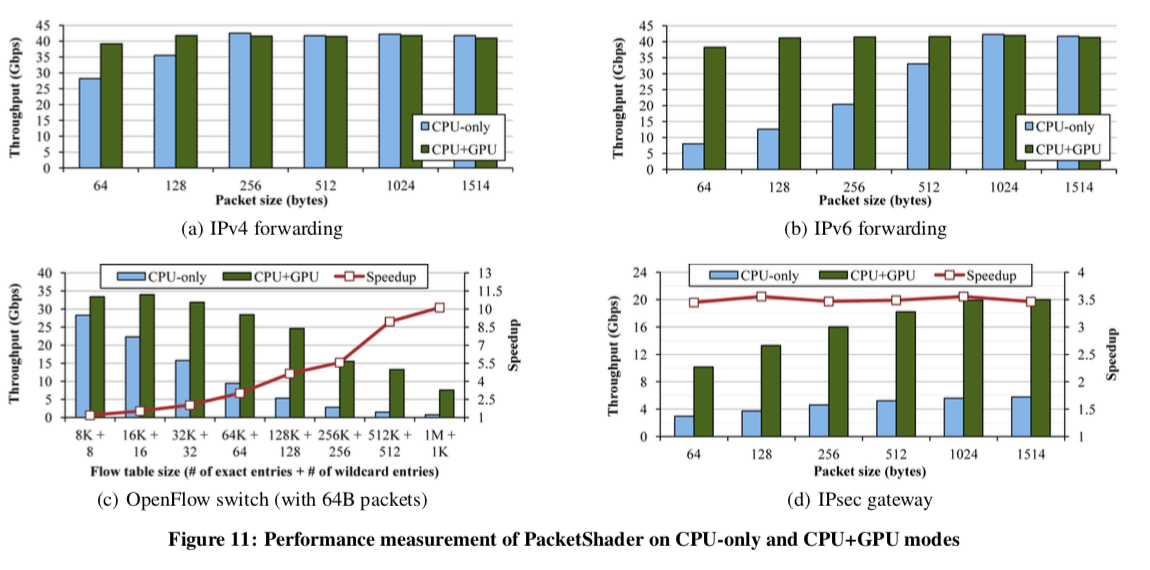
评估
具体的内容参考[1]
参考
- PacketShader: a GPU-Accelerated Software Router, SIGCOMM’10.
