MemC3: Compact and Concurrent MemCache with Dumber Caching and Smarter Hashing
0x00 引言
这篇paper是关于优化memcached内部实现的。主要包含了几个方面,这里只关注optimistic cuckoo hashing 。
As a case study, we focus on Memcached [19], a popular in-memory caching layer, and show how our toolbox of techniques can improve Memcached’s performance by 3× and reduce its memory use by 30%.
主要优化的是针对一下的场景,在论文[2]中有详细的讨论。场景主要的特点就是读占绝大部分,大部分的key-value都比较小。
Most keys are smaller than 32 bytes and most values no more than a few hundred bytes. In particular, there is one common type of request that almost exclusively uses 16 or 21 Byte keys and 2 Byte values.
0x01 Optimistic Cuckoo Hashing
Cuckoo Hash的基本思路是使用不止一个的hash函数来决定一个对象存放的位置,并使用驱逐的方法解决一些冲突的问题。这里的Hash Table的实现使用了类似Cache中组相联的方式,对于个位置,不只是放一个对象,而是一组的Slot。
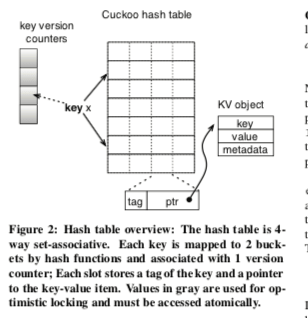
这里的实现使用 了4个slot,paper有这样一个说明,可以看出,使用这样的方式的一个好处就是可以提高空间的使用率。
Our hash table is 4-way set-associative. Without set-associativity, basic cuckoo hashing allows only 50% of the table entries to be occupied before unresolvable collisions occur. It is possible to improve the space utilization to over 90% by using a 4-way (or higher) set associative hash table.
此外,另外的一个好处就是更加缓存友好。一个slot没有直接包含key-value pairt,因为它们的程度不固定。这个slot有两部分组成,一个是信息来自key的一个tag,另外一个是指向完整key-value pair + 元数据的结构。由于这里使用了2个hash函数。所以每次最多查找的slot是8个。另外,对于insert的操作来说,如果bucket都满了,就会驱逐已经存在的元素。如果这个驱逐这个过程被级联的执行了太多次,就会执行hash table的操作。
Tag-based Lookup
之前提到了每一个slot有一个信息来集key的一个tag,这里的用处就是用了提高缓存友好性。tag实际上由key的hash得到,长度是1 byte。这样,对于不想等的key,就有很大的几率可以不同访问完整的key-value结构,而slot在这个时候已经被访问了,有很大的几率这些数据就在Cache中,这样就能提高性能。
After checking all 8 candidate slots, a negative Lookup makes 8 × 0.39% = 0.03 pointer deref- erences on average. Because each bucket fits in a CPU cacheline (usually 64-Byte), on average each Lookup makes only 2 parallel cacheline-sized reads for checking the two buckets plus either 0.03 pointer dereferences if the Lookup misses or 1.03 if it hits.
Tag-based Insert
Tag 除了优化了查找之外,还可以优化insert操作。这个的核心在与这样的计算方法(这里实在是太巧妙了):
b1 = HASH(x) // based on the entire key
b2 = b1 ⊕ HASH(tag) //based on b1 and tag of x
这样做的一个好处就是可以从b2 和 tag 得出 b1. 得知b1时也可以得到b2。这样的好处就是insert操作只需要table中的数据,而不同取回一些keys。
more importantly b1 can be computed by the same formula from b2 and tag. This property ensures that to displace a key originally in bucket b—no matter if b is b1 or b2— it is possible to calculate its alternate bucket b′ from bucket index b and the tag stored in bucket b by
b′ = b ⊕ HASH(tag)
0x03 Concurrent Cuckoo Hashing
Cuckoo的并发是比较难做的,它的驱逐的测量存在很多不确定性。对于并发的情况,这里主要要解决2个问题:
-
Deadlock risk (writer/writer):产生的原因是insert操作会可能移动一些key,而具体的移动情况是未知的,就可能导致deadlock。
-
False misses (reader/writer):在一个key被驱逐到另外一个bucket的时候,存在一段时间是无法被查找到的。
对于第二个问题,将查找一条合法的cuckoo path和执行具体的操作分离开,当得到一条path的时候,从这个path的最后一个开始移动。这样就很好的解决了这个问题。这样的一个结果就是可能在一段时间内,一个key存在两条记录,不过这里这个没有太大的关系。 对于第一个问题,则就是使用了一个简单的办法,同一时间只能由一个writer:
To avoid writer/writer deadlocks, it allows only one writer at a time — a tradeoff we accept as our target workloads are read-heavy.
Optimistic Locks for Lookup
查找的一个优化,就是使用了一种类型OCC(乐观并发控制)的方式,不lock一个bucket,而是给每一个key一个version counter,利用这个version来观测数据是否被修改了。这里利用了single writer的特点。
Optimizing for the common case, our approach takes advantage of having a single writer to synchronize Insert and Lookups with low overhead. Instead of locking on buckets, it assigns a version counter for each key, updates its version when displacing this key on Insert, and looks for a version change during Lookup to detect any concurrent displacement.
Multiple Cuckoo Paths
这个是对于一个inser操作的优化,在查找cuckoo path的阶段,不只是查找一条path,而是同时查找多条path。从其中选择一条最优的来决定最终的insert操作。
0x04 其它
这里只关注了optimistic cuckoo hashing的部分,关于论文的其它部分可以参看原论文。此外,这篇论文有一个进一步优化的版本,之后加上。
Algorithmic Improvements for Fast Concurrent Cuckoo Hashing
0x10 引言
这篇paper是MemC3[2]的进一步的工作,发表的时间晚了一年(2014,想想当时年轻的我,心塞塞的)。这里继续讨论了对hash table的一些优化,主要是对MemC3中的hash table的设计,特别是并发方面。此外,还利用了HTM做的一些优化。
0x11 Improve Concurrency
先来看一看结果,性能数据还是灰常赞的(可怜的TBB,经常被比较,总是被打败).
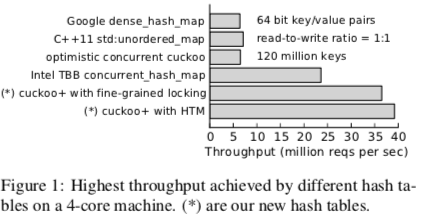
并发方面的优化基于一下基本principle:
P1: Avoid unnecessary or unintentional access to common data. 这个基本不用说了,最基本的套路.
P2: Minimize the size and execution time of critical sections. 同上.
P3: Optimize the concurrency control mechanism. 这里的名堂就多了去了。这里还讨论了使用HTM的优化。
0x12 Algorithmic Optimizations
Lock After Discovering a Cuckoo Path
这个优化是为了减少临界区的大小,这里给出paper中算法的描述就很好理解了:

原算法是先查找是否还有空闲的slot,如果有就添加,没有就找出一个path在添加,这样的话主要的过程是一直被lock的。优化的方式如第二个算法:将lock拆成了几个部分,其中一个最主要的是查找path的过程是不在lock的范围内的。这样的优点就是比较耗时间的操作在临界区之外,缺点是执行根据path的isnert操作时,需要额外的检查。
Breadth-first Search for an Empty Slot
原来采用的查找空slot的方法是贪婪算法,这里优化为BFS算法。原算法的一个优化是同时查找多个可行的path(实际上就是2个),本质上是类似DFS的算法。BFS的优化可以理解为查找了所有的可行的path,来找到一个更加好的。
This optimization is key to reducing the size of the critical section: While the total number of slots examined is still M, this is work that can be performed without a lock held. With BFS, however, at most five buckets must be examined and modified with the lock actually held, reducing both the duration of the critical section and the number of cache lines dirtied while doing so.
Increase Set-associativity
更高的组相联程度有以下方面的影响:
- 会降低查询的性能,需要查找的slot更加多了。而且数据变得更加分散,缓存的友好度降低;
- 会提好写的性能,因为有空slot的可能性提高了。
Fine-grained Locking
经过一番优化之后,这里的临界区都比较小了,采用spin lock是一个更加好的选择。
Here we favor spinlocks using compare-and-swap over more general purpose mutexes. A spinlock wastes CPU cycles spinning on the lock while other writers are active, but has low overhead, particularly for uncontended access. Because the operations that our hash tables support are all very short and have low contention, very simple spinlocks are often the best choice.
0x13 HTM
这里讨论了使用Intel TSX作为lock的一个替代。TSX存在的一个问题是在一些情况下会造成transaction的abort(事务内存),主要是以下的原因:
1. Data conflicts on transactionally accessed addresses;
2. Limited resources for transactional stores;
3. Use of TSX-unfriendly instructions or system calls. such as brk, futex, or mmap.
前面的两个原因通过之前提到的优化就已经被很好缓解了。第三个原因就是在实现中尽量避免了使用这些syscalls,
void elided_lock_wrapper(lock) {
xbegin_retry = 0; abort_retry = 0;
while (xbegin_retry < _MAX_XBEGIN_RETRY) {
// Start transaction
if (status=_xbegin() == _XBEGIN_STARTED) {
// Check lock and put into read-set
if (lock is free)
return; //Execute in transaction
// Abort transaction as lock is busy
_xabort (_ABORT_LOCK_BUSY);
}
// Transaction may not succeed on a retry
if (!(status & _ABORT_RETRY)) {
// There is no chance for a retry
if (abort_retry >= _MAX_ABORT_RETRY)
break;
abort_retry ++ ;
}
xbegin_retry ++;
}
take fallback lock;
}
void elided_unlock_wrapper(lock) {
if (lock is free)
_xend(); // Commit transaction
else
unlock lock;
}
具体地评估数据可以参看原论文[1]. 此外,这个的代码已经来源了在github上: libcuckoo.
参考
- MemC3: Compact and Concurrent MemCache with Dumber Caching and Smarter Hashing,NSDI ’13.
- B. Atikoglu, Y. Xu, E. Frachtenberg, S. Jiang, and M. Paleczny. Workload analysis of a large-scale key-value store. In Proceedings of the SIGMETRICS’12, 2012.
