The RAMCloud Storage System
引言
RAMCloud是一个基于内存的分布式存储系统,所有的数据任何时候都保存在内存之中,RAMCloud达到了3个总体目标: low latency, large scale, 和 durability。RAMCloud各方面技术的应用都是很激进的。RAMCloud的实现的多个方面都已经发了Paper,而且之前也已经看过了3篇Paper,主要设计到RAMCloud的内存分配方式,RAMCloud的Kye/Value索引的实现以及RAMCloud的快速的恢复机制。这篇文章是RAMCloud的一篇综述性的Paper。另外RAMCloud的一篇主要的Paper就是关于其一致性实现的[2]。
架构 & 日志结构式存储 & 容错以及恢复
这几点的内容在前面的Paper中以及基本看过了[3,4,5].
- RAMCloud是一种更加复杂一点的Key/Value的架构,支持索引(不够[4]发表的时间在这篇Paper之后,这里还没有设计到[4]的内容)。数据分区,分布式的内存存储,带副本。
- 内存分配的方式不是传统的malloc或者是类似一些类型的方式,而是一种类似在文件系统中常用的日志结构式存储。
- RAMCloud会将数据持久化到磁盘上,为了支持系统在Crash之后在短时间内恢复,RAMCloud基本的思路就是使用非常大数据的磁盘来提供足够快的恢复时间。RAMCloud好像也不保证完全不丢数据。
- RAMCloud恢复的方式基本还是基于副本和将数据持久化到磁盘上面的方式。
低延时
RAMCloud的一个设计的目标就是将端到端的延迟控制在5us以下,这个在当时的常见的RPC的实现上是非常难以做到的。RAMCloud在实现这么低延迟的RPC实现的时候要处理不少的问题:1. 网络带宽和延迟的问题,RAMCloud设计的时候一台交换机带来的延迟就是10到30 μs,而且一般会经过5台这样的交换机;2. Kernel call,数据包经过内核处理、上下文切换带来的开销;3. 锁等同步操作带来的开销;4. 在追求超低延迟的时候一个CPU Cache确实都要考虑到;5. 批量处理带来的问题,批量处理系统设计中常用的一个提高吞吐量的方法,但是会增加延迟。在网络基础设施本身带来的延迟上面,RAMCloud任务网络技术的发展会解决这些问题,特别是更高速以太网和RDMA之类的技术的使用。另外RAMCloud采用的解决方案,
- Kernel Bypass和轮询。Kernel Bypass是现在很多的优化网络栈使用的方法。Kerbel Bypass的方式绕开了内核,来消除or降低了内核网络栈冗长的处理路径、内核空间和用户空间频繁切换带来的overhead、内核空间和用户空间之间的内存拷贝。RAMCloud让NIC设备使用的内存被之间映射到应用的内存控制之重,使得应用可以直接处理来自NIC的数据。在RAMCloud设计的时候,具有这类功能的NIC还不是很常见,但是RAMCloud认为这个在以后会变的很常见。而且RAMCloud中使用的Infiniband NIC也支持这样的方式。另外,为了避免网络栈在等待事件导致增加延迟,RAMCloud直接使用轮询的方式,优化了使用中断和睡眠唤醒线程上消耗的时间;
- RAMCloud支持传输的方式是多样的,在RAMCloud 1.0中,支持Infiniband、Kernel Bypass方式实现的定制的协议(使用UDP数据包的格式)、TCP。TCP的延迟要比Infiniband方式长50到100 μs。很显然这里直接使用TCP是无法满足RAMCloud设计的要求的;
- 为了降低延迟,RAMCloud在开始设计的时候考虑了单线程的设计,单个现场轮询请求然后处理请求马上恢复。不养方法在处理一个耗时的请求的时候存在严重的缺陷(也是redis的缺陷)。最终RAMCloud还是使用了多线程的设计。RAMCloud的RPCs有一个单独的分发线程(dispatch thread)和一组工作线程(worker threads )合作处理。前者处理网络通信,后者处理实际的请求。为了降低延迟,两类线程之间的交互也是使用轮询的方式。分发线程选择一个空闲的工作线程,将请求相关结构的指针保存到这个工作线程轮询的一个地方即可。
从上面可以看出,为了降低延迟,RAMCloud采用的都是很激进的方法。
时间消耗分析
在Paper中,RAMCloud详细分析了时间消耗的地方。花费在网络上面的时间还是最多的,除此之外,内存确实和线程工作交接上面的时间先后占了主要的部分,
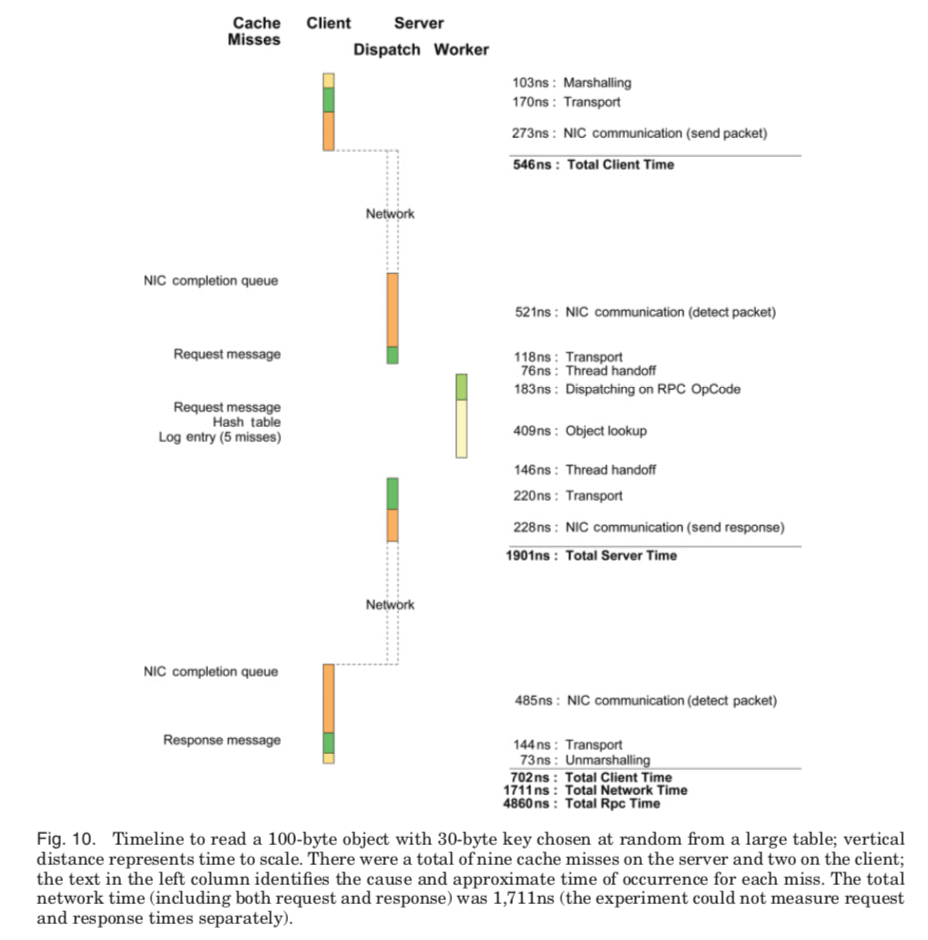
Where Does the Time Go?. Figure 10 shows a timeline for a read of a small object chosen at random from a large table. Three factors account for almost all of the latency:
* Network: 3.2μs out of the 4.8μs total time was spent in the Infiniband network or communicating between the CPU and NIC.
* Cache misses: There were a total of nine L3 cache misses on the server for each read request; Figure 10 displays the reason for each. A normal L3 cache miss takes 86ns, but RAMCloud issues prefetch instructions for network packets and log entries, and this reduces the cost for several of the misses.
* Thread handoffs: The timeline shows about 220ns in direct costs due to thread handoffs between the dispatch and worker threads. However, the handoffs also resulted in 24 additional L2 cache misses that are not visible in the figure.
线性一致性的实现
这部分的内容实际上不在这篇Paper[1]里面。而是在[2]中。[2]主要讨论的是在RAMCloud中至少一次和精确一次RPC语义的实现RIFL (Reusable Infrastructure for Linearizability)。至少一次实现的难度远低于精确一次,RIFL要实现精确一次的语义,要解决四个主要的问题:1. RPC标识,2. 完成记录持久化,3. 重试请求,4. 垃圾回收。
实现
上面提到的几点在RIFL中的实现,
-
RPC标识,RIFL使用2个64bit的值来唯一标识一个RPC请求,一个64bit唯一表示一个客户端,一个64bit序列号唯一表示这个客户端的一个请求。这里主要解决的事这个客户端分配的问题,对于序列号,由客户端自己递增即可。RIFL使用的方式是在分布式中常用的租约机制。这个客户端ID分配有一个Zookeeper来管理,ID在一段时间内有效。另外,为了解决系统中更新这这个ID和有效性检查的overehad,RIFL使用的方式是只有在将要过期的时候才去进行有效性检查。这里还使用了一种cluster clock的机制,
The lease server implements a cluster clock, which is a time value that increases monotonically at the rate of the lease server’s real-time clock and is durable across lease server crashes. The lease server returns its current cluster clock value when- ever it responds to a client request for lease creation or re- newal, and the client includes this time in RPC requests. -
完成记录持久化,RIFL没有给出具体的实现,这个交给在实际使用的时候具体去实现。它要求这个持久化的记录必须满足下面的要求,
... This completion record must include the RPC identifier as well as any results that are returned to the client. Furthermore, the completion record must be created atomically with the mutations of the operation, and it must have similar durability properties. It must not be possible for an operation to complete without a visible completion record, or vice versa. RIFL assumes that the underlying system provides durable storage for completion records. -
重试请求,在大型的分布式系统,仅仅是在超时之后重试还是不够的。下一次请求的时候可能处理的机器or保存相关数据的位置变化了,还要处理在涉及到多个服务器的时候那一个服务器保存了完成记录。RIFL这里的解决方式是一个对象保存的地方要和请求完成记录保存的地方相同,移动的时候必须一起移动。在涉及到多个对象时,选择其中一个可区分的作为主要的对象,
one of them is chosen as a distinguished object for that operation, and the completion record is stored with that object. The distinguished object must be chosen in an unambiguous fashion, so that retries use the same distinguished object as the original request. -
垃圾回收,这里主要就是完成记录的回收的问题。这里要确保回收的记录对于的RPC不会在再次请求。同样,这里也是依赖于租约的机制。
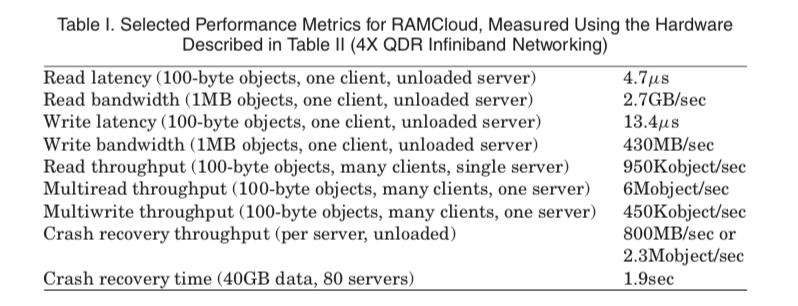
评估
这里的具体的信息可以参考[1],
参考
- John Ousterhout, Arjun Gopalan, Ashish Gupta, Ankita Kejriwal, Collin Lee, Behnam Montazeri, Diego Ongaro, Seo Jin Park, Henry Qin, Mendel Rosenblum, Stephen Rumble, Ryan Stutsman, and Stephen Yang. 2015. The RAMCloud storage system. ACM Trans. Comput. Syst. 33, 3, Article 7 (August 2015), 55 pages. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1145/2806887 .
- Implementing Linearizability at Large Scale and Low Latency, SOSP’15.
- Log-structured Memory for DRAM-based Storage. FAST 2014.
- SLIK: Scalable Low-Latency Indexes for a Key-Value Store, ATC ’16.
- Fast Crash Recovery in RAMCloud, SOSP ‘11.
