KV-Direct: High-Performance In-Memory Key-Value Store with Programmable NIC
引言
KV-Direct[1]是SOSP 2017上的一篇关于利用可编程网卡和FPGA实现Key-Value Store的Paper。号称可在单机上实现1.22 billion的 KV操作。
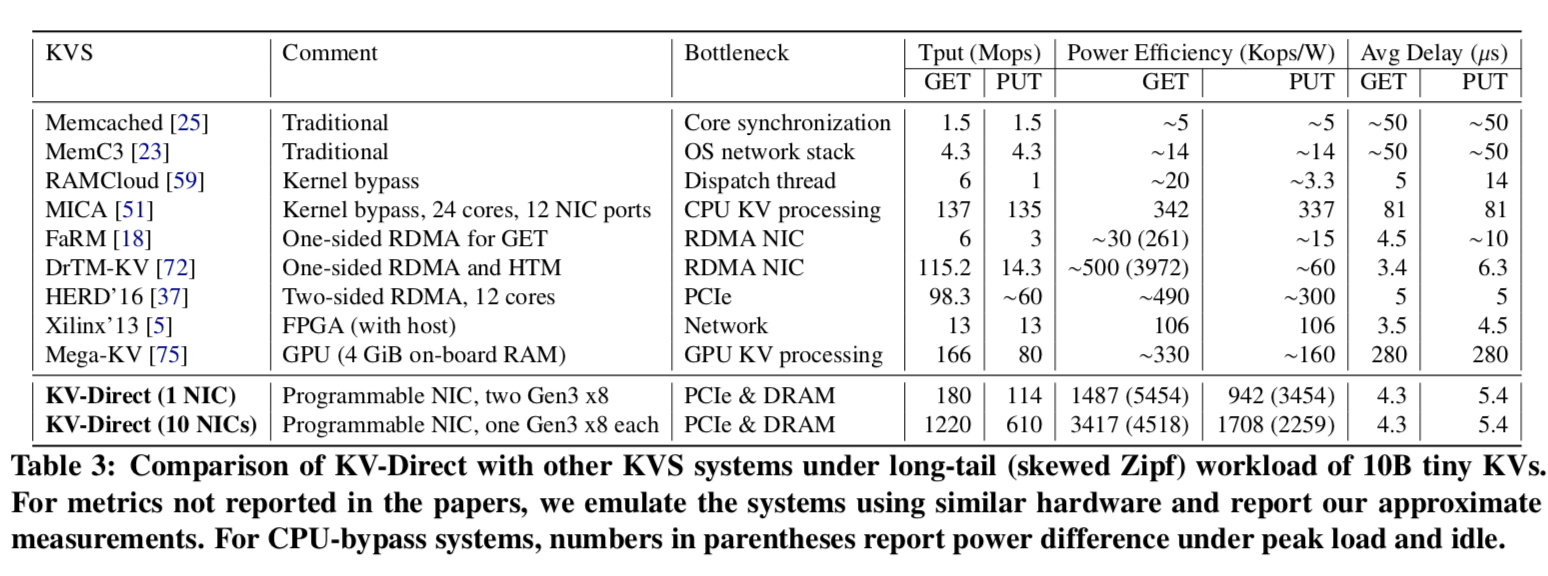
A single NIC KV-Direct is able to achieve up to 180 M KV operations per second (Ops), equivalent to the throughput of 36 CPU cores. Compared with state-of-art CPU KVS implementations, KV-Direct reduces tail latency to as low as 10 μs while achieving a 3x improvement on power efficiency. Moreover, KV-Direct can achieve near linear scalability with multiple NICs. With 10 programmable NIC cards in a server, we achieve 1.22 billion KV operations per second in a single commodity server, which is more than an order of magnitude improvement over existing systems.
KV-Direct支持的基本操作:
基本架构
KV-Direct名字的含义就是支持remote direct key-value access,client可以直接通过KV-Direct operations 来对KVS进行相关操作,bypass CPU。利用可编程网卡和FPGA实现超高的性能。
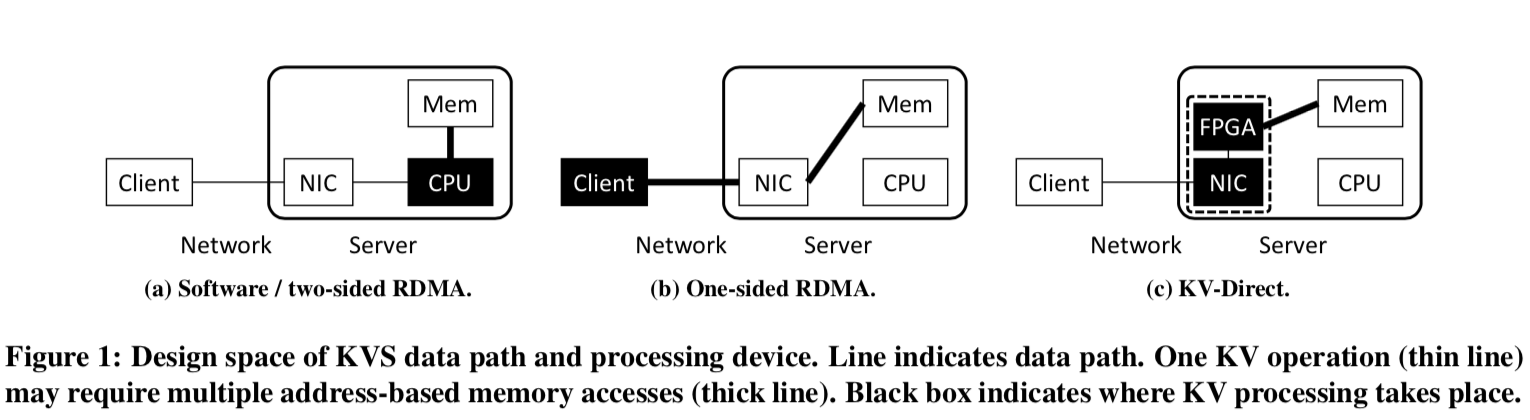
在实现KV-Direct的过程中,主要要解决一下三个困难:
- Minimize DMA requests per KV operation,最小化KV操作的DMA请求;
- Hide PCIe latency while maintaining consistency. 隐藏PCIe延时的同时保持一致性;
- Dispatch load between NIC DRAM and host memory. 分发网卡的DRAM和主机内存的load;
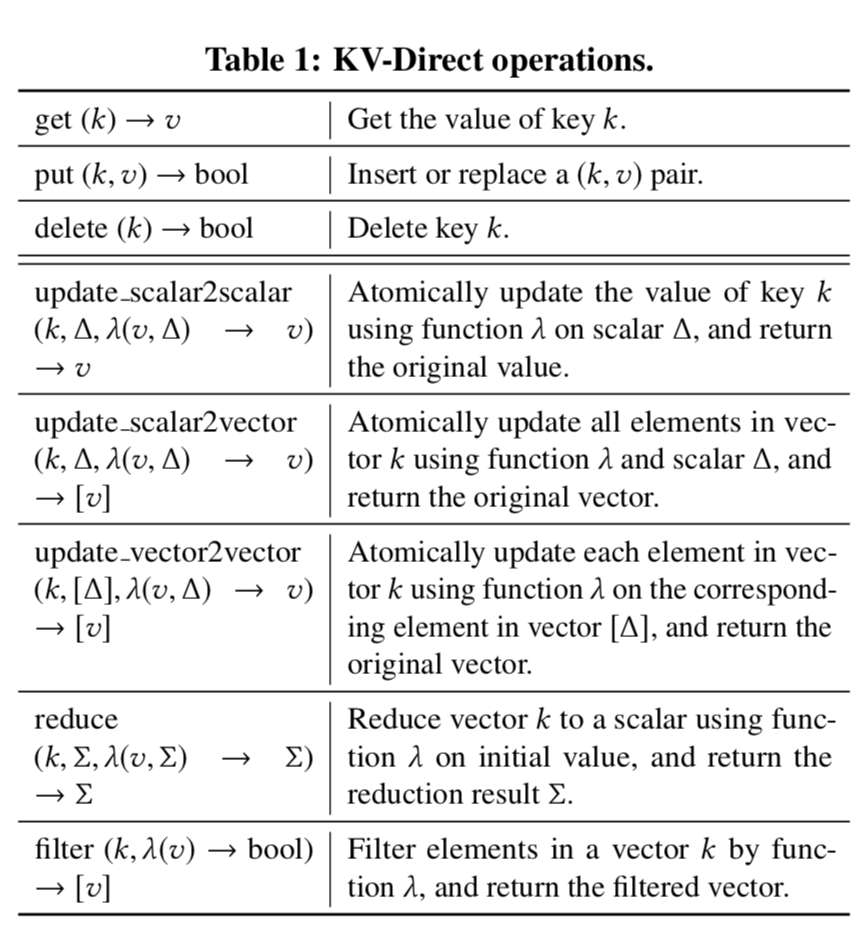
KV-Direct Operations
KV-Direct拓展了RDMA的操作以支持kv操作,在上面的表中有集中的体现。除了常见的get put delete操作之外,KV-Direct还支持2中不同类型的向量操作:1. 发送一个标量去更新server上一个向量中的每一个元素,2. 发送一个向量去一个对应一个地更新server上面原来的向量。 此外,KV-Direct还支持用户定义的更新函数,不过地提前注册、编译到硬件逻辑之中。向量更新操作时,规约和过滤操作是在一个key上进行的,向量的值被当作是一个固定bit宽度的元素数组。
Each function λ operates on one element in the vector, a client-specified parameter à, and/or an initial value (求和符号) for reduction. The KV-Direct development toolchain duplicates the λ several times to leverage parallelism in FPGA and match computation throughput with PCIe throughput, then compiles it into reconfigurable hardware logic using an high-level syn- thesis (HLS) tool.
...
Vector reduce operation supports neighbor weight accumulation in PageRank. Non-zero values in a sparse vector can be fetched with vector filter operation.
KV Processor
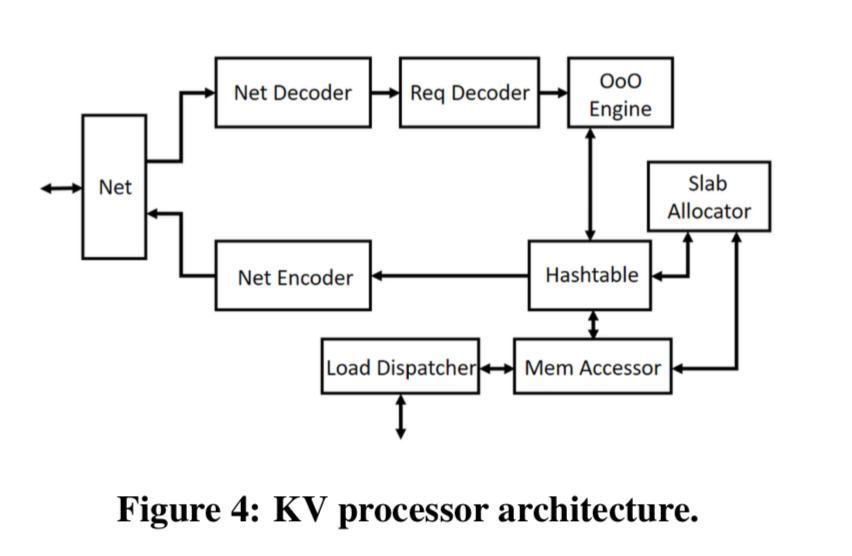
上面的图表示了KV Processor的操作过程:
- 从网络中收到数据包,从中解码除操作,然后吧这些操作缓存到一个保留站里面。这里时由FPGA操作的;
- 之后,乱序执行引擎发出独立的kv操作到操作解码器;
- 根据操作的类型,查询hash table,然后执行对应的操作;
- 当这些操作完成的时候,结构返回乱序执行引擎,在保留站内知道对应的kv操作;
- 然后就执行前面的反操作,给客户端返回数据(如果是需要发挥数据的类型)(这一步论文中没有直接说明,不过看情况应该就是这样的).
Hash Table
这里支持这么高的QPS,hash table的设计也是至关重要的。为了支持变长的key-value。KV存储被分为了2部分,一部分就是hash index,它有固定数量的hash bucket组成,每一个hash bucket有一些hash slots和一些远元数据组成。(也就是说这里的hash table是不支持rehash操作的,必须提前决定好大小)。另外的一部分就是动态分配的部分,使用的slab分配器。对于一些小的key-value对象,就可以直接inline在slot里面,不用使用slab分配器去动态分配内存。
KVs smaller than a threshold are stored inline in the hash index to save the additional memory access to fetch KV data. An inline KV may span multiple hash slots, whose pointer and secondary hash fields are re-purposed for storing KV data. It might not be optimal to inline all KVs that can fit in a bucket. To minimize average access time, assuming that smaller and larger keys are equally likely to be accessed, it is more desirable to inline KVs smaller than an inline threshold.
对于hash冲突的解决,这里没有使用在key-value store里面常用的cukcoo hash or其它类似的一些hash,而是就是更加常见的chaining。原因就是这种方法能更好的平衡写入和读取操作。
When all slots in a bucket are filled up, there are several solutions to resolve hash collisions. Cuckoo hashing and hopscotch hashing guarantee constant-time lookup by moving occupied slots during insertion. However, in write-intensive workload, the memory access time under high load factor would experience large fluctuations. Linear probing may suffer from primary clustering, therefore its performance is sensitive to the uniformity of hash function. We choose chaining to resolve hash conflicts, which balances lookup and insertion, while being more robust to hash clustering.
Slab Memory Allocator
Slab就是为了提高内存分配的性能,这里没什么特别好讨论的。
Slab allocator rounds up allocation size to the nearest power of two, called slab size. It maintains a free slab pool for each possible slab size (32, 64, . . . , 512 bytes), and a global allocation bitmap to help to merge small free slabs back to larger slabs. Each free slab pool is an array of slab entries consisting of an address field and a slab type field indicating the size of the slab entry. The free slab pool can be cached on the NIC.
Out-of-Order Execution Engine
为了解决乱序执行请求直接的依赖问题,这里引入了类似CPU中乱序执行功能中的保留站,并追踪这些执行中的操作和他们的执行上下文。上面提到个,为了隐藏PCIe的延时,需要将操作流水线化,执行中的操作需要有256个才呢充分利用这些资源。然而,直接在FPGA中比较key是不合适的(需要比较key来判断这些操作直接的关系),因为这样很消耗FPGA的资源。这里的解决方案是指用一个hash table将这些操作分类,使用的就是key的hash值。就hash相同的视为是对同一个key的操作,虽然这样可能导致一些误判,但是不会忽略。
Operations with the same hash are organized in a chain and examined sequentially. Hash collision would degrade the efficiency of chain examination, so the reservation station contains 1024 hash slots to make hash collision probability below 25%.
此外,保留站的另外一个功能就是data forwarding(类似流水线中的data forwarding,呀,不知道这个怎么用中文表述 了)。在保留站中保留最近key对应的value,对应后面的操作,如果是get操作,则可以直接返回数据,对于写入操作,则之后返回更新的值,不过由于还要更新到内存里面去,所以还有添加适当的PUT操作。
For atomic operations, the computation is performed in a dedicated execution engine. For write operations, the cached value is updated. The execution result is returned to the client directly. After scanning through the chain of dependent operations, if the cached value is updated, a PUT operation is issued to the main processing pipeline for cache write back. This data forwarding and fast execution path enable single-key atomics to be processed one operation per clock cycle (180 Mops), eliminate head-of-line blocking under workload with popular keys, and ensure consistency because no two operations on the same key can be in the main processing pipeline simultaneously.
DRAM Load Dispatcher
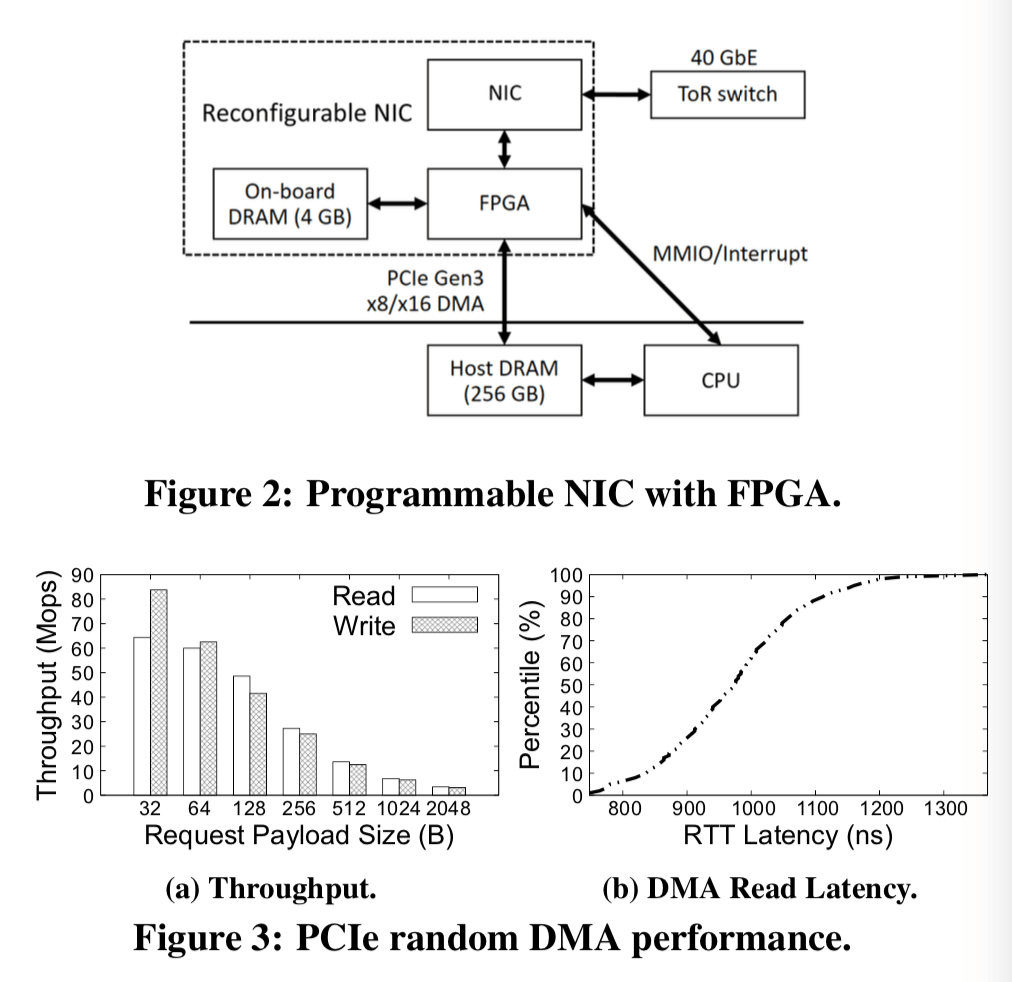
从上面的一幅图可以看出来,NIC中也有4GB的内存使用。KV-Direct将这些内存当cache使用,又将这些内存当中是key-value store的一部分,采用了一个hybrid的方式。
The cache-able part is determined by the hash of memory address, in granularity of 64 bytes. The hash function is selected so that a bucket in hash index and a dynamically allocated slab have an equal probability of being cache-able. The portion of cache-able part in entire host memory is called load dispatch ratio (l).
个人觉得这里重点就是如何利用FPGA去处理这些东西,最后结合OSDI 2016上面的ClickNP这篇文章一起来看看.
评估
只放一张性能比较的图,性能爆表。
参考
- KV-Direct: High-Performance In-Memory Key-Value Store with Programmable NIC,SOSP 2017.
