Reducing the Storage Overhead of Main-Memory OLTP Databases with Hybrid Indexes
0x00 引言
这篇文章的idea也是very excellent,paper的主要目的是减少内存数据库中内存的使用。通过讲结构分为两个部分,一个部分负责读取写入,另外一个只负责读取,通过对后一个的优化减少了大量的内存使用:
The dual-stage architecture maintains a small dynamic “hot” store to absorb writes and a more compact, but read-only store to hold the bulk of index entries. Merge between the stages is triggered peri- odically and can be performed efficiently. Unlike prior work [20, 35, 39, 47, 53], our design offers low latency and high throughput for the point queries and short-range scans that typify the OLTP workloads used with main-memory databases [34, 50].
....
we find that hybrid indexes meet the goals, achieving performance comparable to the original indexes while reducing index memory consumption by up to 70% (Section 6). Also, by using hybrid indexes, H-Store is able to sustain higher throughput for OLTP workloads for more transactions and with fewer performance interruptions due to memory limitations (Section 7).
0x01 基本设计
先给一幅图,基本说明了这个idea的设计思路:
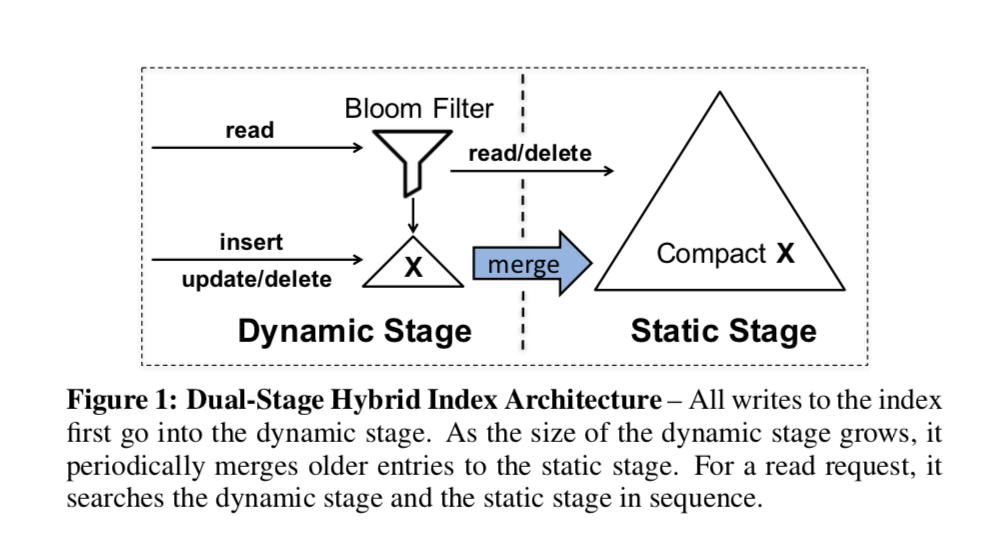
新的数据已开始加入到Dynamic Stage中,此stage只保存少量的数据项,就好比普通的一个数据结构。随着数据的增长,Dynamic Stage增长到一定程度的时候,将变旧的数据批量的迁移到Static Stage。由于这里是只读,这样就可以做很多的优化,之后会提到。此外,对于delete,在Dynamic Stage中的时候和普通的删除没有差别,在Static Stage的时候,先标记为deleted,下一次merge的时候会将其真正的删除。这个设计支持多种的数据结构,讲一个传统的数据结构变为这种Daul-Stage的策略只需要4步:
• Step 1: Select an order-preserving index structure (X) that supports dynamic operations efficiently for the dynamic stage. • Step 2: Design a compact, read-optimized version of X for the
static stage.
• Step 3: Provide a merge routine that can efficiently migrate
entries from X to compact X.
• Step 4: Place X and compact X in the dual-stage architecture
as shown in Figure 1.
0x02 动态到静态的规则
这样先来一幅paper的图,很好的解释了思路:
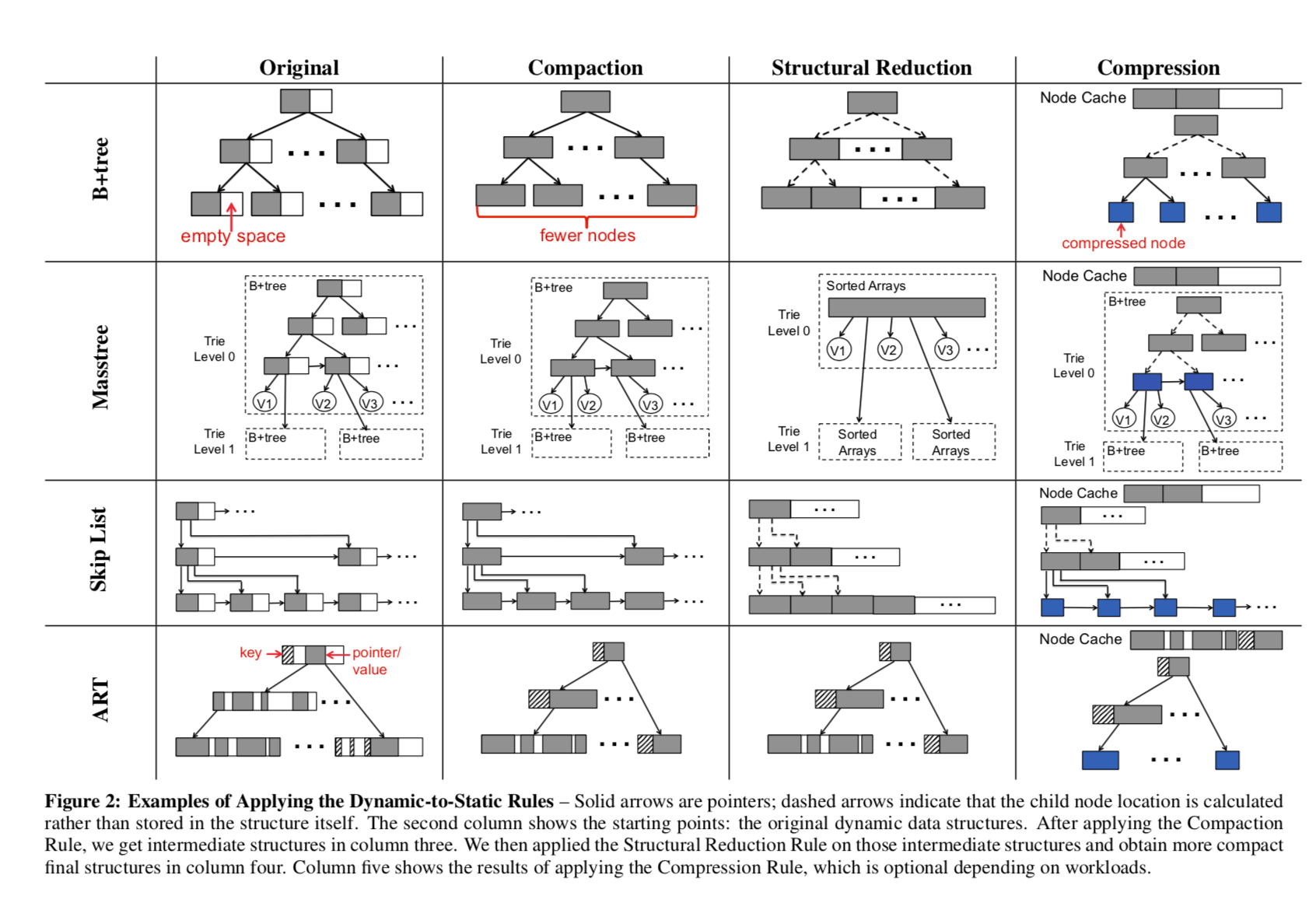
由于是只读的,一般节点中都会为后来要添加的数据预留了空间,这也是造成内存浪费的一个主要原因。这里就可以直接将其去除了。此外,由于结构不会被更新,是固定的,就可以去除很多的冗余的结构,让结构更加紧凑。此外,还可以对数据进行压缩:
• Rule #1: Compaction – Remove duplicated entries and make every allocated memory block 100% full.
• Rule #2:StructuralReduction–Removepointersandstruc- tures that are unnecessary for efficient read-only operations.
• Rule #3: Compression – Compress parts of the data structure
using a general purpose compression algorithm.
Paper中具体讨论对B+tree,Masstree,SkipList,ART的修改。
0x03 Merge
具体的Merge方法和具体使用的数据结构有关系,这里就不具体讨论了。主要看的是Merge那些数据和什么时候Merge。
What to Merge
- Merge-all,一次将Dynamic Stage中所有的数据都merge到Static Stage中去,这个方法最简单直观,但是缺点是merge的时候会有不小的压力,也会将热点的数据merge过去,这有时候不是一个很好的选择。
- Merge-cold,只merge较cold的数据,优点是hot数据可以保存在Dynamic Stage中,缺点是merge操作会更加频繁,而且需要确定哪些数据是cold的,会造成额外的操作。
根据OLTP的特点,paper选取了前者:
Although merge-cold may work better in some cases, given the insert-intensive workload patterns of OLTP applications, we con- sider merge-all to be the more general and more suitable approach. We compensate for the disadvantage of merge-all (i.e., some older yet hot tuples reside in the static stage and accessing them requires searching both stages in order) by adding a Bloom filter atop the dynamic stage as described in Section 3.
When to Merge
这里采用的方法是根据Dynamic和Static数据的比例来决定是否merge的,思路比较简单:
The advantage of a ratio-based trigger is that it automatically ad- justs the merge frequency according to the index size. This strategy prevents write-intensive workloads from merging too frequently. Although each merge becomes more costly as the index grows, merges happen less often. One can show that the merge overhead over time is constant. The side effect is that the average size of the dynamic stage gets larger over time, resulting in an increasingly longer average search time in the dynamic stage.
0x04 评估
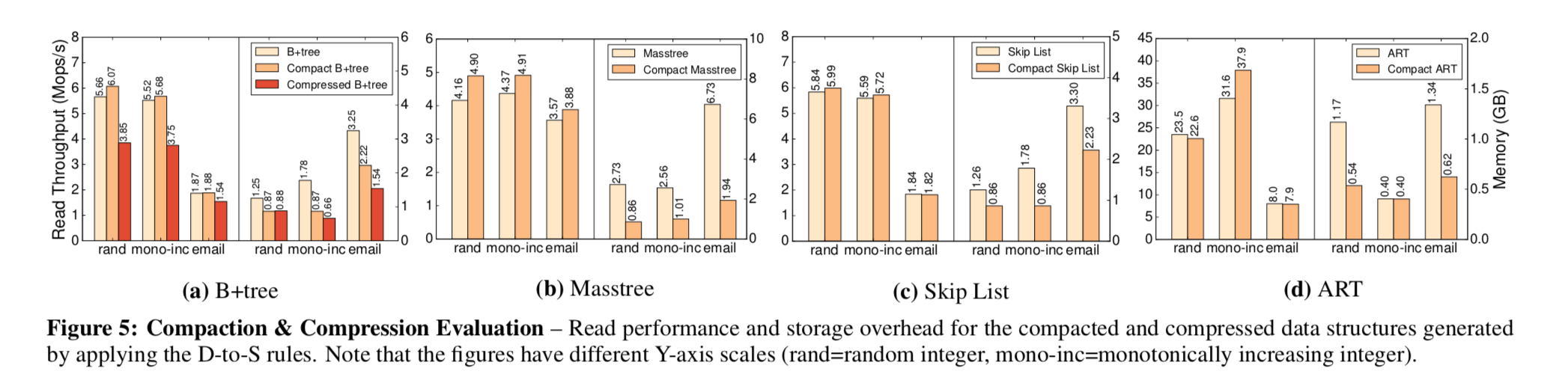
这里只关注了内存方面的数据,paper中的数据是很好看的。
参考
- Reducing the Storage Overhead of Main-Memory OLTP Databases with Hybrid Indexes , SIGMOD ‘16.
