SILT: A Memory-Efficient, High-Performance Key-Value Store
0x00 引言
这一篇讲的是为flash storage设计key-value的问题,SILT,即Small Index Lager Table。SILT最的特点就是每一个key-value只占用0.7bytes的DRAM和平均1.01次的flash读取,
SILT requires approximately 0.7 bytes of DRAM per key-value entry and uses on average only 1.01 flash reads to handle lookups. Consequently, SILT can saturate the random read I/O on our experimental system, performing 46,000 lookups per second for 1024-byte key-value entries, and it can potentially scale to billions of key-value items on a single host.
这里不只是一种基本key-value store的设计,这里给出了三种的设计方案:LogStore, HashStore, and SortedStore。
0x01 基本思路
下面的图是3者之间的一个比较:
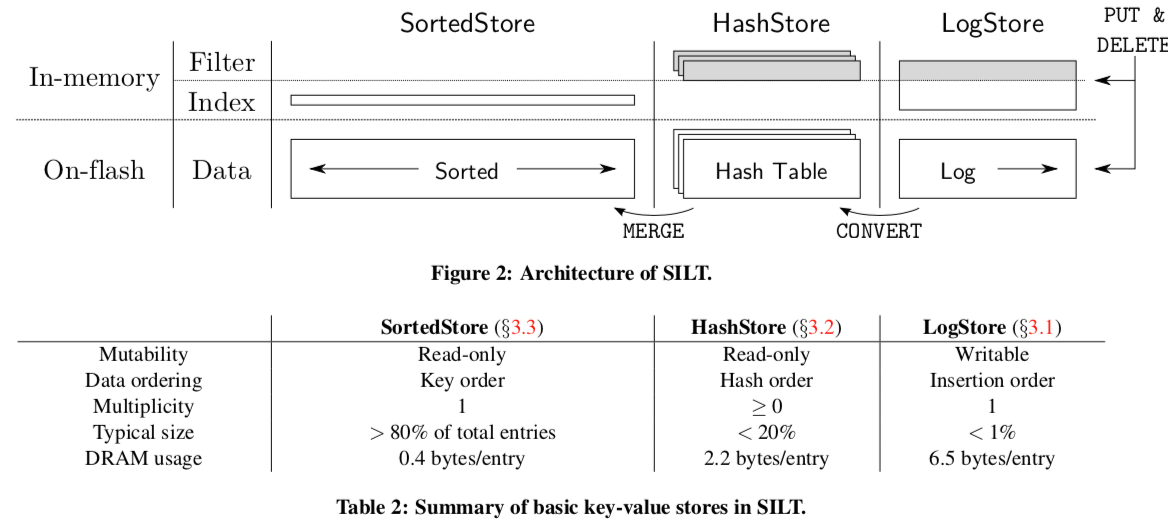
- LogStore,LogStore是一种写优化的设计,写入的时候就是添加到之前数据的末尾,在内存中使用hash tale记录key和对应value在这个log中的offset。这里使用的hash table叫做
partial-key cuckoo hashing。这里的思路其实和bitcask的思路很相似。在上面的图可以看出来,它的DRAM消耗的最大的。为了讲内存的使用限制在一个范围之内,这里对hash table的大小作了限制,当这个table的大小达到指定的大小的时候。这个会被转化为HashStore。 - HashStore,HashStore的数据作为一个保存在flash上面的hash table,这样的话就不用维持一个内存中的index。在内存中保存的是filter,当查询不存在的key的时候,可以避免查询flash上面的数据。
- SortedStore,SortedStore的数据为排好序的。通过使用 entropy-coded tries的方法讲每项的内存消耗降到0.4 bytes。这里的insert的操作消耗是很大的,所以这里使用的周期性地讲HashStore里面的数据和之前的就的SortedStore里面的数据合并为一个新的,同时删除已经无用的数据。
查找的顺序也是按照上面介绍的顺序,如果都没有找到,就说明这个数据不存在。
0x02 LogStore
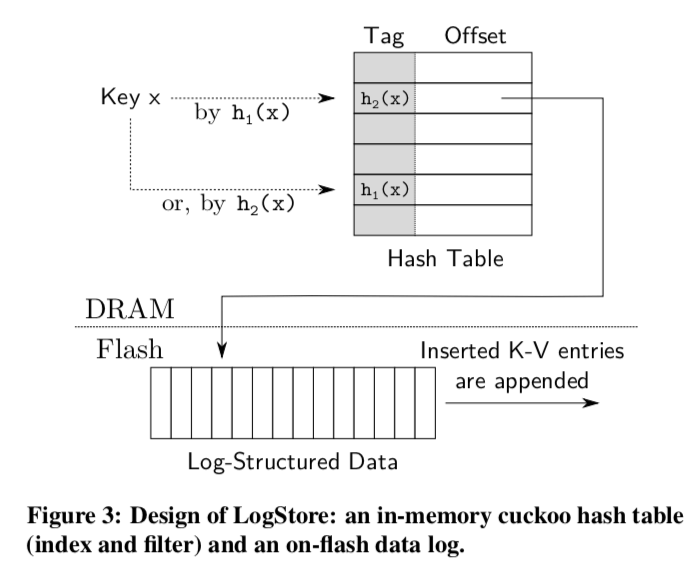
这里使用的hash为cukoo hashing。这里的一个特点就是不保存全部的key,而是保存一个tag。当这个tag匹配的时候,就从flash中取回全部的数据,对比key。使用这种方法要解决的一个问题是在cukoo hah的工作方式中,可能存在驱逐key的行为,这个时候需要key来计算这个tag,而这里的key有保存在flash,这样就有可能导致很多的flash读取的操作。为了解决这个问题,这里使用的方法是使用一个hash值来决定这个数据保存的位置,使用另外一个hash值来作为tag,这样的话可能的hash会一直保存,就不同重新读取计算了,
To find key x in the table, SILT checks if h1(x) matches the tag stored in bucket h2 (x), or if h2 (x) matches the tag in bucket h1 (x). If the tag matches, the (key,value) pair is retrieved from the flash location indicated in the hash entry.
0x03 HashStore
当LogStore的Hash Table达到指定的大小的时候,这个Table就会被冻结。然后将其转化为一个HashStore。这里减少内存使用的部分就是讲Hash Table转到Flah上面,
HashStore saves memory over LogStore by eliminating the index and reordering the on-flash (key,value) pairs from insertion order to hash order (see Figure 4). HashStore is thus an on-flash cuckoo hash table, and has the same occupancy (93%) as the inmemory version found in LogStore.
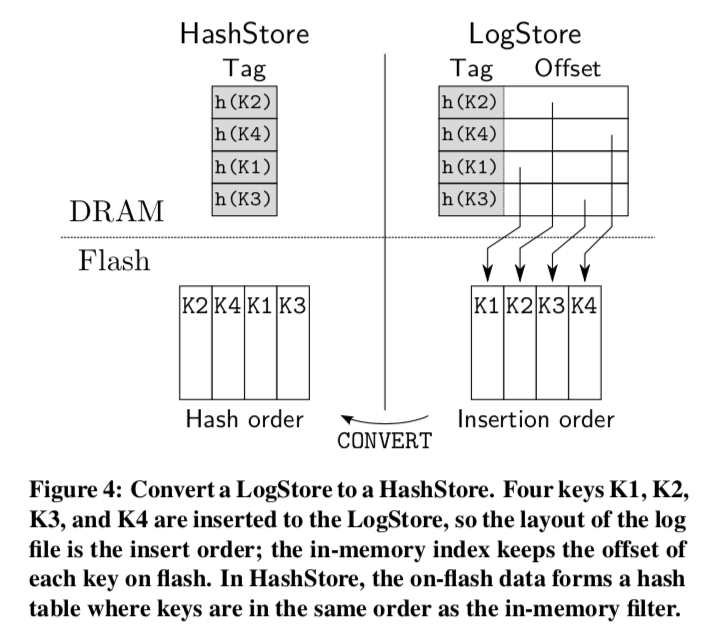
与常用的基于Bloom Filter的过滤器不相同,这里使用的是基于 partial-key cuckoo hashing的方法,创建的方式也很简单,直接使用复制LogStore的Hash Table中的tag部分的数据即可。
0x04 SortedStore
这里的重点就是如何实现上面表格中的0.4bytes/entry的超低的内存占用。这里的trie的表示使用了递归的方法,如果一个Tri的表示计为Repr(T),那么存在:
Repr(T) := |L| Repr(L) Repr(R)
其中L为左子trie的结点的数量。如果为空的话, 为了简化处理这里就表示为-1。如此这个trie的构造算法就是下面的代码。这里L R分叉使用的在这一层的bit为0 or 1.
# @param T array of sorted keys
# @return trie representation def construct(T):
if len(T) == 0 or len(T) == 1:
return [-1]
else:
# Partition keys according to their MSB
L = [key[1:] for key in T if key[0] == 0]
R = [key[1:] for key in T if key[0] == 1]
# Recursively construct the representation
return [len(L)] + construct(L) + construct(R)
# Algorithm 1: Trie representation generation in Python-like syntax.
# key[0] and key[1:] denote the most significant bit and the remaining bits of key, respectively.
如何查询呢:
# @param key lookup key
# @param trepr trie representation
# @return index of the key in the original array
def lookup(key, trepr):
(thead, ttail) = (trepr[0], trepr[1:])
if thead == -1:
return 0
else:
if key[0] == 0:
# Recurse into the left subtrie
return lookup(key[1:], ttail)
else:
# Skip the left subtrie
ttail = discard_subtrie(ttail)
# Recurse into the right subtrie
return thead + lookup(key[1:], ttail)
# @param trepr trie representation
# @return remaining trie representation
# with the next subtrie consumed
def discard_subtrie(trepr):
(thead, ttail) = (trepr[0], trepr[1:])
if thead == -1:
return ttail
else:
# Skip both subtries
ttail = discard_subtrie(ttail)
ttail = discard_subtrie(ttail)
return ttail
也就是上面构造的时候思路的一种逆应用。从这里就可以看出里,这样的构造方式简单易行,缺点在与构造之后添加的操作是很麻烦的,所以这里使用的当HashStore到一定的大小之后一次性合并的办法。在这里在[1]中还有更多细节的东西。
评估
这里具体的信息可以参看[1].
参考
- SILT: A Memory-Efficient, High-Performance Key-Value Store, SOSP’11.
