NetChain: Scale-Free Sub-RTT Coordination
0x00 引言
这篇文章将的是利用可编程交换机做的一个Coordination Service(类似Chubby Zookeeper),是NetPaxos 和NetCache的后续,想法都是将一些东西使用可编程的交换机来实现。
We present NetChain, a new approach that leverages the power and flexibility of new-generation programmable switches to provide scale-free sub-RTT coordination. In contrast to server-based solutions, NetChain is an in-network solution that stores data and processes queries entirely within the network data plane.
0x01 NetChain Overview
NetChain可以看作是在可编程交换机上实现一个key-value store,并且将一个交换机的上面存储的东西复制到多个交换机上,然后在此基础上实现其它的功能(Coordination Services),
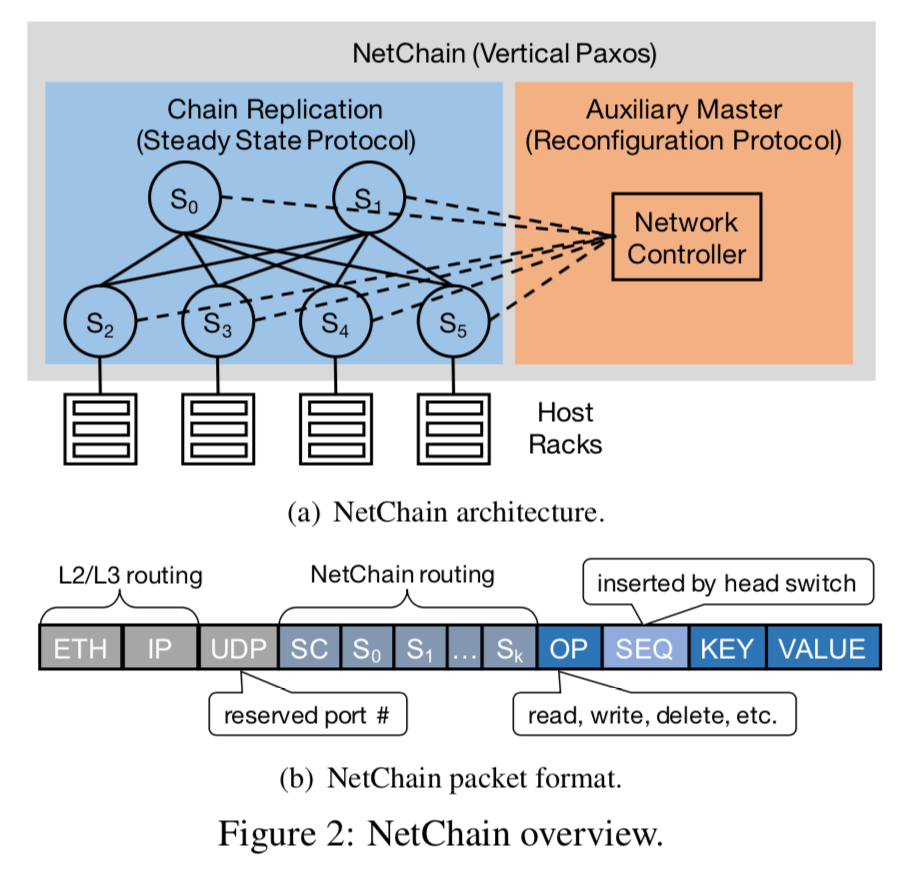
为了将key-value store做到多个交换机上,并保证强一致性和容错能力,NetChain这里使用了Vertical Paxos,并使用Chain Replication来做数据的复制。Vertical Paxos将一个consensus protocol 分为了两部分,一部分是steady state protocol,另外一部分是reconfiguration protocol,这部分在NetChain中被映射为 network data 和 control planes。第一部分通常是一个primary-backup (PB) protocol,处理读写请求和保持强一致性,f+1个服务器可以容忍f个服务器故障。第二部分的reconfiguration protocol 使用的是一个auxiliary master 处理节点加入和离开等的工作。
While it seems to move the fault-tolerance problem from the consensus protocol to the auxiliary master, Vertical Paxos is well-suited to NetChain because reconfigurations such as failures (on the order of minutes) are orders of magnitude less frequent than queries (on the order of microseconds). So handling queries and reconfigurations are mapped to data and control planes, respectively.
由于交换机转发的特点,这里使用的复制protocol就是Chain Replication,通常情况下一个Coordination Service的工作过程就像下面一样:
client → coordination servers → client.
通过NetChain变成了下面这样:
client→ network switches → client
0x02 NetChain Data Plane
Key-Valye Storage
Data Plane就是一个in-network的key-valye store,使用Chain Replication来保证强一致性。如何使用在交换机内实现这些东西呢?
NetChain provides strong consistency: (i) reads and writes on individual keys are executed in some sequential order, and (ii) the effects of successful writes are reflected in subsequent reads. NetChain assumes trustworthy components; otherwise, malicious components can destroy these consistency guarantees.
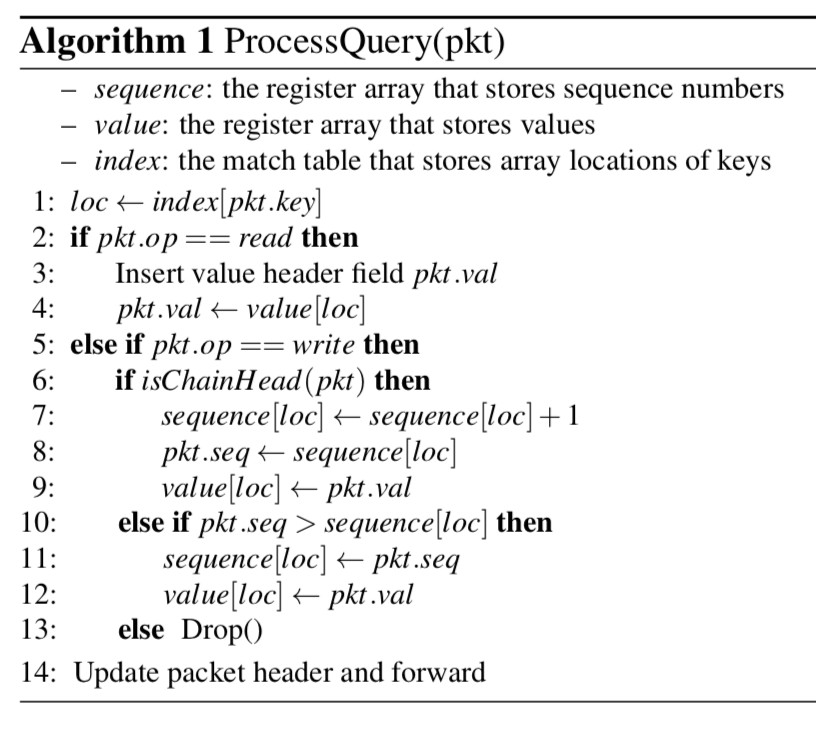
NetChain利用前面的NetCache上面做的一些东西,将key-value store做到了可编程交换机的on-chip memory上面,每一个key作为保存到match table中的一项, 而value保存到一个register array中的一个位置中.
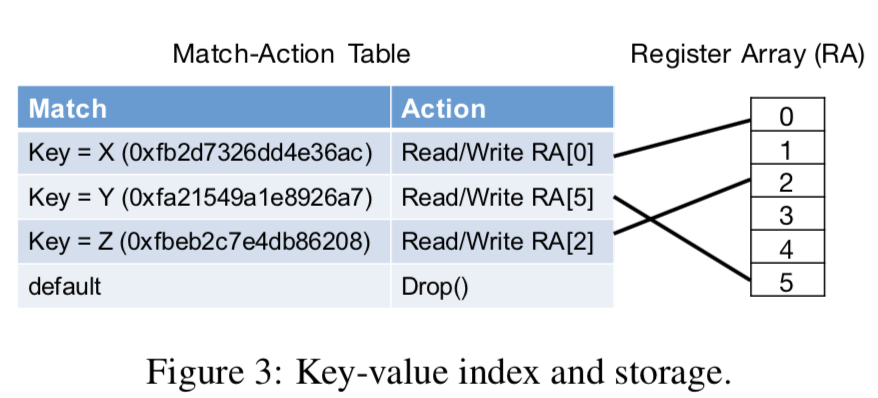
NetChain利用可编程交换机的支持自定义的包格式的功能,在UDP的基础上实现NetChain的包格式(Figure 2(b) )。包里面包含了操作类型,key,value等的字段.
Delete queries invalidate key-value items in the data plane and requires the control plane for garbage collection. Insert queries require the control plane to set up entries in switch tables, and thus are slower than other operations. This is acceptable because Insert is a less frequent operation for the use cases of coordination services.
此外,NetChain还是用将kye-value数据分区存放。NetChain处理数据包:
NetChain Routing
在Chain Replication中,每一个server是需要知道自己的前继和后继的,NetChain这里的使用方式是将这些IP list保存在数据包里面,上面的图有表示。利用一个SC字段来确定下一个节点。
When a switch receives a packet and the destination IP matches its own address, the switch decodes the query and performs the read or write operation. After this, the switch updates the destination IP to the next chain node, or to the client IP if it is the tail.
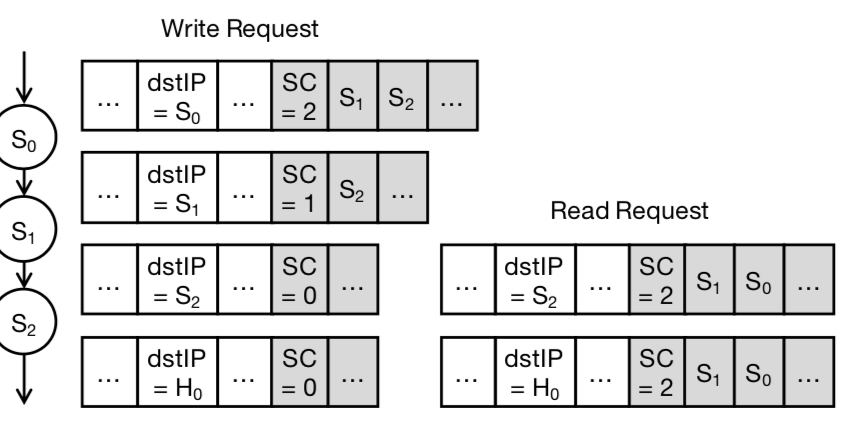
写操作和读操作使用IP list的顺序是相反的。
In-Order Key-Value Update
为了解决数据包转发过程中的乱序的问题,NetChain使用的方式就是一个sequence numbers,使用方式在上面的伪代码的图中有体现。第一个交换机给写操作一个单调递增的se-quence numbers,其它的交换机对于这些操作必须按照这个顺序处理。
0x03 NetChain Control Plane
Control Plane作为NetChain里面的一个组件只用来处理交换机的switch tables和将交换机的信息注册到NetChain中。
Fast Failover
当一个交换机出现故障时,这里解决的办法也是类型Chain Replication中的办法。由于NetCain中使用了一致性hash,一个交换机被映射到多个的虚拟结点,这样就可能导致比较多的更新操作。
Since each virtual node is in f +1 chains, a switch failure affects m( f + 1)/n chains in total. This implies that we need to update m( f + 1)/n switches for one switch failure in fast failover. While m( f + 1)/n is fewer than the number of servers, it still incurs consid- erable reconfiguration cost as m/n can be a few tens or hundreds.
为了减少这类更新结点,这里使用的方法就是在交换机里面添加一条新的规则: 如果目的地址就是失败的结点,那么就将这个数据包直接给失败结点的下一个结点,后者直接通知客户端(根据结点所处的位置)。
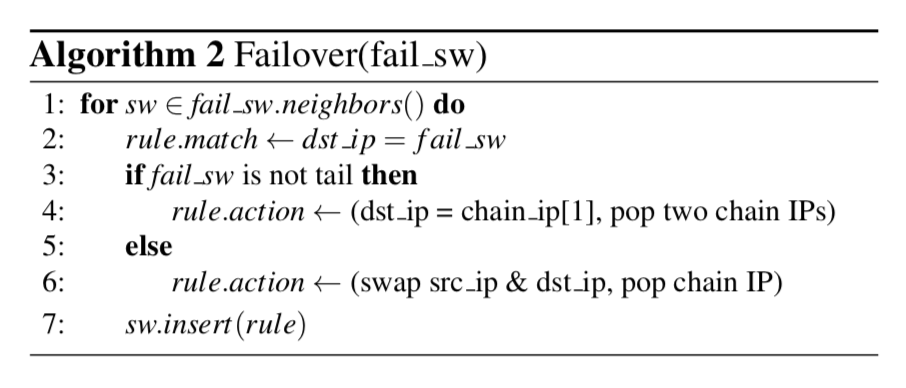
Failure Recovery
对于重新加入NetChain的交换机,主要的是要解决数据同步与一致性的问题。
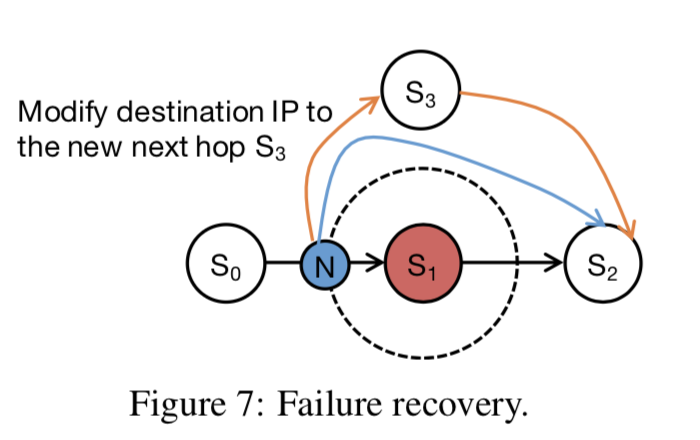
步骤:
-
Pre-synchronization,拷贝要添加位置的下一个结点的数据,在新加入的结点上添加规则;
-
Two-phase atomic switching,为了保证一致性,NetChian必须保证any node in the chain has newer values than its next hop,这里也分步骤进行:
-
Stop and synchronization,在数据和规则都准备好时就停止同步,必要的时候要停止写操作:
Since no new queries are forwarded to S2, the state on S2 and S3 would eventually become the same. In this phase, the chain stops serving write queries, but still serves read queries with S2. -
Activation,新加入的结点作为结点开始工作,并必要的时候需要修改规则。
-
对于中间的交换机按照上面的步骤进行就可以了,对于head or tail的交换机,想要其它一些额外的工作。对于head结点的重新加入,要处理的就是sequence number的问题,由于必须保证这个sequence number是递增的,这里使用的方式就是一个额外的session number,每次head改变就会递增这个session number 。当新添加入的结点是tail时,就可以去除上面需要的停止写操作的行为了:
we only need to copy the state from S0 that are updated before we finish dropping all queries on S1’s neighbor switches, as no new read queries are served. Then in Phase 2, we activate the chain by forwarding the queries to S3.
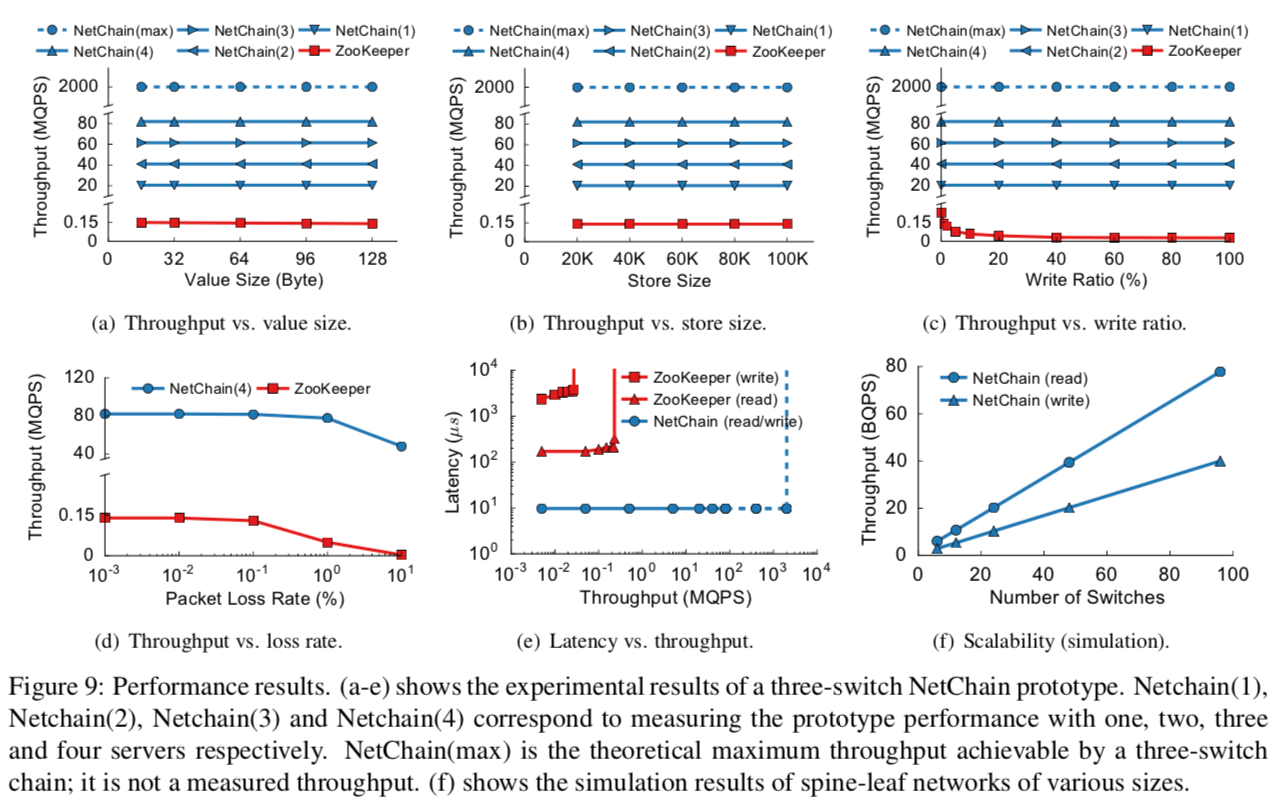
0x04 评估
参考
- NetChain: Scale-Free Sub-RTT Coordination, NSDI 2018.
