Dostoevsky: Better Space-Time Trade-Offs for LSM-Tree Based Key-Value Stores via Adaptive Removal of Superfluous Merging
0x00 引言
这篇Paper是SIGMOD‘17上面的Monkey的后续的文章,都来自哈佛大学同一个实验室,讲的都是LSM-tree的一些优化。这篇Paper消除一些不必要的merge的问题,
..., we introduce Lazy Leveling, a new de-sign that removes merge operations from all levels of LSM-tree but the largest. Lazy Leveling improves the worst-case complexity of update cost while maintaining the same bounds on point lookup cost, long range lookup cost, and storage space. We further introduce Fluid LSM-tree, a generalization of the entire LSM-tree design space that can be parameterized to assume any existing design. Relative to Lazy Leveling, Fluid LSM-tree can optimize more for updates by merging less at the largest level, or it can optimize more for short range lookups by merging more at all other levels.
We put everything together to design Dostoevsky, a key-value store that adaptively removes superfluous merging by navigating the Fluid LSM-tree design space based on the application workload and hardware.
0x01 基本思路
了就下面的LSM-tree的复杂度对理解Paper的内容很重要,
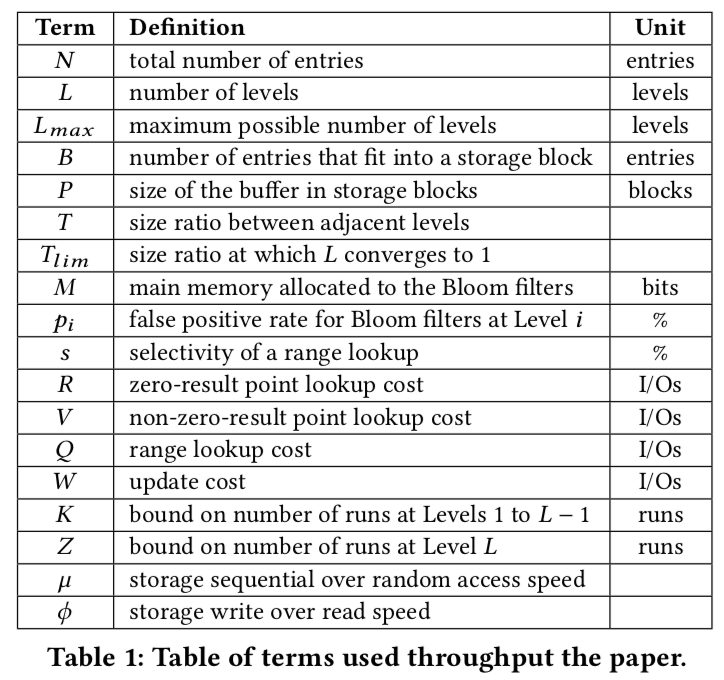
下面是Paper中出现的一些符号代表的意思,
Dostoevsky的内容主要就是三点:
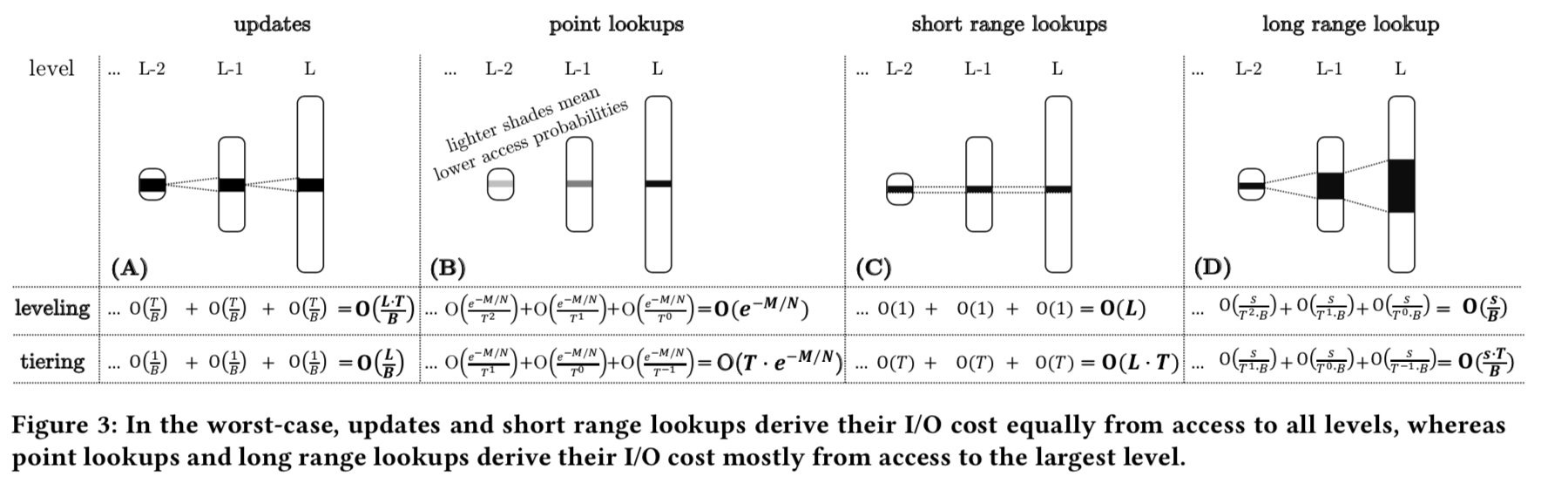
- Lazy Leveling,第一点是最核心的,基本思路就是结合LSM-tree中leveing和tiering合并策略,在除了最后(也就是最大的一层)使用leaving的方法,在其余的层使用的是tiering的方法。这么做基于这样的考虑:在上面的表格给出的复杂度可以看出,在较小的levels上面使用leveling的方法,会明显的增加更新操作的成本,而对查找的提高却不是很明显。这样Lazy Leveling的思路就是只在largest level使用level的方法。下面的图是使用这种方法的一个复杂度的分析,
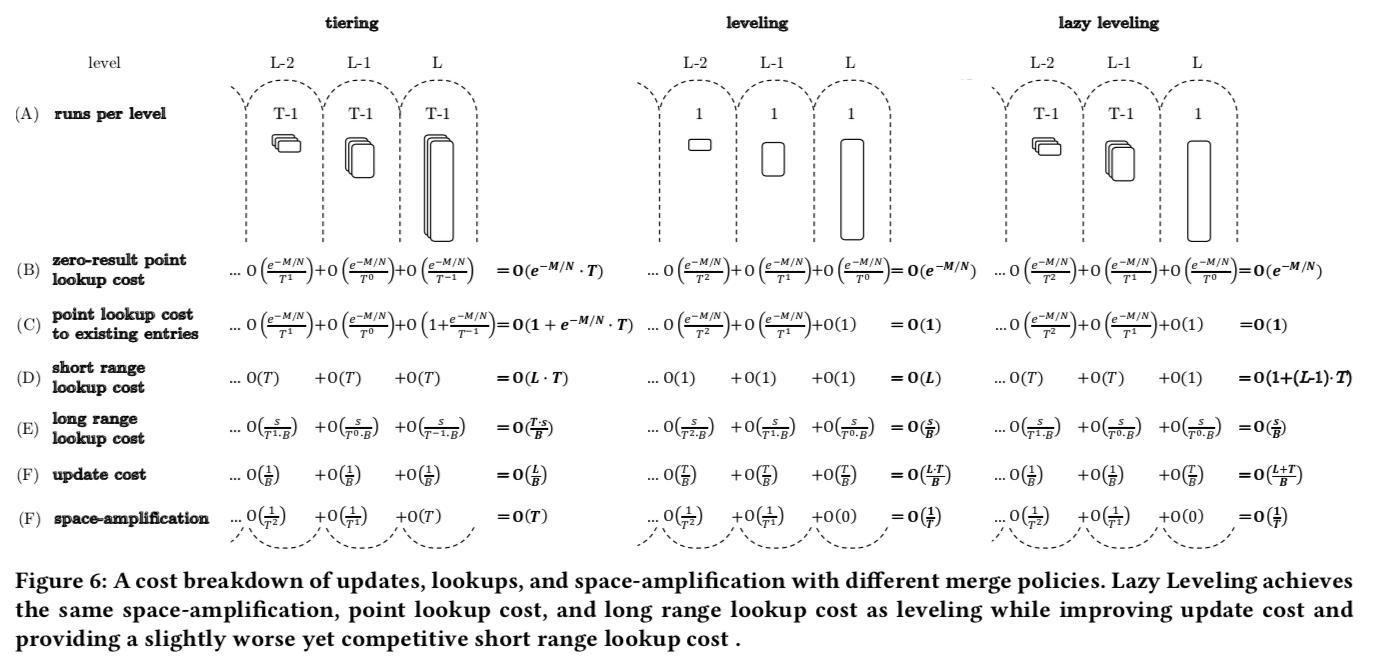
这里的具体的分析可以参看[1],这部分关于Bloom Filter如何取舍和内存分配等的内容和SIGMOD‘17上的[2]很类似。
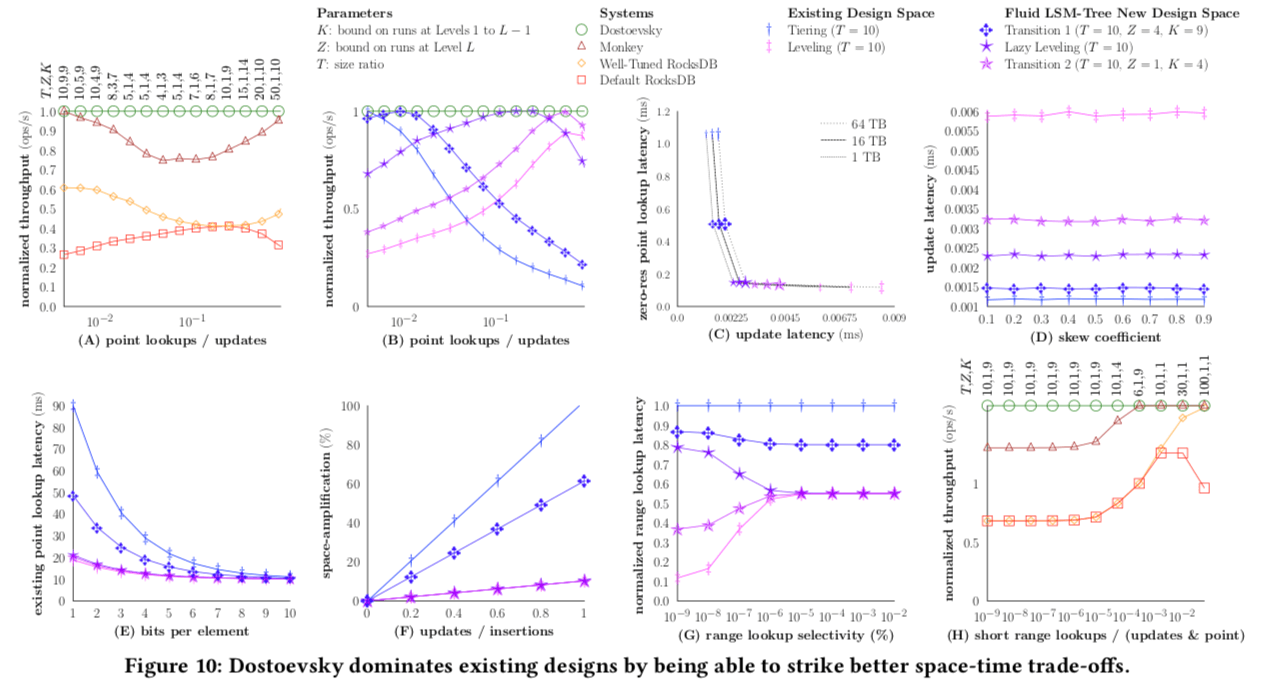
上面的这幅图很好的展示了这样做的一个效果。
-
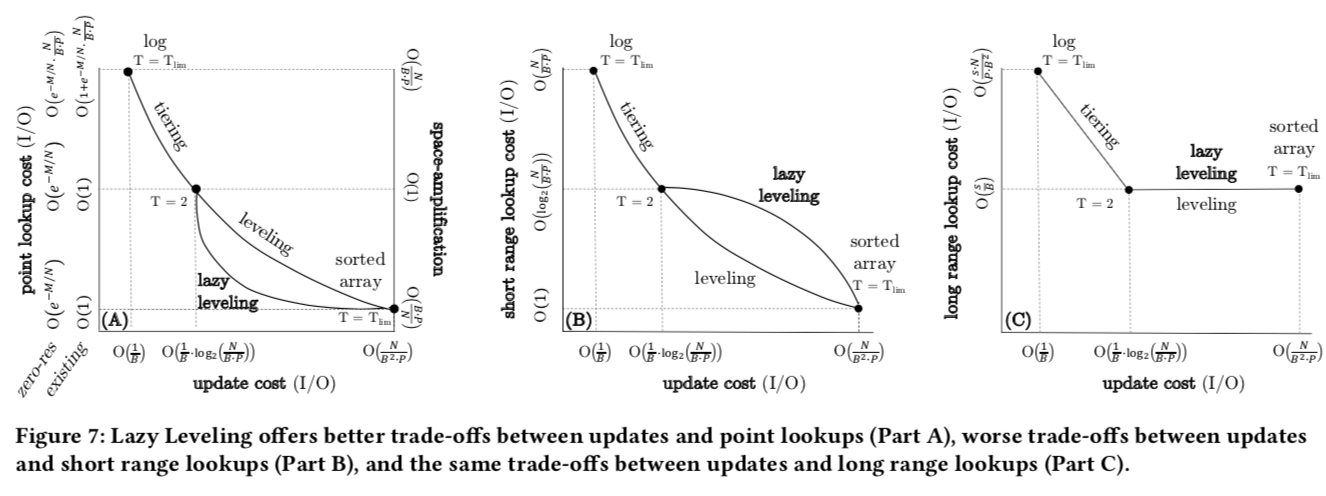
在上面的图中可以看出来,Lazy leveling的方式比较适合混合类似的workload的,比如混合了updates、point loopup和long range loopup。Leveling模式的和Tiering模式则适合查找为主和更新为主的workload。为此Paper这里了Fluid LSM-Tree,在Lazing leveling的基础上实现了更加灵活的方式。在Fluid LSM-Tree最多由Z个部分组成,而其余的则为K,这样就有:
- K =1 and Z =1时就是leveling模式;
- K = T −1 and Z =T −1就是tiering模式;
- K =T −1 and Z =1就是lazy leveling模式;
这里Paper中也对这样得方式进行了具体得分析,下面是这样的策略的一个复杂度:
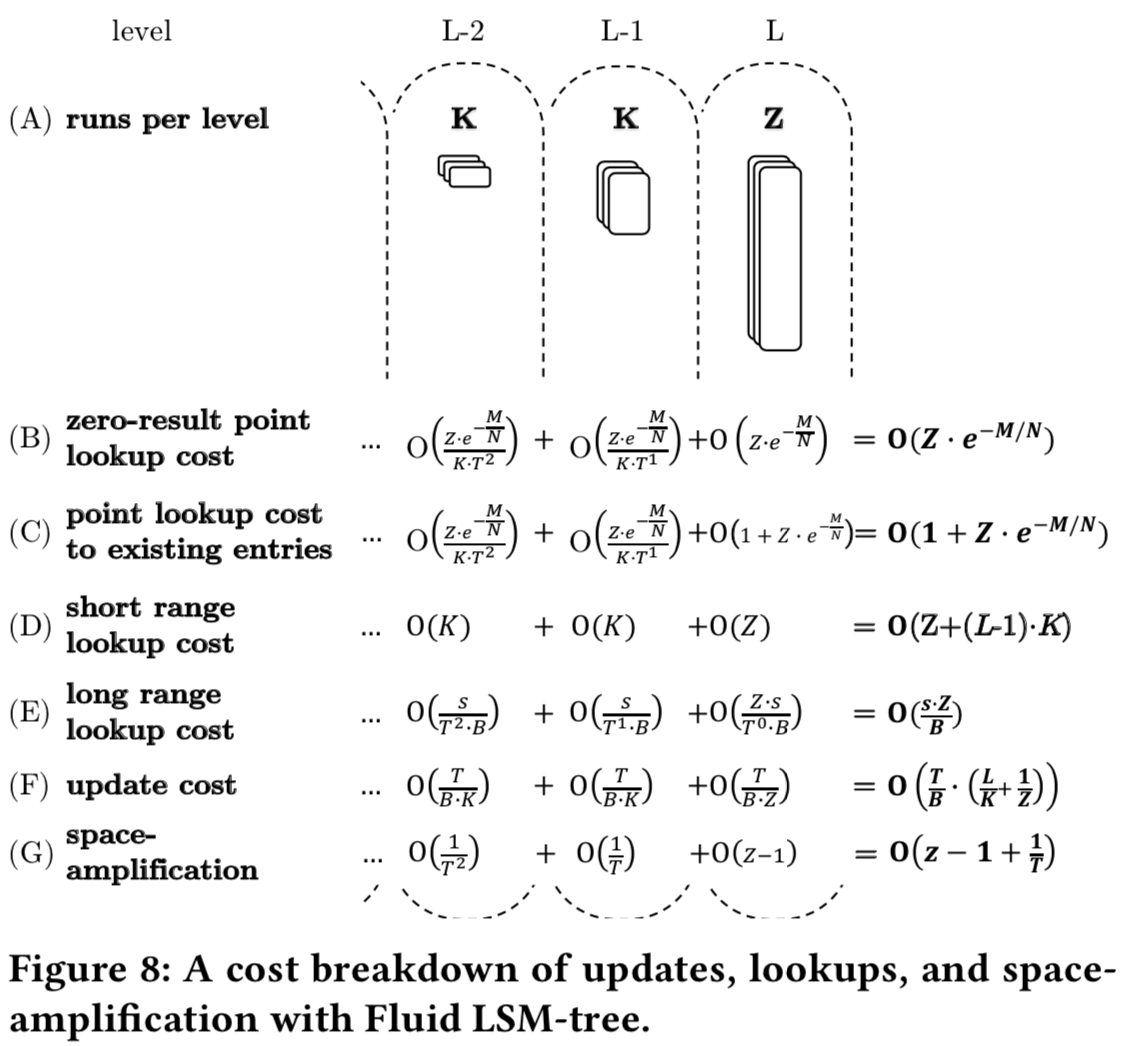
这里的Z和K根据系统情况进行调整,这个是Fluid LSM-tree一个核心的地方,这里就是三个参数的调整:K、Z和T。
-
Dostoevsky,Dostoevsky的目的就是在一定限制条件下将这三个参数调整的最优的值,
We now introduce Dostoevsky to find and adapt to the best tuning of Fluid LSM-tree subject to a constraint on space-amplification. Dostoevsky models and optimizes throughput with respect to up- date cost W in Equation 12, zero-result point lookup cost R in Equation 10, non-zero result point lookup cost V in Equation 8, and range lookup cost Q in Equation 11. It monitors the proportion of these operations in the workload and weights their costs using coefficients w, r, v, and q, respectively.下面几个计算方式: \(\\ Equation 12: W = \frac{\phi}{\mu\cdot B}\cdot(\frac{T-1}{K+1}\cdot(L-1)+\frac{T-1}{Z-1}), \\ Equation 10: R = e^{-\frac{M}{N}\cdot\ln(2)^{2}}\cdot Z^{\frac{T-1}{T}}\cdot K^{\frac{1}{T}}\cdot \frac{T^{\frac{T}{T-1}}}{T-1},\\ Equation 8: V = 1+R-p_{L},\\ Equation 11: Q = K\cdot(L-1)+Z+\frac{1}{\mu}\cdot\frac{s}{B}\cdot(Z+\frac{1}{T}), \\\) .
利用上面的公式和下面的the weighted worst-case throughput τ计算公式: \({,} \\ Equation 14:\tau = \Omega^{-1}\cdot(\omega\cdot W + r\cdot R + v\cdot V + q\cdot Q)^{-1},\) .
通过迭代K Z和T的可能的取值来计算求得 τ得最大值。迭代的复杂度: \(\\ T可能的取值的范围的量级为 \lceil\log_{2}(\frac{N}{PB})\rceil, \\ 而由于Equation 14对于K和Z来说都满足凸函数的性质(可以参考数据优化和凸优化的教材),\\ 它们可以在对数时间内找到一个T下面的最优的值,所以(这里没有具体证明)复杂度就是: \\ O(\log_{2}(\frac{N}{B\cdot P})^{3}),\)
0x02 评估
具体可参看[1].
参考
- Niv Dayan, Stratos Idreos. 2018. Dostoevsky: Better Space-Time Trade-Offs for LSM-Tree Based Key-Value Stores via Adaptive Removal of Superfluous Merging . In Proceedings of 2018 International Conference on Management of Data (SIGMOD’18). ACM, New York, NY, USA, 16 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3183713.3196927.
- Monkey: Optimal Navigable Key-Value Store, SIGMOD 2017.
