HOT: A Height Optimized Trie Index for Main-Memory Database Systems
0x00 引言
Height Optimized Trie (HOT) 是一种新的为Main-Memory Database设计的新的数据结构。实现了非常的性能和非常低的内存占用:
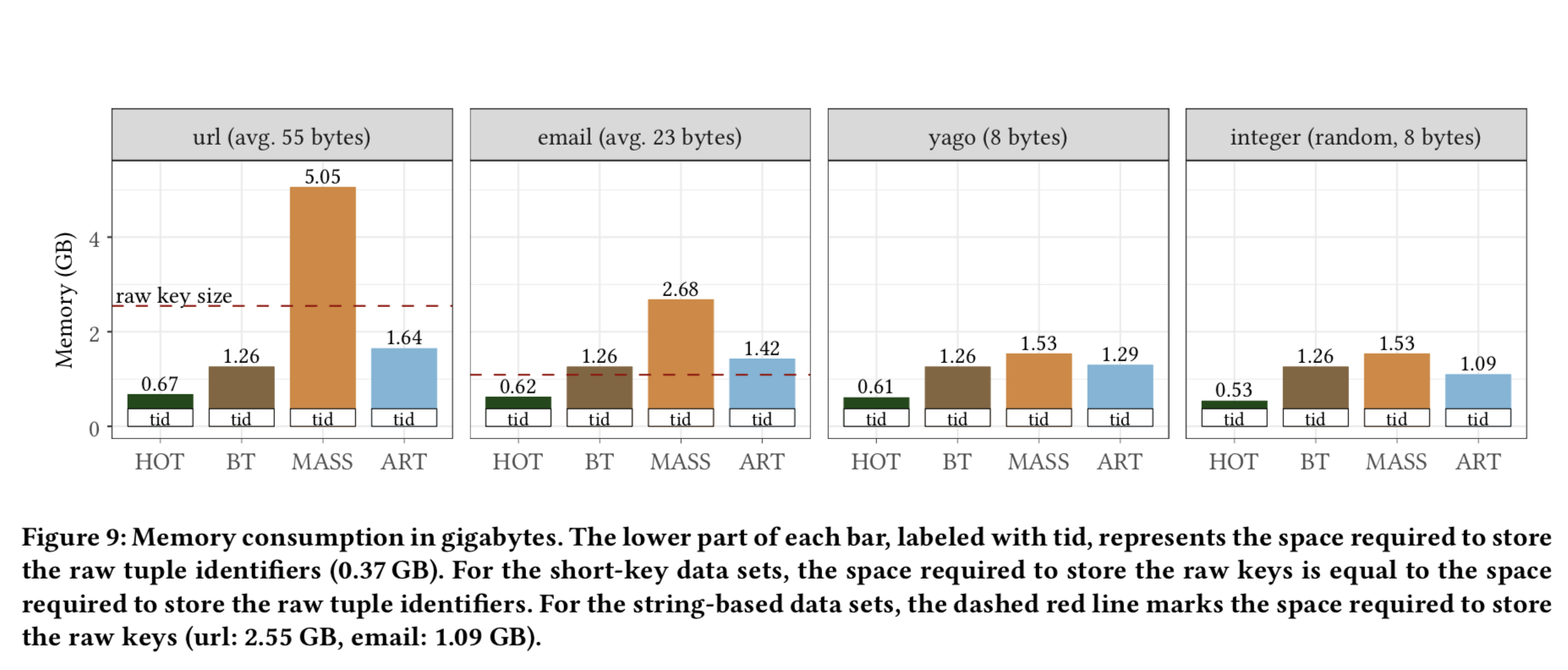
从这里看,HOT的内存占用低到惊人。在上面的几种结构来说,HOT、BTree、Masstree以及ART,后面的三种相对的结构都比较直观,而HOT这里就稍微复杂精巧一些。HOT开源的实现代码也比较复杂。
### 0x01 基本思路
在介绍HOT的思路之前先来看看之前是如何优化Radix Tree的内存占用的。低一个基本的方法是压缩路径,对于一个长链,可以压缩为一个结点。第二个是ART[2]的办法,使用自适应的节点大小(还有其它的一些方法)。这些方法的一个特点就是一个节点的大小都是固定的,比如在ART是固定的1byte。HOT这里使用的方法是自适应的节点大小(在bitwise trie中为1bit,在ART中为1byte,在HOT中这个是不确定的)。可以想象,对于key很长的例子,它肯定是稀疏的(至少在这个key中部分段是稀疏的),要不然key的数量就爆表了。这样的话稀疏的话就可以将每一层到下一层代表的bit数变大,高度自然就变小了。密集则反之,可以想象到如果这些key密集地出现不同,那么这个密集的区域是很小的,因为32bit长的变化就是42亿多了,如果这么密集的不同那么key的数量就会非常大。
... we propose to set the span of each node adaptively depending on the data distribution. Thus, dense key regions (e.g., near the root) will have a smaller span than sparse regions (e.g., at lower levels), and a consistently high fanout can be achieved. Instead of having a fixed span and data-dependent fanout as in a conventional trie, HOT features a data-dependent span and a fixed maximum fanout k.
下面这个example很好的表示了基本思路:
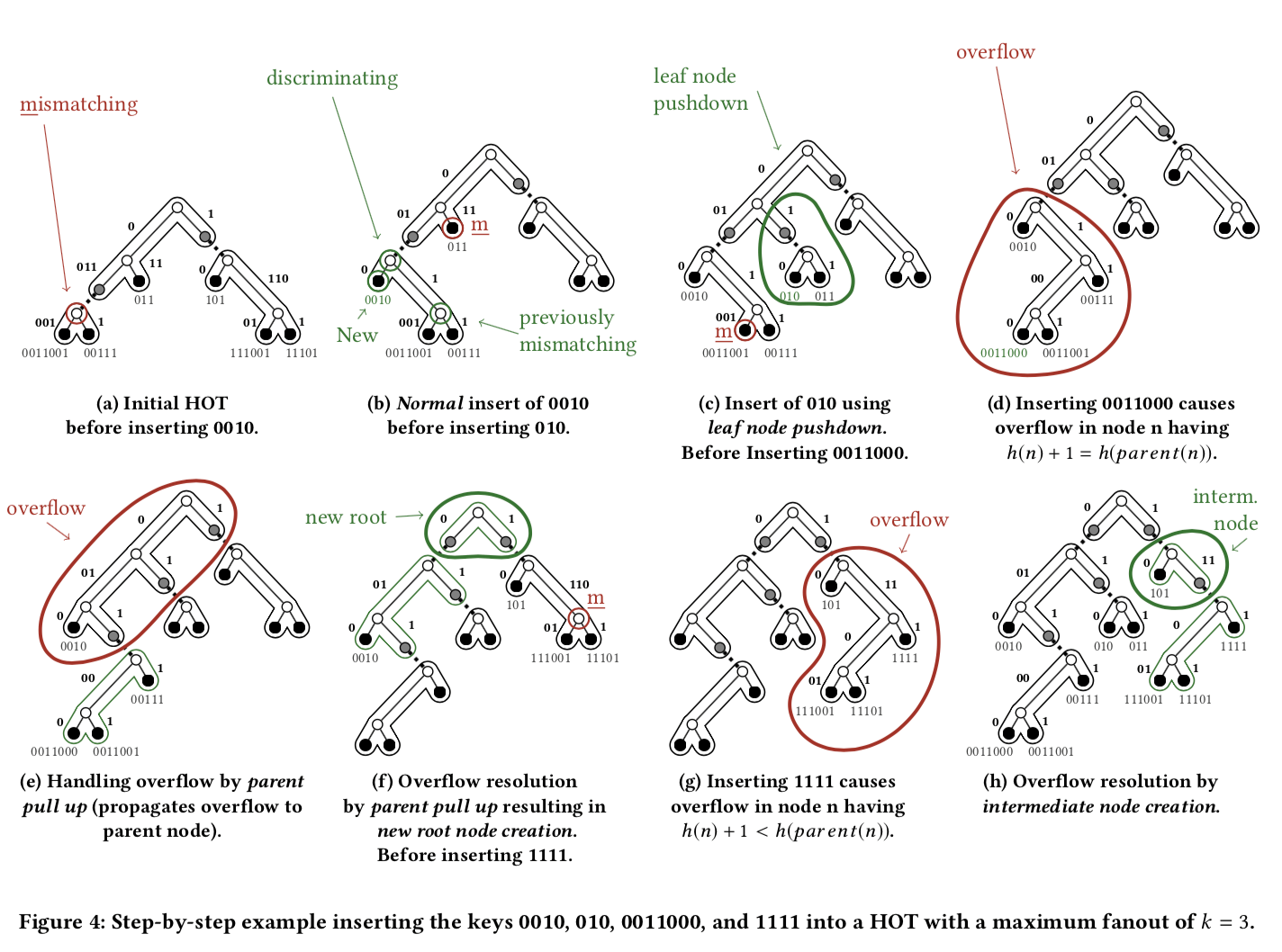
这里要注意HOT里面的几个术语(注意树递归定义的特点):
-
compound node,Paper中就将这种node称为Node。 每个compound节点代表来一个binary Patricia trie, fanout为K,一个保存了n个key的binary Patricia trie有n-1个内部结点。由此,一个HOT的compound node就最多包含了K-1个内部结点。这里将binary Patricia trie一个结点称为一个BiNode。也就是说一个CNode就是多个BiNode组合而来的
-
高度,每一个CNode的高度h这样定义, \(\\ \\ h(n) = \left\{ \begin{array}{ll} 1, \; n.m=0 \\ \max_{i=1}^{n.m}(h(n.children[i])) + 1, else.\\ \end{array}\right.\\\)
in the rest of the paper, we use the following terminology: whenever we denote a node in a binary Patricia trie we use the term BiNode. In all other cases, the term node stands for a compound node. In this terminology, a node contains up to k − 1 BiNodes and up to k leaf entries.
HOT是中trie的变体,每一个节点都是保存了Key的一个前缀。另外,HOT又像是一个基于比较的一个多路的结构。
0x02 基本操作
这么的例子都是以K=3来讲的。Paper中具体说明的只有添加的操作,没有其它的,如删除等。 对于添加操作,要先找到添加的位置,当沿着”路径”找到不匹配的时候就认识找到了添加的位置。具体的添加的操作有几种的case:
- 第一种case为normal case,如上面的图中a所示,局部修改一个CNode,这里的情况就是这个CNode还可以添加这个新的BiNode,这样的话直接添加到这个CNode计科。
- 第二种为leaf-node pushdown,如上面的图中c所示。这种case出现在mismatching的BitNode为叶子节点而影响的节点为内部节点的情况(h(n) > 1)。这里将也来的叶子节点取代,新的节点包含现在的和原来的。这种操作不会影响到树的高度;
insert(hot, key):
n = traverse hot for key
m = traverse n until mismatch
if isLeafEntry(m) and h(n) > 1:
# leaf node pushdown
l = createNode(m, key)
n' = replaceNode(n, m, l)
else:
d = createBiNode(m, key)
n' = replaceBiNode(n, m, d)
handleOverflow(n')
handleOverflow(n):
if not isFull(n)
# normal path
return
n' = split(n)
p = parentNode(n)
if height(n') == height(p):
# parent pull up
e = createBiNode(n'[0], n[1]')
p' = replaceBiNode(p, n, e)
handleOverflow(p')
else
# intermediate node creation
p' = replaceNode(p, n, n')
这里还有一个要解决的问题就是Overflow。当前面的两种添加的Case都不能处理时,就要发生Overflow。如上面的图d所示,在添加了0011000之后。在上面的伪代码中,这个操作发生在normal case中, 而且新产生的n’的isFull判断为true的时候。有两种cases处理Overflow:
-
parent pull up,这种处理方式是将overflow node中的root BiNode移动到parent node中去。这种情况下可能会增加树的高度。root BiNode在移动之后,重新变为 k-constrained 的node。但是parent node也可能发生overflow。这种情况下就需要递归处理,
Overflow handling therefore needs to be recursively applied to the affected parent node. ..., because the root node is also full, overflow is eventually resolved by creating a new root, which is the only case where the overall height of the tree is increased. Thus, similar to a B-tree, the overall height of HOT only increases when a new root node is created. -
intermediate node creation,这里是将前面提到的root BiNode移动到一个新的node中,而不是移动到parent node中。当 h(n) + 1 < h(parent(n))满足时,使用这样的方式。
0x03 结点
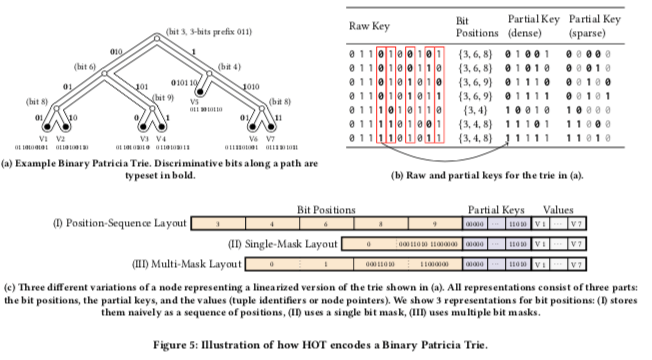
操作的实现就是根据一层Span的大小来逐层查找,逻辑上并不复杂。在HOT的实现是,充分利用CPU提供的一些如SIMD指令的指令。下图是一个HOT的例子,以及表示其Node如何编码的示例图,这里有几个重要的思路。在下图的简单HOT中,一共有7个Key,位置{3, 4, 6, 8, 9}为discriminative bit, 这里注意discriminative bit不是指存在不同的bit,应该对应到trie的结构上面。partial keys (dense)就是将这些discriminative bit提取出来之后的部分,在下吗的节点Layout的设计中,Partial Keys保存在一次,方便使用SIMD指令进行指令级别的并行操作。
-
这里实际使用Partial Key是一个优化的sparse partial keys,sparse partial keys为了解决dense partial key添加性能不高的问题。加入在下吗的trie中添加key0110101101,会导致bit 7成为一个新的discriminating bit ,这样的话涉及到相关数据都需要重新计算。sparse partial keys和dense partial key不同的地方在于只会取出哪些对应的BiNode从root BiNode路径上面的部分,而其他的部分设置为0。考虑下吗的V7,路径上面的是1,1,1,对应的另外两个bit就设置为0,
The difference to dense partial keys is that for sparse partial keys, only those discriminative bits are extracted that correspond to inner BiNodes along the path from the root BiNode and that all other bits are set to 0. Thus, sparse partial key bits set to 0 are intentionally left undefined. In case of a deletion this allows to remove unused discriminative bits. -
K这里设置为32,是一个在CPU Cache友好和快速更新之间权衡的一个值。这样的话,一个节点可以处理31bit positions,由于区分32个key。实际上大部分时候这个数量都小于32。实际上在Node Layout设计上面,使用8-bit, 16-bit, or 32-bit 的三种数组来保存partial key。处理Parital Key,Node中还保存了Bit Positions和Values。Values这里没什么特别的。在保存Bit Positions上面,简单的思路是直接保存位置信息,如下面的(I)中表示的一样。(II)中优化的方式是用Bit Mask,同时利用x86上面的一些特殊指令如PEXT来加速处理。在需要的时候可以使用多个bitmask,
To summarize, the node layout has two dimensions of adaptivity. The first dimension is the size of the partial keys (8, 16, or 32 bits), and the second dimension is the representation of the bit positions (single-mask or multi-mask). In both cases we choose representations that adapt to the data distribution at hand.
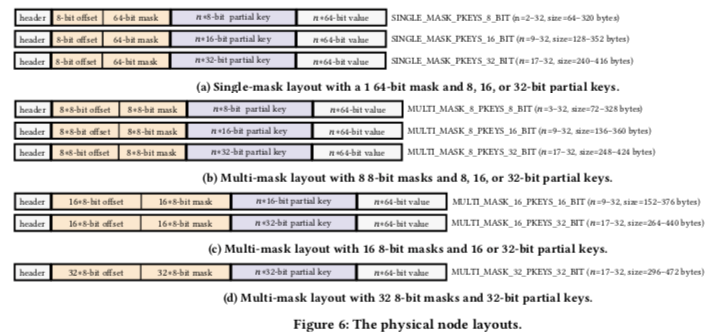
- Node Physical Layout设计上面,Node主要包含了4个主要的部分。Header部分,包含了subtree的高度信息、一个用于标记usred entried的bit mask,如果是并发版本的话还包含了一个lock的信息。在Single Mask的版本中,8bit的offset信息表示了从mask中提取出的开始byte的位置,另外的三种multi-mask layout类型中,offset和mask的数量不同其它的和single mask相同。
在HOT中一些基本操作的实现方式如下,
-
查找,查找操作代码,直接就是C语言的代码。里面一个最核心的函数是retrieveResultCandidates。retrieveResultCandidate这里就是分发的一个功能,根据node的类型使用对用的查找函数。在下面的代码中可以看出来,第一部分是取出partialKey,在SingleMask的版本中,就是一个节点的pext指令的应用,早Multi-Mask的版本中,要进行一个循环去除mask的多个部分组合为一个完整的mask。然后就是searchPartialKeysxx函数,这里利用了avx2的指令去实现,从这些代码中也可以看出来HOT是如何将数据保存到这些结构中的。这里的设计很精巧,也比较难以理解。如何在lookup函数中就是循环调用retrieveResultCandidate函数,如果取出的candidates信息,使用clz(candidates)取到这个node中对应的s子节点,然后循环操作,知道node为leaf node。
-
添加,添加的时候一个优化就是使用sparse partial key替代来dense partial key。在进行添加操作时候,会进行一个查找操作,确认对应的key是否以及存在。不存在的时候,如果引入了新的discriminative bit,需要进行partial key的创建操作,
Next, if the mismatching bit position is not contained in the set of the node’s discriminative bit positions, all sparse partial keys are recoded using a single PDEP instruction to create partial keys containing also the mismatching bit position. For instance, to add bit position 7 to the sparse partial keys depicted in Figure 5a, the _pdep_u32(existingKey, 0b111011) instruction is executed for each key. -
在优化上面,这里会先预取节点的前面4个cache line。同时将node类型的信息表吗在指针的least-significant bits指针中。
TID lookup(Node* root, uint8_t* key) {
Node* node = root;
while (!isLeaf(node)) {
uint32_t candidates = retrieveResultCandidates(node, key);
node = node->value[clz(candidates)];
if (!isEqual(loadKey(getTid(node)), key))
return INVALID_TID; // key not found
return getTid(node);
}
}
uint32_t retrieveResultCandidates(Node* node, uint8_t* key) {
switch (getNodeType(node)) {
case SINGLE_MASK_PKEYS_8_BIT:
uint32_t partialKey = extractSingleMask(node, key);
return searchPartialKeys8(node, partialKey);
case MULTI_MASK_8_PKEYS_8_BIT:
uint32_t partialKey = extractMultiMask8(node, key);
return searchPartialKeys8(node, partialKey);
// ...
case MULTI_MASK_32_PKEYS_32_BIT:
uint64_t partialKey = extractMultiMask32(node, key);
return searchPartialKeys32(node, partialKey);
}
}
uint32_t extractSingleMask(SMaskNode* node, uint8_t* key) {
uint64_t* keyPortion = (uint64_t*) (key + node->offset)
return _pext_u64(*keyPortion, node->mask);
}
uint32_t extractMultiMask8(MMask8Node* node, uint8_t* key) {
uint64_t keyParts = 0;
//load all 8-bit mask into a single 64-bit mask
for (size_t i=0; i < node->numberMasks; ++i)
((uint8_t*) keyParts)[i] = key[node->offsets[i]];
//SIMD approach to extract multiple 8-bit masks in parallel
return _pext_u64(keyParts, node->mask);
}
uint32_t extractMultiMask16(MMask16Node* node, uint8_t* key) {
//...
}
uint32_t extractMultiMask32(MMask32Node* node, uint8_t* key){
//...
}
int searchPartialKeys8(Node* node, uint32_t searchKey) {
__m256i sparsePKeys = _mm256_loadu_si256(node->partialKeys8);
__m256i key = _mm256_set1_epi8(searchKey);
__m256i selBits = _mm256_and_si256(sparsePKeys, key);
__m256i complyKeys = _mm256_cmpeq_epi8(selBits, sparsePKeys);
uint32_t complyingMask = _mm256_movemask_epi8(complyKeys);
return bit_scan_reverse(complyingMask & node->usedKeysMask);
}
int searchPartialKeys16(Node* node, uint32_t partialKey) {
//...
}
int searchPartialKeys32(Node* node, uint32_t partialKey) {
//...
}
0x04 并发
HOT这里使用了在ARTrie中采用的一种策略,称之为 Read-Optimized Write EXclusion (ROWEX)。在ROWEX并发控制策略中,reader不用获取lock,它们的操作时wait-free的。writer则需要获取lock。添加和删除操作在这里主要范围5步进行,1. 在遍历trie的过程中,确认需要进行新高的节点集合,用affected nodes表示。2. 从下到上的方式获取这些节点的lock。3. 对这些节点进行检查,检查是否这些节点已经“过时”了,检查不通过的情况下可以进行重试操作。4. 检查通过的情况下执行直接的添加/删除操作,5. 释放所有的locks。
-
这里一个核心的操作时确定所有的受影响的节点集合。这里有4中情况需要处理,1. 再次情况,2. leaf-node pushdown,3. parent pull up,4. intermediate node creation,
-
(i) In case of a leaf-node pushdown, the set of affected nodes solely consists of the node containing the mismatching BiNode. If an overflow occurs, all ancestor nodes of this node are traversed, and added to the set of affected nodes until either (ii) in case of a parent pull up, a node with sufficient space or the root node is reached or (iii) in case of an intermediate node creation, a node n fulfilling height (parent(n)) >= heiдht(n) is reached. Finally, the direct parent of the last accessed node is added. -
另外一个核心的操作时使得node变成obsolete状态而不是直接回收内存。这个时在很多的额并发控制方法中都使用的策略,比如Linux Kernel中的RCU机制,以及很多的机遇epoch的机制等。实际上这里也是使用了基于epoch的策略,
... Whenever writers modify a currently read node, the reader is able to finish the lookup—on the now obsolete—node. To actually reclaim the memory of obsolete nodes HOT uses an epoch based memory reclamation strategy, which frees the memory of obsolete nodes whenever no more reader or writer accesses the corresponding nodes.
0x05 评估
这里的具体信息可以参看[1]。 Paper中的数据显示HOT各方面的性能都很不错。
参考
- HOT: A Height Optimized Trie Index for Main-Memory Database Systems,SIGMOD 2018.
- The Adaptive Radix Tree: ARTful Indexing for Main-Memory Databases, ICDE 2013.
