PebblesDB: Building Key-Value Stores using Fragmented Log-Structured Merge Trees
0x00 引言
这篇Paper也讲的是如何优化LSM-Tree写入放大问题。与前面有写过的WiscKey不同,PebblesDB在LSM-Tree的结构上面做了很大的优化,不像WiscKey一样的依赖于SSD之类的硬件。它的使用了一种新的叫做Fragmented Log-Structured Merge Trees (FLSM) 的数据结构,基本思路和Skip List中的一些思想类似。从算法上面比较好的解决了这个写入放大的问题,
We evaluate PebblesDB using micro-benchmarks and show that for write-intensive workloads, PebblesDB reduces write amplification by 2.4-3× compared to RocksDB, while increasing write throughput by 6.7×. We modify two widely-used NoSQL stores, MongoDB and HyperDex, to use PebblesDB as their underlying storage engine. Evaluating these applications using the YCSB benchmark shows that throughput is increased by 18-105% when using PebblesDB (compared to their default storage engines) while write IO is decreased by 35-55%.
这篇Paper主要讲了2个方面的内容,一个是FLSM的数据结构,一个是在这个数据结构上面的实现的PebblesDB的Key-Value数据,这里不关心PebblesDB的实现,因为没有什么特别的东西。
0x01 FLSM基本思路
FLSM的存储布局:
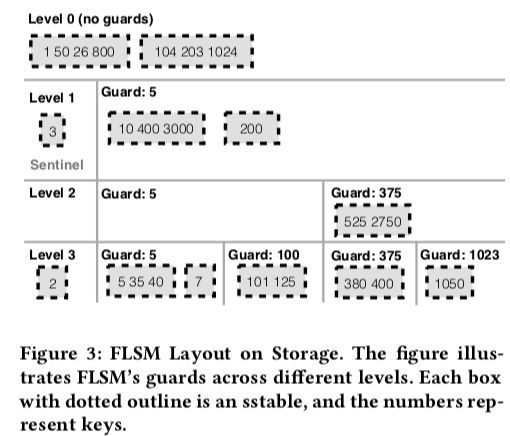
LSM-Tree写入放大一个很重要的原因就是上层的更少的数据合并到下层更加大的数据的时候,下层所有的数据都会被重写。为了解决这个问题,FLSM把每层的sstable分割成更小的单元。FLSM compaction的时候,不是将上层下层的合并重新,而是简单地在下一层合适的位置添加一个新的fragment。FLSM可以做到数据在大部分的层中只会被写入一次。
Doing so ensures that data is written exactly once in most levels; a different compaction algorithm is used for the the last few highest levels. FLSM achieves this using a novel storage layout and organizing data using guards.
0x02 Guards
Guards是FLSM中核心的概念,基本的思路来自Skip List。前面说到FLSM将每层分为了更小的单元,为了更快的找到数据所在的单元,这里使用了Guards。这里为什么可以和基本的工作方式联想一下Skip List即可。传统的LSM,每一层包含了不相交的数据的sstabls,也就是说一个数据最多在这些sstables中出现一次。FLSM则改变了这种方式,它由每一层的多个sstables的范围是可以重叠的(注意这里是sstables,FLSM每一层多个的sstable,而且每一个Gruard下面也可以由多个),也就是说一个数据在多个的这些sstabls里面。
The FLSM data structure discards this invariant: each level can contain mul- tiple sstables with overlapping key ranges, so that a key may be present in multiple sstables. To quickly find keys in each level, FLSM organizes the sstables into guards (inspired from the Skip-List data structure)
FLSM的每一层都包含了多个Guards,对于这一层来说,Guards将数据范围分为了不相交的几个部分。每一个Guard对应一个key,越下层的level的gaurd越多。在更上层出现的Guards,在下面的层中都会出现,这里和Skip List很详细。可以想象一项,如果把这些Guards纵向的连起来,整个的结构就很想一个Skip List。如果一个Guard G-i的Key为K-i,G-i+1的Key为K-i+1,那么keys范围在[Ki,K-i+1) 都会attach到G-i上面。Keys小于第一个的Guard的会存在一个特殊的哨兵Gurad下面,最后一个的Gruad的下面保存在是keys >= K-n的一些sstable。第0层是没有Gruad的,因为Key-Value的数量比较少。FLSM的层是部分有序的,Gruad之间的数据范围是没有重叠的,但是一个Gurad下面的多个sstables的数据范围是可以重叠的。
Selecting Guards
有了Guard,当然就要考虑这些Guard是从哪里来的。这里选择出Guard的方式和Skip List里面的方法也很类似,使用的也是一个随机的方法,这种简单的方式也可以避免数据倾斜的问题。 FLSM不要去Gurad的Key实际存在,这里完全猜到,如果要求Key实际存在,那么删除这个Key的时候就比较麻烦,而且带不来什么好处。一旦在一层一个Guard被选定,那么这个Gurad也会成为这一层下面的level的Guard,
Much like skip lists, if a key K is selected as a guard in level i, it becomes a guard for all higher levels i + 1, i + 2 etc. The guards in level i + 1 are a strict superset of the guards in level i. Choosing guards in this manner allows the interval between each guard to be successively refined in each deeper level.
这里Papper中还讨论了另外的一种选择的部分。现在的部分存在的一个问题就是它没有考虑到compaction的时候分区sstabls的带来的IO成本,这里Paper没有详细讨论,只是说这个是未来的工作。
Inserting and Deleting Guards
在选择了Guard之后,它并不是同步的被添加到FLSM里面的。添加一个新的Guard可能会导致分裂一些sstables或者移动一个sstables。如果这个Guard不是在最下面的一层,这个Guard就会被添加到多层里面,就有会在多层上面做一样的操作,这样同步不是一个很好的选择额,这里使用的是异步添加的方式。 选定的Guard会先被添加到保存在内存中一个叫做uncommitted集合中,在下一个compaction周期,sstables会根据旧的和uncommitted的Gurad来进行分区compact 。需要根据uncommitted的Guard拆分的sstable会被compact到下一册之中,这样,这些uncommitted的Guard就“committ”了,被持久化到了存储设备上面,加入到了Gurad是的集合之中。
对于Guard的删除操作,在Paper中认为这个在很多情况下是没有必须要的。这个删除Guard的操作在两种情况下是有用的,一种是当这个Guard是空的,一个是这些数据在这一层上面分布不均匀。同样,删除的操作也是异步的,先添加到一个保存在内存的集合里面,然后在下一个compaction周期的时候,由于这个Guards被删除,sstables将会被重新安排。这里在每一层的操作都是lazy的。在一层中一个Guard G被删除的时候,属于它的sstabls就会被合并到与它相邻的Guard 后者是合并到它的下一层去。这里要住哟的就是FLSM中一个Guard在这一层被删除了,那么在它上面的层里面的Guard也必须被删除,而在它下面的Guard则可以选择不删除,
During compaction, guard G is deleted and sstables belonging to guard G will be partitioned and appended to either the neighboring guards in the same level i or child guards in level i + 1. Compaction from level i to i + 1 proceeds as normal (since G is still a guard in level i + 1). At the end of compaction, FLSM persists metadata indicating G has been deleted at level i. If required, the guard is deleted in other levels in a similar manner. Note that if a guard is deleted at level i, it should be deleted at all levels < i; FLSM can choose whether to delete the guard at higher levels > i.
0x03 FLSM Operations
-
get()操作;在memtable里面的查找操作和一般的LSM没有区别。在memtable没有查到的话,想要到各层sstables。在下面的任何一层查到了就直接返回。在具体的一层查找的时候,先对Guards进行二分查询,定位到一个Guard下面的sstabls,然后在这个Guard下面的sstables里面查着,注意这里是这个Guard下面所有的sstabls都要查找。
-
范围查询这里要处理的问题就是一个Guard里面的sstables的值的范围存在重叠的问题,这里使用的是类似merge sort的方法解决。
... a binary search is performed on each sstable to identify the smallest key overall in the range. Identifying the next smallest key in the range is similar to the merge procedure in merge sort; however, a full sort does not need to be performed. When the end of range query interval is reached, the operation is complete, and the result is returned to the user. - put()操作,也是先添加到memtable,在memtable满了之后,先被添加到level 0,需要的时候进行compaction操作。这里FLSM会避免进行合并重写的操作,而是直接attach到下面一层合适的Guard下。
- 更新 & 删除,这里和LSM的操作没有很大的区别,也是添加一个包含新的updated sequence number的数据(update) 后者是一个删除的标志(delete).
- Compaction,这里当一个Guard下面的sstabls数量达到一定的阈值的时候,就会进行compaction操作。这些sstales首先会被归并,然后根据下面一层的Guars进行拆分,然后就是attach到正确的Guard下面。
For example, assume a guard at Level 1 contains keys {1, 20, 45, 101, 245}. If the next level has guards 1, 40, and 200, the sstable will be partitioned into three sstables containing {1, 20}, {45, 101}, and {245} and attached to guards 1, 40, and 200 respectively.
在大部分的情况下,FLSM都不需要重写sstables,两个例外:
-
最下面的一层(Paper中的叫法是the highest level,这篇总结将这些level看成类似倒置的树),由于下面没有level,它只能选择重写合并(如果没有达到一定的条件添加新的level的话);
-
另外一个情况就是倒数第二层,如果它的compaction操作,选择添加到下一层的操作会导致合并到一个大的sstable的时候(这里有点模糊),
Second, for the second-highest level, FLSM will rewrite an sstable into the same level if the alternative is to merge into a large sstable in the highest level (since we cannot attach new sstables in the last level if the guard is full).FLSM例外的一个优点就是这些compaction操作是很容易并行操作的,因为不同的Guard之间不会产生其它的Guard。
0x04 Limitations & Asymptotic Analysis
通过上面的分析很容易看出来,FLSM通过放松数据的有序状态,达到更加好的写入性能。但是鱼与熊掌是不可兼得的,写入性能的提升一般就因为着读性能的降低(这里WiscKey也是同样的问题),这里在PebblesDB里面使用了一些方法来缓解这个问题。关于FLSM各类操作的复杂度分析,原论文有详细的论述,
0x05 评估
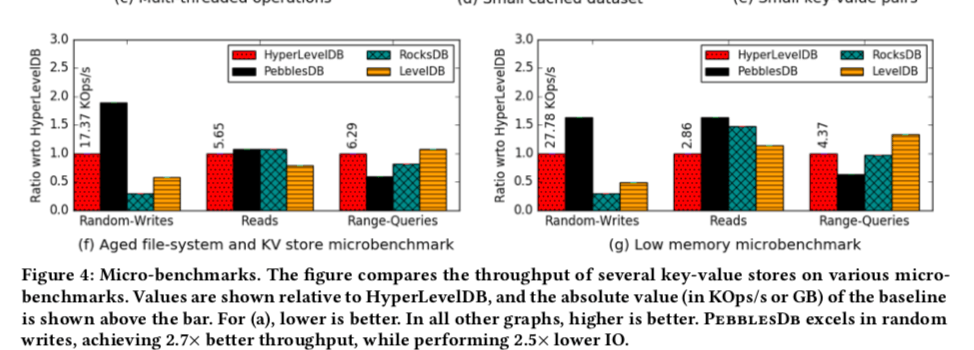
一个基本的性能信息:
参考
- Pandian Raju, Rohan Kadekodi, Vijay Chidambaram, and Ittai Abra- ham. 2017. PebblesDB: Building Key-Value Stores using Fragmented Log-Structured Merge Trees. In Proceedings of ACM Symposium on Operating Systems Principles (SOSP’17). ACM, New York, NY, USA, Article 4, 18 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3132747. 3132765.
