Application Crash Consistency and Performance with CCFS
0x00 引言
这篇Paper将的文件系统中Crash一致性和性能之间的权衡的问题。Paper的基本思路是提出了stream的抽象,在一个stream之内,操作都是顺序的,但是在不同的stream的时候,操作可以被灵活地重新排序相当于一种带限制的重排序的方式,
Further, we show that ccfs performance under standard file-system benchmarks is excellent, in the worst case on par with the highest performing modes of Linux ext4, and in some cases notably better. Overall, we demonstrate that both application correctness and high performance can be realized in a modern file system.
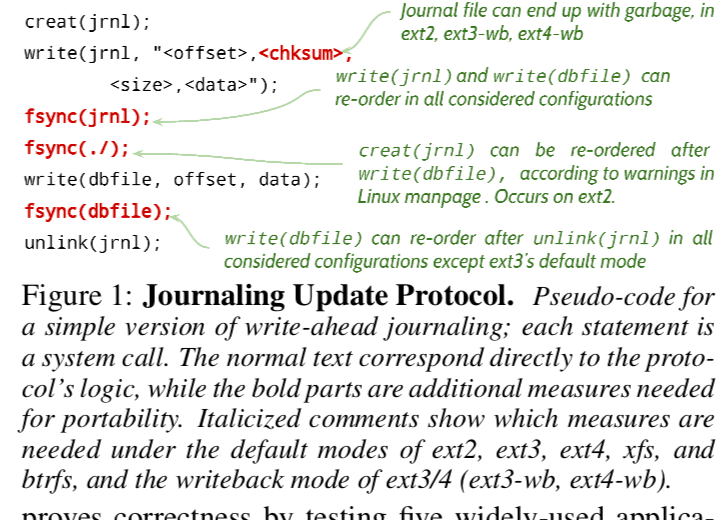
一段文件操作的代码,为了保证准确性,大量使用了fsync操作。
0x01 基本思路
通过stream的抽象,CCFS保持来应该要保持的顺序,同时对不需要保持的顺序可以自由地重排序,从而达到实现强一致性保证的前提下有保证高性能。在CCFS中,stream是一个短暂存在的对象,也不一定与一个特定的文件or文件夹关联。一个文件开始的时候属于一个stream,之后可以属于另外一个。stream的使用是很灵活的,
setstream(s) call that creates (if not already existing) and associates the current thread with the stream s. All future updates in that thread will be assigned to stream s; when forking (a process or thread), a child will adopt the stream of its parent.
为了发挥stream带来的优化的空间,CCFS也对ext4中使用的日志方式进行来改进,不同的stream可以支持同时运行不同的事务。当一个类似于fsync的操作发生时,只有与这个stream相关的部分才会执行fsync的操作。但是由于文件系统的结构已经一些元数据的等的原因,不同的stream之间有时候也要保持一定的全局的顺序才能保证一致性,Paper中针对这个问题也提出了它的解决方法。CCFS中使用的几个技术:
- Hybrid-granularity Journaling,通常的文件日志操作的粒度为blocks。CCFS使用了hybrid-granularity journaling的方法,事务运行的时候以一个byte-range为粒度,而事务提交的时候以blocks为粒度。CCFS使用这种方式的原因是不同的streams可能修改文件系统中的同一个的块。用更加细粒度的操作分开stream之间的相互影响,
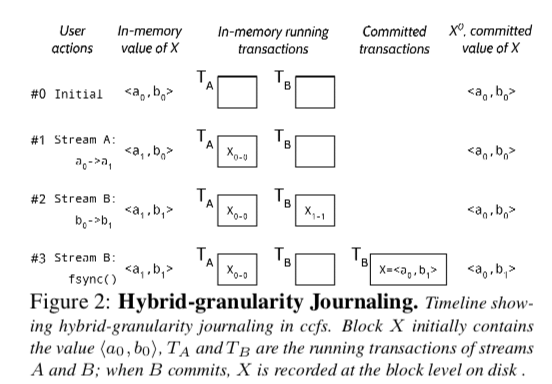
- Delta Journaling,处理上面的混合粒度日志, delta journaling的思路是记录变化。在不同的streams都要操作的数据结构中,比如记录全局的空闲空间的结构。用一个例子说明这个的思路: 对于一个整数,A B stream都想去修改,A想加上i,而B想减去j。则在日志中记录这个增加值的操作和减去值的操作,在事务提交的时候真正地去应用这个操作,
In ext4, shared metadata structures requiring delta journaling are the free inode count and the free block count, which concern the global state across the file system. Delta journaling is also needed for the nlink and the modification time fields of directory inodes, since multiple streams can modify the same directory.
-
Pointer-less Data Structures,ext4中使用的一些以指针为基础的操作也为不同的stream的分开操作提供了一些障碍。比如ext4中的 orphan list结构。通过一些实现上的优化消除一些可以不需要指针的结构,使用其它的方法解决,
To make directories pointerless, ccfs replaces the offset in each entry with a deleted bit: deleting an entry sets the bit. The insert and scan procedures are modified appropriately; for example, the insert procedure recognizes previously deleted entries in the directory and uses them for new entries if possible. -
Order-less Space Reuse,这里是为了解决这样一个问题,A刚刚是否的一个block马上就被B使用了,然而B在A之前提交,A还没有提交就Crash了。这个就会操作不一致的状态。ext4目前的解决方式是只有提交了事务的block才能被重新使用,在CCFS中,除了原来的方法,还在inode和directory-entry也使用了相同的方法。
0x02 顺序保持
ext4默认日志只记录了元数据,而连数据也记录的话会严重地降低性能。selective data journaling (SDJ) 是一种结合了两者的方法,它日志也记录数据,不过只会记录需要记录的部分的数据,追加操作只会记录数据块的指针,
A hybrid approach, selective data journaling (SDJ), preserves order of both data and metadata by journaling only overwritten file data; it only journals the block pointers for file appends. Since modern workloads are mostly composed of appends, SDJ is significantly more efficient than journaling all updates.
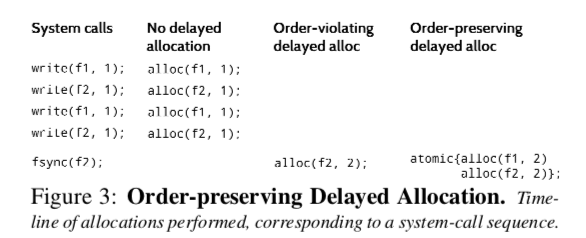
CCFS也采用了这样的方法。另外CCFS使用率order-preserving delayed allocation的方法在保持顺序的同时支持ext4的延迟分配技术,
Whenever a transaction Ti is about to commit, all allocations (in the current stream) that have been delayed so far are performed and added to Ti before the commit; further allocations from future appends by the application are assigned to Ti+1. Thus, allocations are delayed until the next transaction commit, but not across commits.
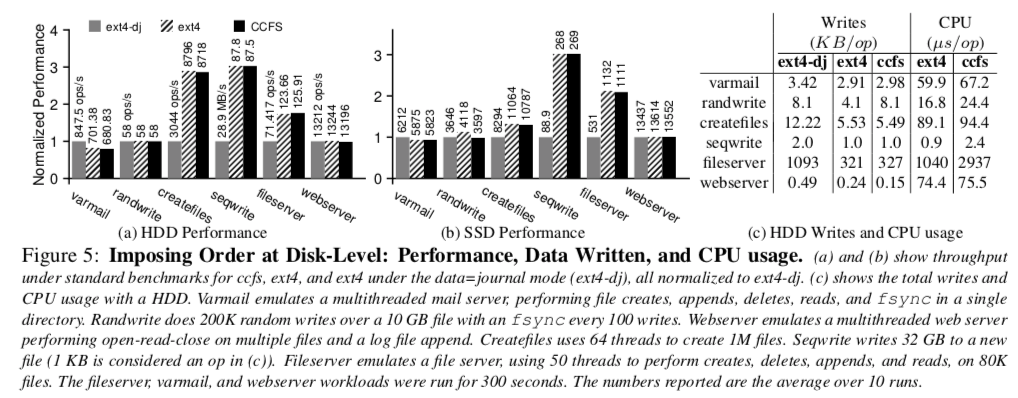
0x03 评估
具体的信息可以参看[1],
参考
- Application Crash Consistency and Performance with CCFS, FAST’17.
