HashKV: Enabling Efficient Updates in KV Storage via Hashing
0x00 引言
这篇Paper主要讲的是在WiscKey上面的优化。基本的思路是在WiscKey的Key Value分离设计的技术之上,通过Hash将分区的方式来解决WiscKey中的一些问题,比如GC成本太高的问题。
HashKV uses hash-based data grouping, which deterministically maps values to storage space so as to make both updates and GC efficient. We further relax the restriction of such deterministic mappings via simple but useful design extensions. We compare HashKV with state-of-the-art KV stores via extensive testbed experiments, and show that HashKV achieves 4.6× throughput and 53.4% less write traffic compared to the current KV separation design.
0x01 基本设计
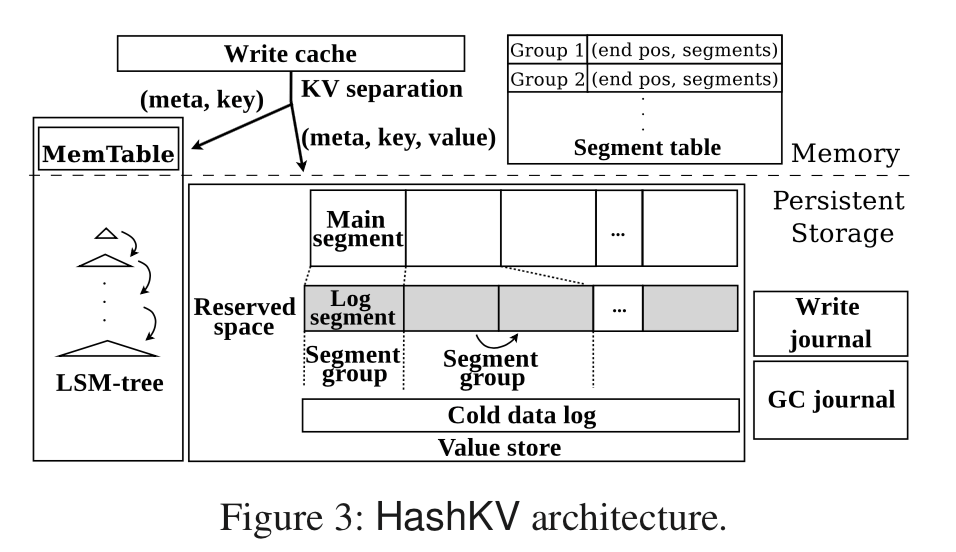
HashKV的基本设计如上图所示。采用了类似WiscKey的Key Value分离的设计。HashKV有下面几个设计:
- Hash-based data grouping,这里不在将Value都写在一个log,而是使用Hash的方式写入到若干固定数量的Log的,这里要同一个key的不同版本的数据都写入到同一个group,很显然这个做到很简单。
- Dynamic reserved space allocation,动态预留的空间分配;
- Hotness awareness,将冷数据分开保存,避免在处理其它hot数据的时候要额外处理这些可以避免处理的冷数据;
- Selective KV separation,小的key就没必要分开保存了,直接向传统的方式一些Key-Value保存在一起;
注意这里根据Hash分区的设计不是根据Hash值来将LSM-tree差分为几个小的LSM-tree,而是根据Hash值将分离保存的Value保存到不同的vLog。很显然,这里这样做的事一个缺点就是增加了写入的“随机性”,即写入不在那么顺序了,而是变得更加分散,这个对性能是一个负面的影响;
几个设计要点
-
Storage Management,Value-Store被分为Main-Segment,写入操作的时候,先写入Main Segment,如果这个满了,会分配Log Segment,如此一个Log Segment满了的话会继续分配。这里为了加速GC操作,和WiscKey一样,Value-Store中也保存了Key。这些相关的Main Segment和Log Segment被记为一个Segment Group,这些Segment的信息会被保存存到一个MemoryTable里面。
-
GC,GC这个是HashKV主要优化WiscKey的地方,这里GC的灵活性比WiscKey高了不少。它可以根据选择可能获得最多收益的Segment Group进行GC操作。
HashKV sequentially scans the KV pairs in the segment group without querying the LSM-tree. Since the KV pairs are written to the segment group in a log-structured manner, the KV pairs must be sequentially placed according to their order of being updated. For a KV pair that has multiple versions of updates, the version that is nearest to the end of the segment group must be the latest one and correspond to the valid KV pair, while other versions are invalid. -
Hotness Awareness,这里是稍微优点违反了Hash分区的。基本思路就是给一个Key一个标记。这里如果判定一个Key是一个“冷”的话,就可以将其保存到一个其它的地方。判断思路:
Currently, we treat the KV pairs that are updated at least once since their last inserts as hot, or cold otherwise (more accurate hot-cold data identification approaches can be used). For the hot KV pairs, HashKV still writes back their latest versions to the same segment group via hashing. However, for the cold KV pairs, it now writes their values to a separate storage area, and keeps their metadata only (i.e., without values) in the segment group. -
Crash Consistency, 这里有两个方面,一个是写入的时候保证一致性,基本的思路是先写入KV pairs到Value Store,然后记录更新的元数据,在早日志中写入提交的记录,然后才是在LSM-tree中更新,
(i) flushing the cached KV pairs to the value store; (ii) appending metadata updates to the write journal; (iii) writing a commit record to the journal end; (iv) updating keys and metadata in the LSM-tree; and (v) marking the flush operation free in the journal (the freed journaling records can be recycled later).GC操作的是要是先写GC的日志,如何在写入目前还是合法的数据,再去更新LSM-tree,最后标记GC操作完成,
(i) appending the valid KV pairs that are over- written as well as metadata updates to the GC journal; (ii) writing all valid KV pairs back to the segment group; (iii) updating the metadata in the LSM-tree; and (iv) marking the GC operation free in the journal.
0x02 优化
这里总结了HashKV几个优化的点:
-
缓解增加的随机写入的开销,前面提到的分区的方法使得写入不在那么顺序,这里的优化方式是批量处理,一个很常见的方法。
-
小Value内联,小的Value就没必要分开保存到Value的vLog里面,这样可以提高性能;
Thus, we propose selective KV separation, in which we still apply KV separation to KV pairs with large value sizes, while storing KV pairs with small value sizes in entirety in the LSM-tree. A key challenge of selective KV separation is to choose the KV pair size threshold of differentiating between small-size and large- size KV pairs (assuming that the key size remains fixed). We argue that the choice depends on the deployment environment. -
范围查询,由于Value分离的操作增加了很多的随机读取,这里采用了类型WiscKey中有点像预读的设计;
HashKV currently leverages the read-ahead mechanism to speed up range scans by prefetching values into the page cache. For each scan request, HashKV iterates over the range of sorted keys in the LSM-tree, and issues a read-ahead request to each value (via posix fadvise). -
冷数据分开保存,这里前面已经提到了。
这里额外的几个问题:
- 写入不在那么“顺序”对性能产生多大的影响?
- 分区的方式可不可以就是对一个vLog进行“分段”的处理;
- GC操作的时候感觉增加了不少的写入操作。
0x03 评估
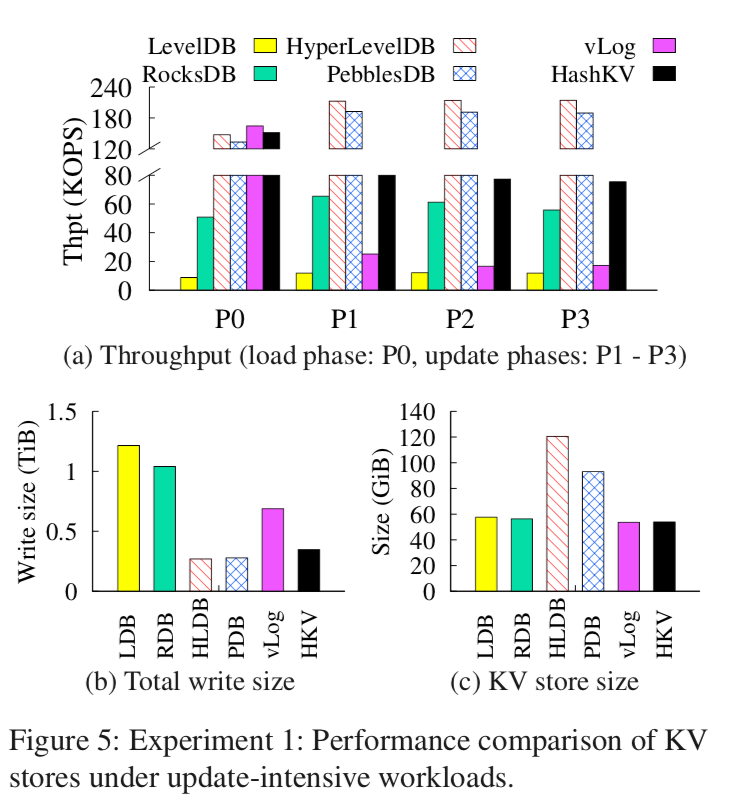
这里的具体信息可以参看[1],
参考
- HashKV: Enabling Efficient Updates in KV Storage via Hashing, ATC ’18.
- WiscKey: Separating Keys from Values in SSD-conscious Storage, FAST ’16.
