HopsFS: Scaling Hierarchical File System Metadata Using NewSQL Databases
0x00 引言
这篇Paper讲的是在Hadoop FS基础上的一个进化。主要讨论如果优化Haddop的NameNode。Hadoop FS基于的是GFS的设计,其元数据是保存在NameNode的内存中。在Google的GFS的下一代的CFS中,这部分的元数据被保存到了分布式的存储系统之上(Bigtable?)。CFS目前还没有发表论文介绍。这篇Paper的基本思路也差不多。它通过讲分布式文件系统的元数据保存到NewSQL之上,实现了比原来的Hadoop FS强大得多的拓展性。这里可以看作是Hadoop FS中NameNode设计的一个进化,基本的工作方式还是没有变化了,而且HopsFS和Hadoop FS的客户端还是兼容的,只是使用Hadoop的客户端可能某些功能就发挥不出来,
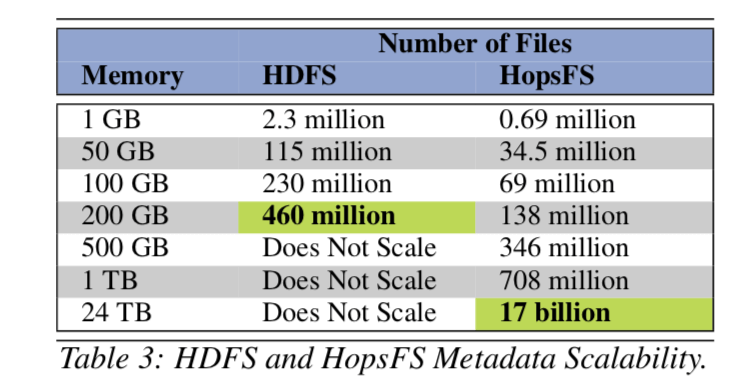
we introduce HopsFS, a next generation distribution of the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) that replaces HDFS’ single node in-memory metadata service, with a distributed metadata service built on a NewSQL database. ... Metadata capacity has been increased to at least 37 times HDFS’ capacity, and in experiments based on a workload trace from Spotify, we show that HopsFS supports 16 to 37 times the throughput of Apache HDFS.
0x01 基本设计
不像Ceph这样分布式存储系统和Hadoop FS存在很大的架构上面的区别,HopsFS基本架构和Hadoop FS是一脉相承的,
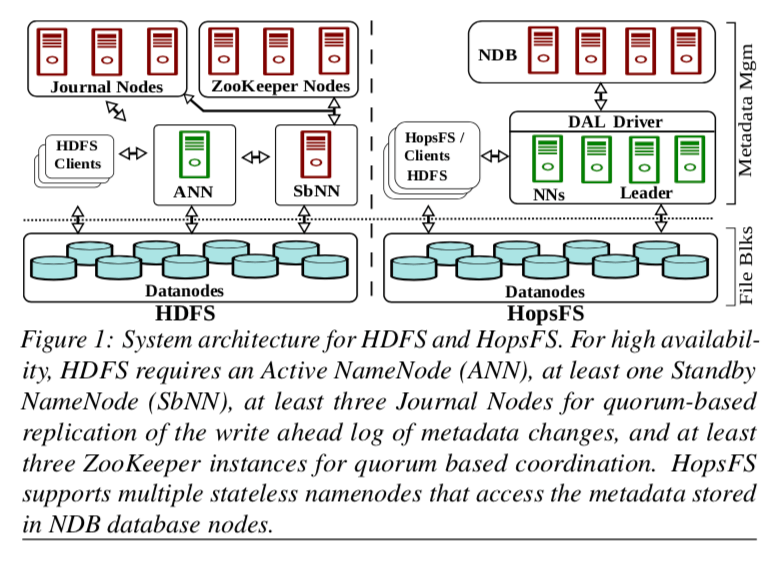
在原来的Hadoop FS(就是GFS的方法),NameNode是通过复制来实现可用性的,而一个时间点只会有一个活动的NameNode。在使用了NewSQL(Paper中使用的MySQL Cluster,不过这里具体使用哪一个并不重要),这些复杂容错等的操作都不需要HopsFS自己去操心的,这些锅都甩给了这个NewSQL去完成。而且NewSQL提供的事务处理能力也为操作的实现提供了很大的方便。此外就是不必要同一个时间段内只能有一个的NameNode了,
Clients can choose between random, round-robin, and sticky policies for selecting a namenode on which to execute file system operations. HopsFS clients periodically refresh the namenode list, enabling new namenodes to join an operational cluster.
0x02 关系模型
这里是HopsFS实现的一个很基础很重要的一个部分了。就是如何将Hadoop FS的结构映射到SQL的关系模型之上。
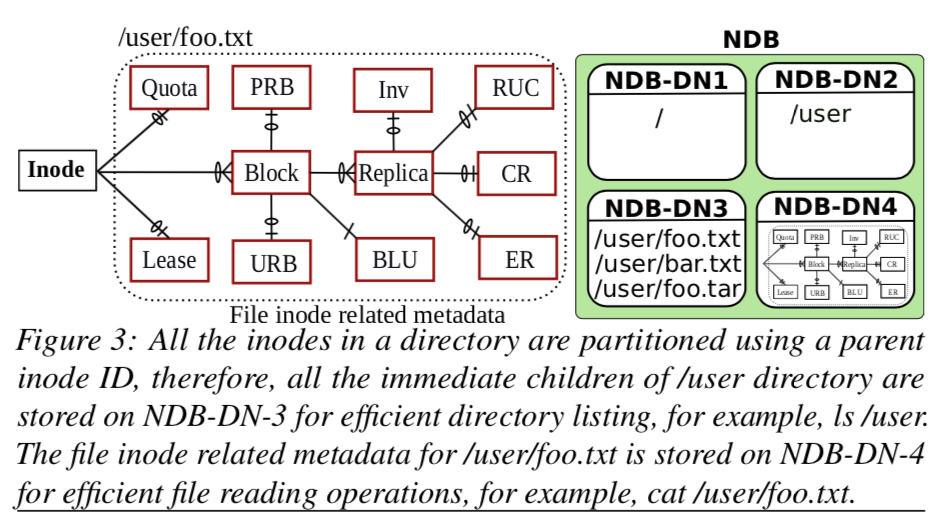
上面的图就表示了Hops基本的tables的设计,下面是一个说明:
- Inode表,这里的inode和普通的单机的文件系统中的inode类型,也是一个文件or目录的一些元数据,这个table中的每一行都代表了一个文件or一个目录。元数据比如有这个inode包含的blocks信息,还是就是blocks的文件信息,另外,由于FS是有树形的结构的,这里还会好看了父节点的信息;
- Block,Block的信息保存在这个table中;
- Replica,Block会被复制几份保存,Block副本的信息保存在这里;
- Under-replicated blocks table (URB),处于复制状态的Blocks的信息;
- Pending replication blocks table (PRB),等待被复制的Blocks的信息会被保存到这里;
- Corrupted replicas (CR) table,被发现发生错误的Block的信息会被保存到这里;
- Replica under construction (RUC) table,保存客户端写入一个新的Blocks的副本时,这个Blockxx会被保存在这里;
- Excess replicas (ER) table,当一个暂时故障的DataNode恢复之后,可能造成某些Blocks的副本的数量超过要求,这个超出的Blocks的信息保存在这里;
- Invalidation (Inv) table,保存被列入删除的Blocks的信息;
为了实现更好的可拓展性和处理hotspot的问题,Hops这里使用的方法是分区的方法,使用的分区的方式是根据inode的信息。这里要处理下面几个问题:
-
根据inode分区的时候如何处理一个目录下面的文件。这里的处理方法是根据父节点的inode的ID来分区,这样同一个目录下面的文件和目录会被分到一个分区;而文件or目录相关的元数据如blocks、副本和checksum等,直接根据文件or目录本身来分区就可以了;
-
root inode的问题。root inode会被非常频繁的使用,所以这里在所有的NameNode都缓存了root inode的信息,而且root inode本身是不可变的;
-
root固定保存的另外一个问题就是最上层的目录也很有可能成为热点,而根据父节点的ID分区的方式有导致了这些信息被保存在一个分区上面,这样也是一个问题。这里的解决办法是在这一层是用另外的分区的方式,
HopsFS uses a configurable directory partitioning scheme where the immediate children of the top level directories are pseudo-randomly partitioned by hashing the names of the children. By default, HopsFS pseudo-randomly partitions only the first two lev- els of the file system hierarchy, that is, the root directory and its immediate descendants.
0x03 事务操作
将文件系统的元数据都保存到了NewSQL之后,接下来就是要在此的基础之上实现文件系统的各个操作了。这里将的是inode上面的操作。这讨论具体的操作之前,先看一下要处理的问题:
-
由于Paper中使用的NDB最高只能提供read-committed级别的隔离基本,这个对于HopsFS的操作还是不够的。为了处理在一个inode上的操作的冲突问题,这里使用了在inode相关的row上加锁的方法。这里的锁也是分种类的。当需要请求多个锁时,为了避免死锁,这里就是使用了安装规定的顺序来获取锁,
To solve this problem, we have reimplemented all inode operations so that they acquire locks on the metadata in the same total order, traversing the file system tree from the root down to leave nodes using left-ordered depth-first search.此外还要处理锁升级的问题:
all data needed in a transaction is read only once at the start of the transaction at the strongest lock level that could be needed during the transaction, thus preventing lock upgrades. -
Inode Hint Cache,由于和一般的单机的文件系统一样,HopsFS是按照路径的一段段来获取最终的文件信息。这样导致的结果就是要多个的来会操作才能回去到最终的文件信息。为了优化这里,HopsFS采用了hints的方法,简单地说就是一种cache的方法,
... inodes have a composite primary key consisting of the parent inode’s ID and the name of the inode (that is, file or directory name)... Each namenode caches only the primary keys of the inodes. Given a pathname and a hit for all path components directories, we can discover the primary keys for all the path components which are used to read the path components in parallel using a single database batch query containing only primary key lookups.
对于Inode的具体的操作,都会表现为在上面上面说明的table上面的操作。在操作的散步lock、excute和update中,最需要处理的就是lock步骤。HopsFS基本的操作如下:
1. Get hints from the inodes hint cache
2. Set partition key hint for the transaction BEGIN TRANSACTION
LOCK PHASE:
3. Using the inode hints, batch read all inodes
up to the penultimate inode in the path
4. If (cache miss || invalid path component) then
recursively resolve the path & update the cache
5. Lock and read the last inode
6. Read Lease, Quota, Blocks, Replica, URB, PRB, RUC, CR, ER, Inv using partition pruned index scans
EXECUTE PHASE:
7. Process the data stored in the transaction cache
UPDATE PHASE:
8. Transfer the changes to database in batches
COMMIT/ABORT TRANSACTION
上面的基本步骤也比较清晰的说明了,对于LOCK PHASE,首先是很区文件or目录所有的inode信息,如果可以加锁的话,这里需要加的路径上面最后的一个inode的锁就可以了,要注意的是,HopsFS这里使用的锁是hierarchical locking,也就是说在一个父节点加了锁,也就意味着它的所有的子节点也都加了锁,这里也是需要获取会路径上面所有的inode的一个原因。其中EXECUTE PHASE存在的原因更多是优化性能。这些操作会先保存在一个per-transaction cache中,在操作的结尾,就是UPDATE PHASE一次性的提交到数据库。这样就能减少不少的数据库访问。
0x04 大规模操作的处理
对于一下子可能影响到非常多的inode的操作,比如移动操作(move)。这里就需要额外的机制来处理。
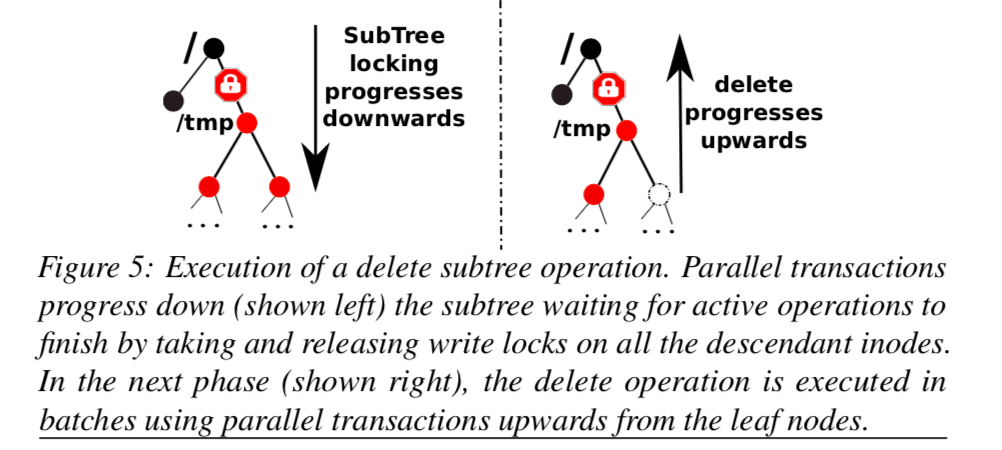
这里主要就是处理下面几个问题:
-
还是row级别的锁是不符合的,改用了subtree lock。这里的操作都是基于子树的(subtree),使用了一个操作的协议subtree operations protocol,基本情况是,
our subtree operations protocol uses an application-level distributed locking mechanism to mark and isolate the subtrees. ... We implement this serialization property by enforcing the following invariants: (1) no new operations access the subtree until the operation completes, (2) the subtree is quiesced before the subtree operation starts, (3) no orphaned inodes or inconsistencies arise if failures occur.具体的信息可以参考[1]。
-
处理失败的subtree操作,由于subtree的操作可能需要比较长的时间,在这个时间内操作的NameNode如果使用的话会留下没有完成的subtree操作。其它的NameNode在遇到了一个subtree lock之后,会去查看相关的NameNode是否正常工作,如果处于非正常工作的状态,就需要清理操作。另外对于操作没完成会导致系统不一致的操作,比如delete,会有重试解决。
-
还有的一个问题就是subtree lock和前面的row级别的锁的兼容性的问题,
Both inode and subtree locking mechanisms are compatible with each other, respecting both of their corresponding locks. That is, a subtree flag cannot be set on a directory locked by an inode operation and an inode operation voluntarily aborts the transaction when it encounters a directory with a subtree lock set.
0x05 评估
具体的信息可以参看[1]
(补充) Size Matters: Improving the Performance of Small Files in Hadoop
这篇文章也和这里的HopsFS相关。众所周知Hadoop FS之类的文件系统都是为大文件设计的。而在这篇Paper中认为HDFS中有25%的文件小于16KB,而且42%的操作都发生在这些小文件上面。HopsFS在使用了NDB做为元数据保存的位置是,同样使用NDB来保存一些小的文件来实现HopsFS对于小文件的优化。另外这篇Paper还是很会写啊,一页就能写完的内容硬是写了13页。m(._.)m
0x10基本思路
这里的一个方法叫做Inode Stuffing。这里和一些单机文件系统使用的小文件直接内联到inode里面的优化的思路是一致的。
Inode stuffing has two main advantages. First, it simplifies the file system operations protocol for reading/writing small files, that is, many network round trips between the client and datanodes (in the large file storage layer) are avoided, significantly reducing the expected latency for operations on small files. Second, it reduces the number of blocks that are stored on the datanodes and reduces the block reporting traffic on the namenode.
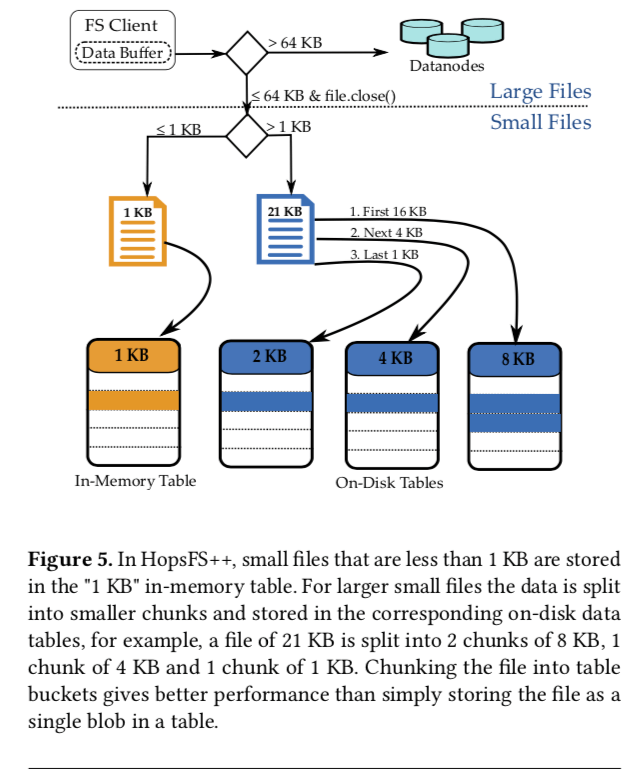
根据文件的大小来选择将文件保存到memory table里面还是将这些内容保存到硬盘上面。这里使用的硬盘为NVMe SSD。
0x11 评估
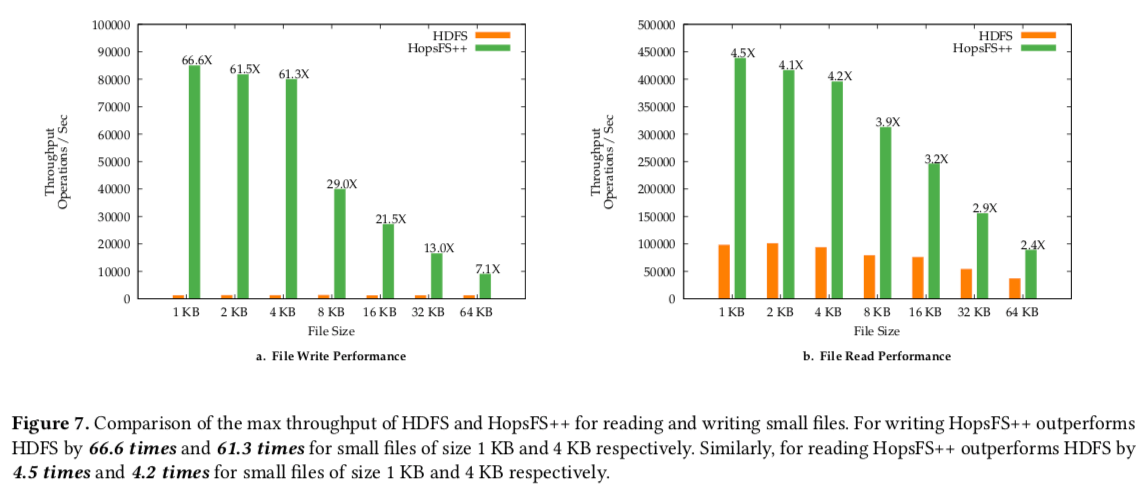
这样的方式对小文件的性能优化从Paper的文件来看还是很有效果的,具体的数据可以参看[2]。
参考
- HopsFS: Scaling Hierarchical File System Metadata Using NewSQL Databases, FAST ’17.
- Size Matters: Improving the Performance of Small Files in Hadoop, Middleware’18.
