A Write-Friendly and Cache-Optimized Hashing Scheme for Non-Volatile Memory Systems
0x00 引言
非易失性内存(NVM)是现在的一个研究热点。对于现在存在的一些hash table的算法都不能很好的适应NVM的环境,其主要原因就是NVM写的成本相对来说比较高,而常规的设计会造成很多额外的写操作。这篇paper的主要目的就是减少额外的写操作,同时为cache优化。
0x01 基本思路
这篇paper使用的方法叫做Path hashing ,方法理解起来很简单,文章中的一段话加上一幅图即可:
Storage cells in the path hashing are logically organized as an inverted complete binary tree. ... All nodes in the remaining levels are non-addressable and considered as the shared standby positions of the leaf nodes to deal with hash collisions. When hash collisions occur in a leaf node, the empty standby positions of the leaf node are used to store the conflicting items. Thus insertion and deletion requests in path hashing only need to probe the leaf node and its standby positions for finding an empty position or the target item, resulting in no extra writes.
基本思路就是出路原来位置槽的部分外,还有额外的共享的standby cells,这些cells使用了解决hash冲突的,同时又不造成额外的写操作。
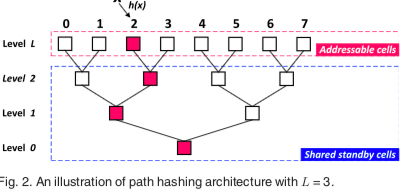
Position Sharing
倒置的树形结构,除了最高的一层外,更高的层的standby cell是有多个slot共享的,越低共享的slot就越多。可想而知,越向下数量越少就节约了空间。如果都使用一样的节点数量,达到下面层的数据项是越来越少的,这样就会浪费空间。
Double-Path Hashing
一盒hash函数的情况下,每一个key可以放置的位置是L+1个(L是高度),一个基本的思路使用2个hash函数,这样的话可选择的位置就增加了接近2倍。但是实际上这样的方法并不是很好,两个hash有可能有不少的重叠的地方。更加简单更加好的方法就是一个hash函数计算在前半部分的slot,一个计算在后半部分的slot。
Path Shortening
去除没有数据的level,消除了不必要的查询。
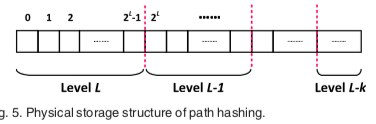
算法
Path hashing的基本算法和普通的hash table没有区别,算法也简单直观,直接就直接给出paper中的描述就可以了: 插入,可以插入的位置都要考虑到。我们这里也发现了path hasing的一个缺点,没有rehash的逻辑。(个人认为这里有一个比较好的解决方法,不知道行不行得通).
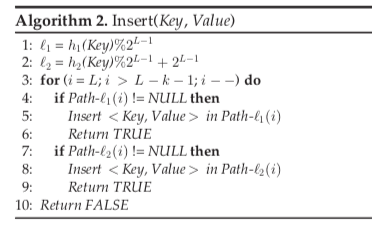
其它的query,delete操作都比较简单,就不重复了。
缓存优化
简而言之,就是将一些”level”“压”到一起:
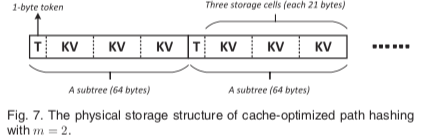
简单有好玩的新思路,good idea。
0x02 评估
这里的具体信息可以参看[1],
SmartCuckoo: A Fast and Cost-Efficient Hashing Index Scheme for Cloud Storage Systems
0x10 引言
这篇Paper也是关于Hash Table设计上面的优化,这篇Paper和上面的Path Hashing来自同一个大学。SmartCuckoo关注的是在Cuckoo Hash中驱逐问题处理。SmartCuckoo通过分析Cuckoo Hash在Key驱逐时候可以构成的subgraph来知道选择更优的驱逐策略。
0x11 基本思路
在Cuckoo Hash中,如果一个Key可选的位置已经被其它的Key占据了,Cuckoo Hash就会讲其中的一些位置中的Key驱逐。这样的策略在大部分的时候都是很有用的,但是存在这样的一些问题,一个驱逐的时候可能导致级联的驱逐操作,而且操作的次数可能很多,另外一个就是驱动的位置之间可能形成环,这样实际上驱逐是不能成功的,这里一般的策略就是给驱逐指定一个最大的次数。如果超过了这个次数,就需要对其进行一些rehash的处理。而SmartCuckoo从这里出发,通过对驱逐的情况建立一个Graph,分析不同的情况,知道选择更加好的驱逐的策略。SmartCuckoo将一个subgroup里面每一个顶点有有且仅有一条出边的称之为maximal subgraph。这个的subgraph会存在一个环,而对应的就是no-maxinimal-subgraph,这样的subgraph不存在环。这里SmartCuckoo引入来cuckoo graph的概念,表示在一个Cuckoo Hash中驱逐可形成的graph。
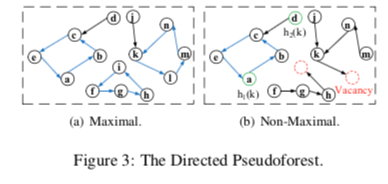
Paper中讨论的是使用两个hash函数的情况。在一个Key新添加到一个Cuckoo Hash中的时候,SmartCuckoo根据在这些subgraph形成的pseudoforest里面新增的顶点的数量分为三种情况,
New item insertions can be classified into three cases, i.e.,v+2,v+1,and v+0. As each item is represented as an edge in the pseudoforest, different placements of the item will increase the graph’s vertex count differently (by two, one, or zero)
而SmartCuckoo的设计就是根据这三种情况选择合适的添加策略,
-
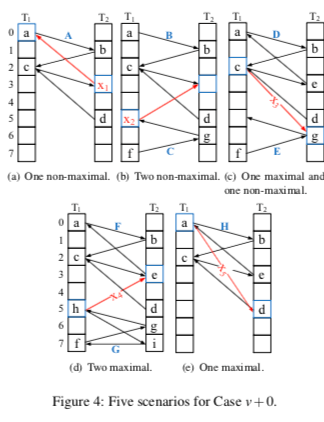
v + 0,这里表示可选的两个都已经在pseudoforest中了,这里又细分为5中情况,如下面的图所示,
- 如果都位于一个non-maxinal的subgraph中,直接使用驱逐策略。
- 如果位于两个non-maxinal的subgraph中,使用驱逐策略之外还要将这两个subgraph合并。
- 如果一个为non-maxinal,一个maxinal,选在一个non-maxinal的驱逐。
- 其它的两种情况都需要进行rehash的操作。
-
对于v+1的情况,这里比v+0的情况简单很多,这样的操作会导致两个subgraph合并,然后直接进行添加操作即可,不用驱逐操作。
-
对于v+2的情况,表示这里会新添加一个subgraph,在赋予这个新添加的一个唯一的subgraph ID之后的操作和v+1的是一样的。
除了添加的操作,还要考虑的就是删除的操作。删除中要处理的就是一个subgraph分裂的问题,这里使用相当于删除原来的,新添加两个的做法,
... Deleting an item from the hash tables is equivalent to removal of an edge in the corresponding subgraph, which causes the subgraph to be separated into two subgraphs. We assign each of the two subgraphs a new ID, and update the IDs of each member vertex of the two subgraph in their corresponding buckets
实现
在SmartCuckoo的实现上,subgraph的操作主要就是利用并查集来实现的,
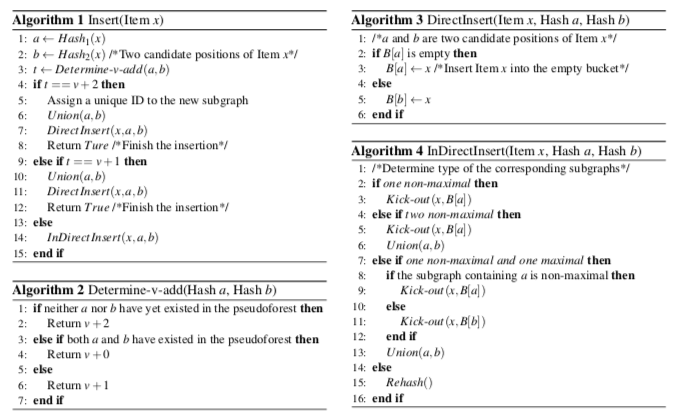
另外,SmartCuckoo有在Github上面开源,不过这个开源的代码看起来写的比较差,emmmmm。
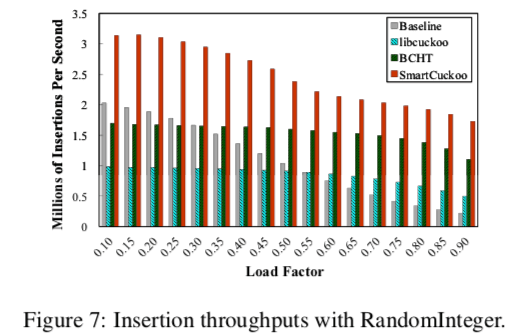
0x12 评估
这里的具体信息可以参看[2],
参考
- A Write-Friendly and Cache-Optimized Hashing Scheme for Non-Volatile Memory Systems, TPDS 2018.
- SmartCuckoo: A Fast and Cost-Efficient Hashing Index Scheme for Cloud Storage Systems, ATC ‘17.
