RFLUSH: Rethink the Flush
0x00 引言
这篇Paper也和前面的一篇一样,讨论的是Flush的一些优化。与前面的从文件系统方面的优化不同,这里优化的方向是直接优化Flush操作本身。这篇Paper主要的优化思路是使得Flush更加细粒度化,可以指定一段范围内(a range of logical block addresses (LBAs))的数据Flush(RFLUSH (Range Flush))。通过这种方式,
Performance evaluation using the prototype shows that the inclusion of RFLUSH improves the throughput by up to 6.5x; reduces the write traffic by up to 43%; and eliminates the long tail in the response time.
这篇Paper的核心的内容很短,主要还是Range Flush的思路。
0x01 基本思路
几个基本的问题:
-
在哪里使用,Paper主要的优化的目标就是fsync(),fsatasync()接口。另外可以优化的就是常见的WAL机制;
-
Flush那些数据,Range Flush一个核心的内容就是找出这个Range里面的数据。Paper中比较了基于pages、blocks和inode number几种方式,说明前两者均存在比较明显的问题,就选择了最后一种的方式;
-
处理元数据,另外的要处理的一个问题就是元数据的问题。文件更新的时候一般都要更新元数据,在Paper中测试使用的F2FS文件系统中,简单的更新需要更新的元数据会导致不好的小的随机的写操作,而且处理起来也很麻烦。为了解决这个问题,Paper中的解决方式是一次就更新一个比较大的区域,这部分是需要更新的的元数据的一个超集,类似一种连接聚合的方式。这种方式看似会出现下面的问题,
Consider a case in which there are two different files A and B, whose inode structures are located in a single block. When the fsync requests occur for the files con- currently, forcing the entire metadata area by one fsync request might corrupt data integrity, violating ordering constraints between data and metadata of another file (e.g., file B’s metadata is persisted before file B’s data block).但是这个实际上在现在的一些文件系统中不是问题。比如F2FS使用的log的方式就可以处理,ext4处理的方式则是限制更新元数据和数据的顺序,
F2FS logs individual inode structure on an update, instead of an entire block, thereby preventing undesired interference that can be caused by interleaved fsyncs. Ext4 resolves this issue by forcing all dependant data prior to persisting the modified metadata block. Thus, in the above example, both data A and B are flushed to non-volatile storage before the metadata block when an fsync request occurs either for file A or B. -
与存储协议集成,Paper中使用了Open Channel的方式,
Another possibility for incorporating extensions into the standard storage API is to use the open-channel SSD architecture [4, 23]. In this architecture, the host system implements many of the functionalities needed to manage flash memory (e.g., garbage collection). Also, by utilizing veiled information behind the storage device interface, this architecture enables the management of flash memory to meet the demands of the host system. We use the latter approach since the host-manageable architecture allows easy integration of the extensions for RFLUSH.
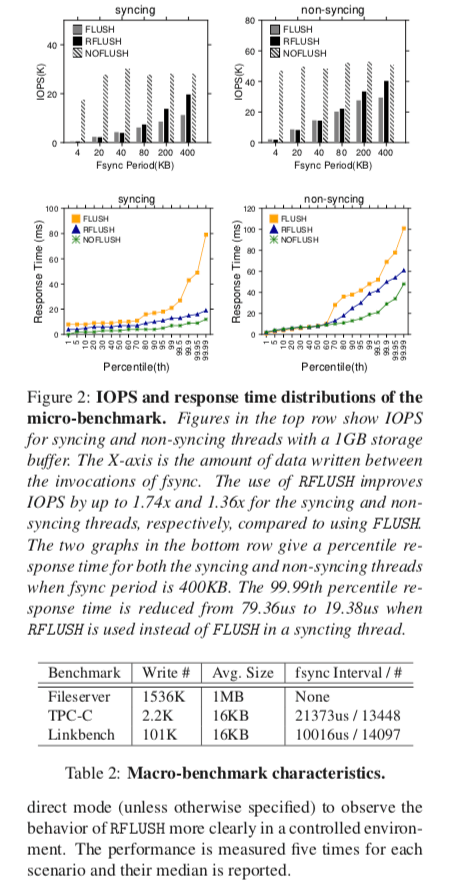
0x02 评估
具体信息可以参看[1]:
参考
- RFLUSH: Rethink the Flush, FAST’18.
