UpBit: Scalable In-Memory Updatable Bitmap Indexing
0x00 引言
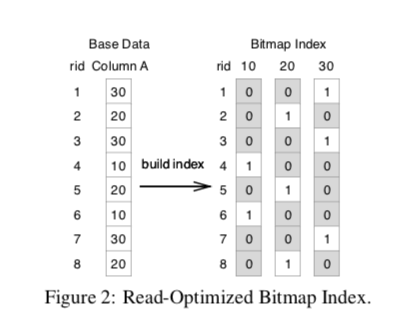
Bitmap索引在一些情况下是一种非常有用的索引。它在一个字段的取值范围只是确定的一个较小的集合时很有用。一个基本的bitmap index如下图。途中一个字段的取值可能为3个值,每一个可能的取值会用一个bitvector标识。很显然,这样的方法在取值的范围更加大的时候会有很多的内存的消耗,而且存在优化的空间。所以bitmap index会采取一些压缩编码的测量。这样的好处就是减少了内存的使用,缺点就是每次的更新操作都需要进行解码编码的操作,减低了更新操作的性能。
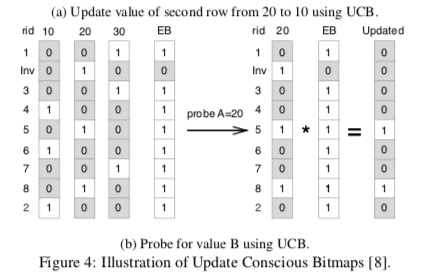
已有的一些解决办法比如Update Conscious Bitmaps,使用了将一些更新的信息追加到结构的末尾。同时将原来的位置的值置为无效,如果只是删除的话直接置为无效几个。这个标记有效的结构为另外的一个bitvector。
0x01 基本思路
UpBit使用的思路是同时维持一个V bitvector,标记值,另外一个U bitvector,标记更新。基本的结构和操作如下,
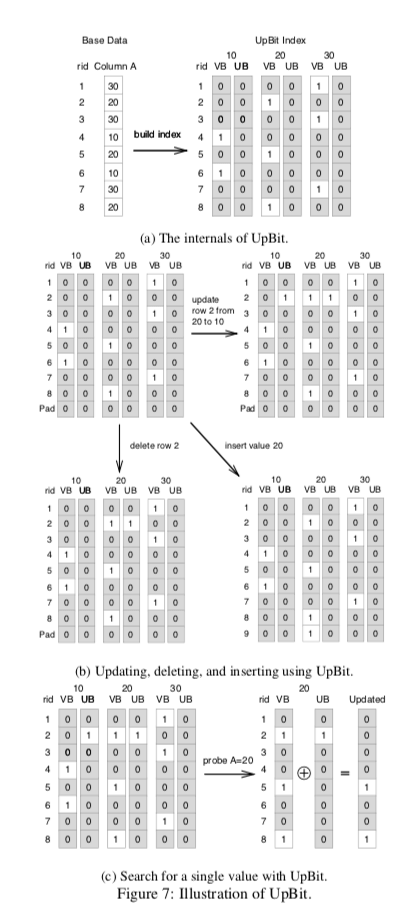
这样看来会增加空间的消耗。但是实际上这个增加的很小。一个原因是这个U bitvector在开始的时候均为0,这个很容易拥一个很小的空间表示,而不用实际去分配这样一个bitvector。另外,在添加了这个U bitvector之后怎么操作还是很显然的。
... In particular, the current value of a row of the UpBit is given by the XOR between the corresponding position of the value and the update bitvectors. The update bitvectors distribute the burden of each update to multiple bitvectors, keeping the update cost low, and, at the same time, the compressibility of these bitvectors high in order to have minimal impact on read performance.
这样一看上去好像还是增加成本了。为什么还能加快更新操作呢?这里主要的原因是在U bitvector的数值更加简单,一般只有小部分的位被设置。这样不仅可以更加高效地处理,而且还能有效地压缩保存,
The aggregate size of the uncompressed bitvectors for UpBit is twice as much as for a read-optimized bitmap index, however, at any point in time each update bitvector has only a small number of bits set to one. This allows for negligible storage and CPU decoding overhead.
0x02 操作
UpBit操作的思路一般都比较简单,
# Algorithm 1: Searching UpBit for value val.
search (index: UpBit, value: val)
Find the i bitvector that val corresponds to
if Ui contains only zero then
return Vi
else
return Vi ⊕ Ui
endif
# Algorithm 2: Deleting row k with UpBit.
delete_row (index: UpBit, row: k)
Find the val of row k
Find the i bitvector that val corresponds to
Ui[k] = ¬Ui[k]
# Algorithm 3: Get value of row k using UpBit.
get_value (index: UpBit, row: k)
foreach i∈{1,2,...,d} do
temp_bit = Vi.get_bit(k) ⊕ Ui.get_bit(k)
if temp_bit then
Return val i
end if
end for
获取kth的值复杂一些,
#Algorithm 4: Get kth bit of a bitvector using UpBit.
get_bit (bitvector: B, row: k)
pos = fence_pointer.nearest(k)
while pos < k do
if isFill(B[pos]) then
value,length = decode(B[pos])
if (pos+length)∗31 < k then
pos += length
else
Return value
end if
else
if pos∗31−k < 31 then
Return B[pos]&(1 << (k%31))
else
pos++
end if
end if
end while
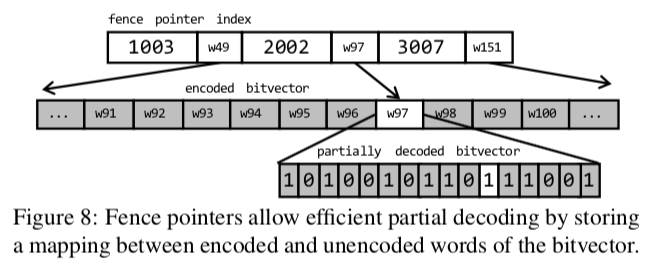
上面算法的一个优化策略就是fence pointers 。可以看作是一个分段的思想,可以避免要解码前面的所有的数据,只要解码一部分即可,
合并操作
在更新、删除和添加等update的操作积累了一定数据之后,就需要将U bitvector的数据合并到V bitvector中,
merge (index: UpBit, bitvector: i)
Vi=Vi⊕Ui
comp_pos=0
uncomp_pos = 0
last_uncomp_pos=0
for each i ∈ {1,2,...,length(Vi)} do
if isFill(Vi[pos]) then
value,length+ = decode(Vi[pos]) uncomp_pos+= length
else
uncomp_pos++
end if
if uncomp_pos−last_uncomp_pos > THRESHOLD then
FP.append(comp_pos,uncomp_pos)
last_uncomp_pos = uncomp_pos
end if
comp_pos + +
endfor
Ui ← 0s
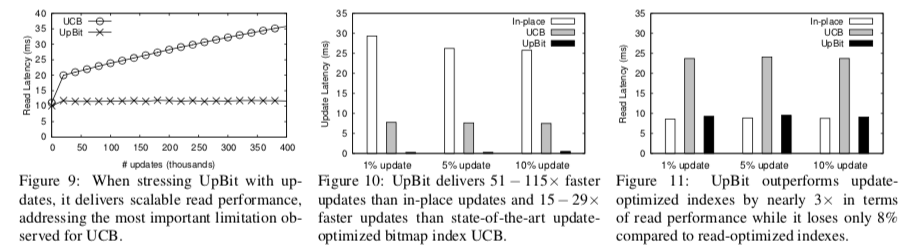
0x03 评估
这里的具体的信息可以参看[1],
参考
- UpBit: Scalable In-Memory Updatable Bitmap Indexing, SIGMOD’16.
