F2FS: A New File System for Flash Storage
0x00 引言
SSD有种它自己的特点。Linux的Ext FS,XFS FS等主要还是为HHD设计,优化的出发点也是HHD的工作方式。而SSD的工作方式和HHD有着本质的不同. F2FS是Linux上的一个为SSD设计的FS,另外F2FS是一个Log Structured的FS(所以先看一下[2,3]),现在在很多的智能手机上已经使用了(苹果也号称它的新的APFS是为SSD优化设计的,不过找不到具体技术细节的东西)。
The detrimental effects of random writes could be reduced by the log-structured file system (LFS) approach and/or the copy-on-write strategy. For exam- ple, one might anticipate file systems like BTRFS and NILFS2 would perform well on NAND flash SSDs; unfortunately, they do not consider the charac- teristics of flash storage devices and are inevitably suboptimal in terms of performance and device lifetime.
0x01 基本思路
On-Disk Layout
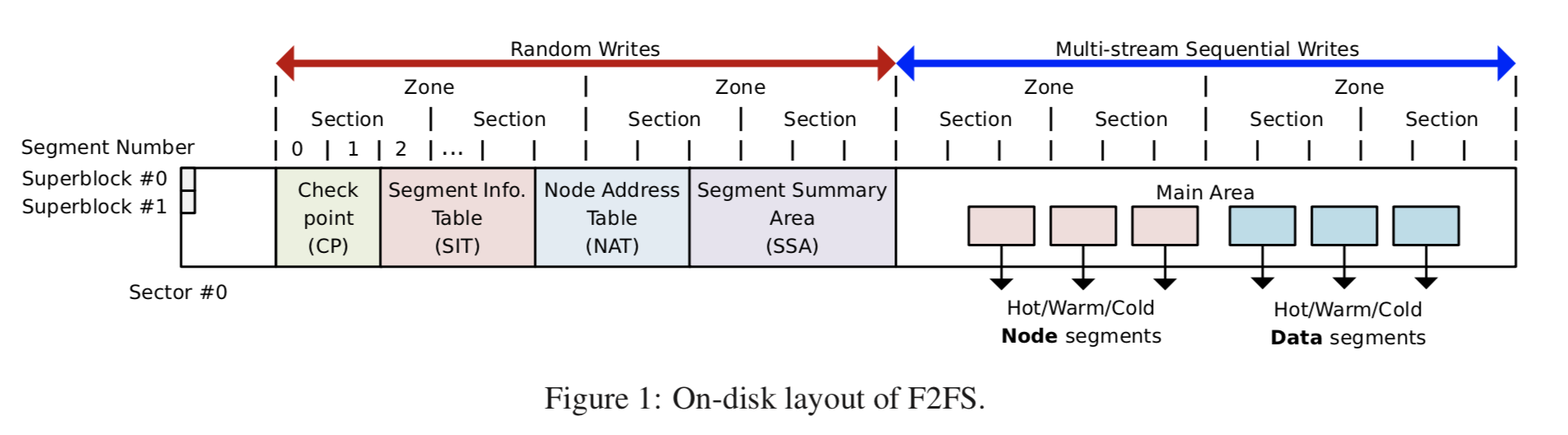
F2FS将SSD分为固定程度的segment,连续的segment组成section,一些section 组成zone。F2FS分为6个区域:
-
Superblock: 初始化之后就不变的,文件系统的元数据;SB
-
Checkpoint:保存了文件系统状态,和LFS中的一样,也是2个轮流使用的;CP
-
Segment Information Table:segmemt相关的信息; SIT
-
Node Address Table :Node地址表;NAT
-
Segment Summary Area : 保存Main Area中block的信息; SSA
-
Main Area: 保存数据的地方。MA
A node block con- tains inode or indices of data blocks, while a data block contains either directory or user file data.
结构图,这个图很清晰地表示了F2FS的结构:
看一看一个读文件的过程加深理解,假设读取“/dir/file” :
- 读取包含root的inode的block,这个位置信息在NAT中;
- 从root inode的块中,找到dir的目录项,得到dir的inode number;
- 通过NAT,根据dir的inode number找到物理位置;
- 读取dir对应的block;
- 在dir的block中找file的inode number,重复3,找到inode;
- 根据inode的信息读取file的数据,数据保存在MA中;
File Structure
与LFS中的inode map不同,F2FS使用 “node”结构,每一个node有一个唯一的node id。使用这个id,NAT可以找到node block。node block可以表示inode,direct和direct node。
An inode block contains a file’s metadata, such as file name, inode number, file size, atime and dtime. A direct node block contains block addresses of data and an indirect node block has node IDs locating another node blocks.
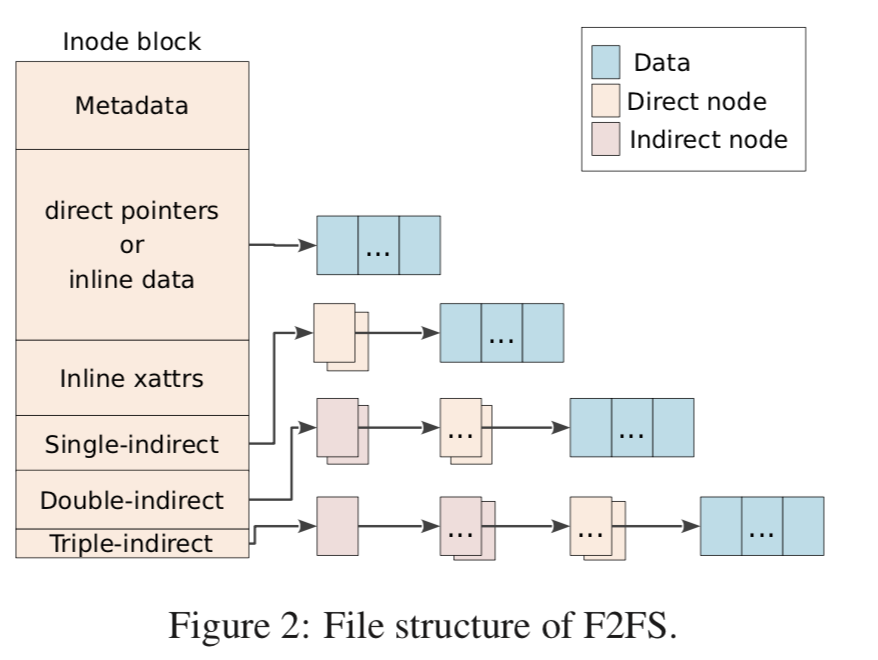
这里基本结构和常见的没有很多区别。也使用了一些常见的优化方法,比如小文件内联。这里要注意到与LFS不同的地方,LFS是尽可能的避免随机写,F2FS这里是存在一些随机写的(看上面的结构图),比如更新NAT。由于SSD随机写的性能远高于HHD,这个是合理的。
Directory Structure
没有什么特别的。可以说就是一个映射关系表而已。
In F2FS, a 4KB directory entry (“dentry”) block is composed of a bitmap and two arrays of slots and names in pairs. The bitmap tells whether each slot is valid or not. A slot carries a hash value, inode number, length of a file name and file type (e.g., normal file, directory and symbolic link). A directory file constructs multi-level hash tables to manage a large number of dentries efficiently.
0x02 Logging
Multi-head Logging
Logging当然是Log Structured的核心内容啦。与LFS使用”一个“log不同,F2FS使用了”多个”log。根据数据的“冷热”程度分为hot, warm and cold。
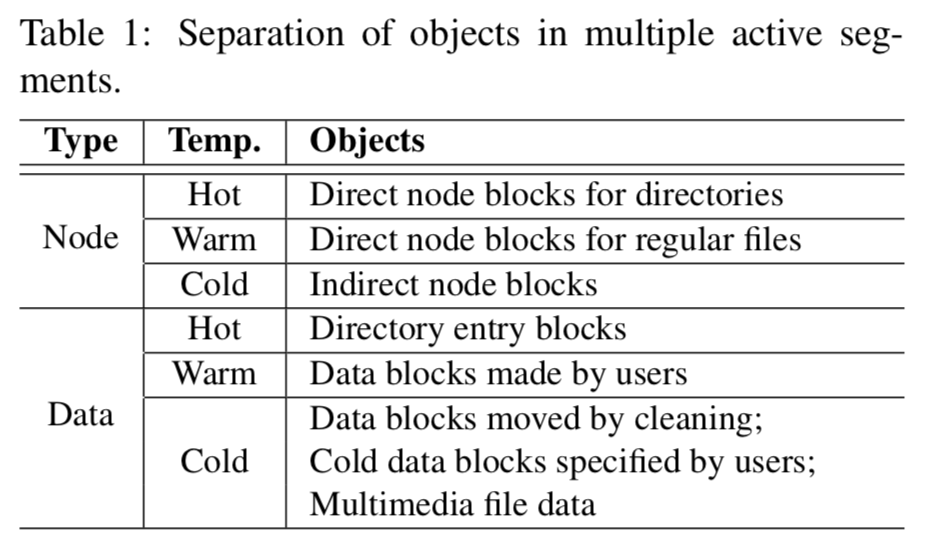
F2FS使用了一些方式来判断冷热程度。如上表所示。
Cleaning
Cleaning类似LFS中GC的过程,不够正对SSD做了一些优化。首先,以section粒度来进行cleaning。基本的思路和常见的比如LFS的相似:
-
Victim selection。找到需要回收的section;
-
Valid block identification and migration,移动存活的block;
-
Post-cleaning process,只有在一个checkpoint之后,这个被回收的才真正被标记为空,可以被重新使用。
After all valid blocks are migrated, a victim section is registered as a candidate to become a new free section (called a “pre-free” section in F2FS). After a checkpoint is made, the section finally becomes a free section, to be reallocated. We do this because if a pre-free section is reused before checkpointing, the file system may lose the data referenced by a previous checkpoint when unexpected power outage occurs.
Adaptive Logging
在 normal logging和threaded logging 2中logging策略中. 与LFS不同,F2FS根据系统状态选择不同的策略,这里考虑带了SSD相对较高的随机写性能:
if there are more than k clean sections, where k is a pre-defined threshold, normal logging is ini- tiated. Otherwise, threaded logging is activated. k is set to 5% of total sections by default and can be configured. ...
There is a chance that threaded logging incurs undesirable random writes when there are scattered holes. Nevertheless, such random writes typically show better spatial locality than those in update-in-place file systems, since all holes in a dirty segment are filled first before F2FS searches for more in other dirty segments.
0x03 Checkpointing and Recovery
这里与CP区域的关系比较大,在CP区域保存一下信息:
- Header and footer,用途类似LFS中的时间戳;
- NAT and SIT bitmaps,标记目前的NAT,SIT blocks;
- NAT and SIT journals,保存最近更新的NAT SIT项,避免频繁更新NAT SIT;
- Summary blocks of active segments,还没有写入SSA区域的SSA blocks;
- Orphan blocks,如果一个inode在关闭之前被删除,它就被记录为孤儿inode(这个与linux中的文件操作相关,比如两个process同时操作一个文件,一个进程在另外一个关闭之前将这个文件删除了,那么只有到这个进程关闭之前才会将这个文件删除).
恢复:
After a sudden power-off, F2FS rolls back to the latest consistent checkpoint. In order to keep at least one stable checkpoint pack while creating a new pack, F2FS maintains two checkpoint packs. If a checkpoint pack has identical contents in the header and footer, F2FS considers it valid. Otherwise, it is dropped.
此外,F2FS也使用了常见的Roll-Forward Recovery 方式
F2FS implements an efficient roll-forward recovery mechanism to enhance fsync performance. The key idea is to write data blocks and their direct node blocks only, excluding other node or F2FS metadata blocks. In order to find the data blocks selectively after rolling back to the stable checkpoint, F2FS remains a special flag in- side direct node blocks.
参考
- F2FS: A New File System for Flash Storage, FAST’15.
- “Operating Systems: Three Easy Pieces“ (Chapter: Log-structured File Systems) by Remzi Arpaci-Dusseau and Andrea Arpaci-Dusseau. Arpaci-Dusseau Books, 2014.
- The Design and Implementation of a Log-Structured File System, TOCS 1992.
