Optimizing the Block I/O Subsystem for Fast Storage Devices
0x00 引言
这篇Paper讨论的是如何优化Linux的Block I/O Subsystem以使用新的高速的硬件,这里面主要提出了6条改进方案,这些措施有些之间是相互不兼容的,也就是说不能同时使用。此外,这里讨论的是如何对内核做更改来优化,而不是在现在的内核上调整参数设置来优化性能:
In this article, we explore six optimizations for the block I/O subsystem: polling I/O completion, eliminating context switches from the I/O path, merging discontiguous requests, reconfiguring an I/O scheduler for an SSD, resolving the read-ahead dilema, and avoiding a lock contention in a request queue.
另外,这篇Paper长达48页,所以这里这会总结改进方案的基本原理以及能获取到的好处,和存在的缺点,不具体讨论细节。 Linux内核基本的Block IO处理示意图:
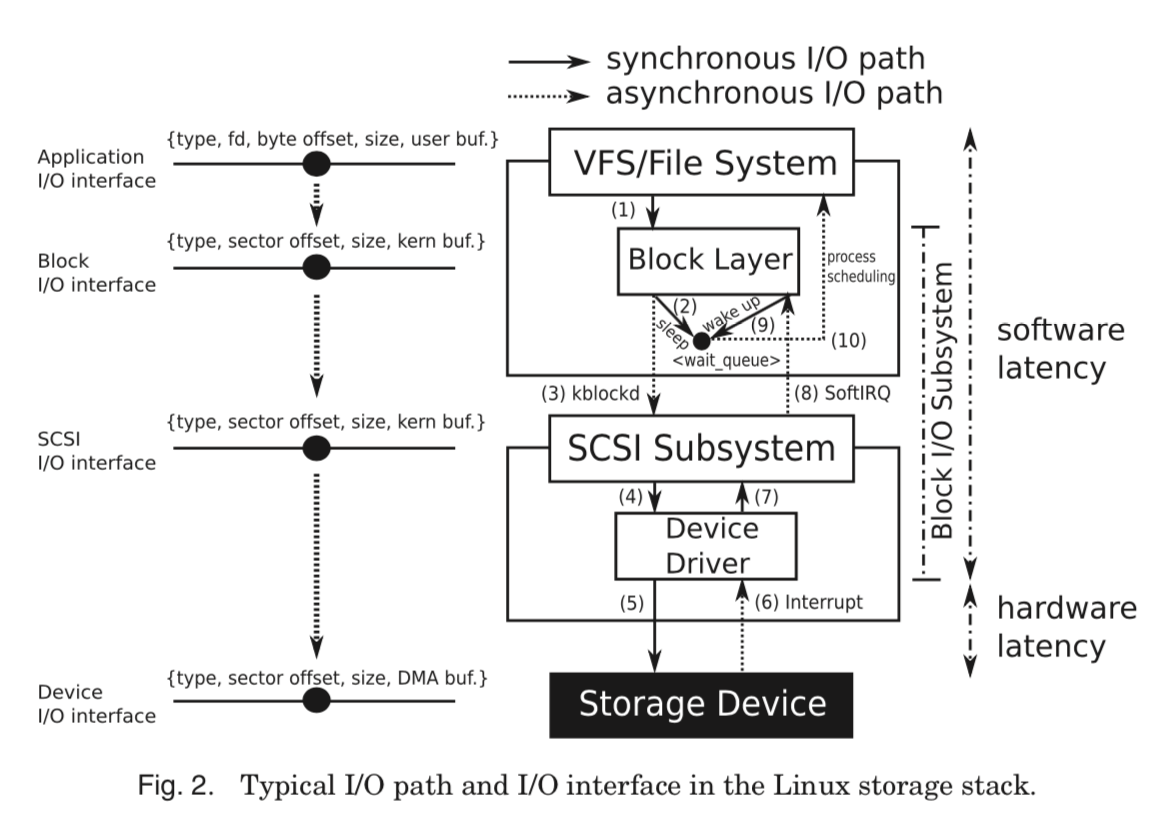
0x02 目前存在的问题
这些问题是针对高速存储硬件而言的,对于一些较低速的硬件如HHD,可能就不是问题。
High Software Latency 高软件延时
来源:
- 中断,目前一般使用中断的方式通知IO相关操作的消息;
- Delayed Execution,延迟执行,对HHD中的常见优化;
Low Random Throughput,低随机操作的带宽
来源:
- Narrow Device I/O Interface,狭隘的设备IO接口,只留出的操作的余地很小;
- Disk-Oriented Configuration,主要是面向HHD的一些设计,比如CFQ IO调度器,粗粒度的timer,预读确实高成本;
0x03 优化的基本的方法和性能相关值的度量
对于优化基本的方向就是两个:
- Reducing per-request latency,减少每个请求的延时;
- Amortizing per-request latency,平摊延时;
性能相关的值:
- Device bandwidth,设备带宽,这个是有设备本身决定的;
- Application throughput,应用带宽,应用能使用的带宽;
- Hardware latency,硬件延时,这个也是由设备本身决定的;
- Software latency,软件延时,从发出IO请求到得到IO请求完成通知的时间。
优化的6个基本阶段:
The optimizations are summarized in the following:
O1. using polling instead of interrupts;
O2. establishing a synchronous I/O path;
O3. dispatching discontiguous requests through an extended I/O interface;
O4. adjusting block I/O subsystem configurations to an SSD;
O5. avoiding harmful block prefetching; and
O6. using double buffering for I/O requests.
下面就是讨论了一些具体的方法,这里是从一个方法出发解决现有的问题,但方法本身也带来了额外的问题,然后提出改进策略,直到达到一个较好的结果。
0x04 SyncPath: Designing a Synchronous I/O Path
SyncPath设计为block layer的一个子系统,对应优化方法中的O1 O2。分为这些步骤处理IO请求:
- 预先为数据传输准备DMA缓冲区;
- 请求设备的互斥锁;
- 初始化DMA传输,然后轮询请求完全情况;
- 完成请求之后释放资源;
- 通知用户进程IO请求完成;
这里直接就绕开了现在处理方式。对于提高随机读写和顺序读以及随机的混合操作有正向的效果,对于顺序写由反向的效果。
O1 and O2 directly lead to performance improvement under several workloads. SyncPath attains a 1.58 ∼ 2.47 times improvement over SCSI INTR under the random read, the random write, and the random mixed workload.
...
On the contrary, the sequential write throughput drops from 479MB/s to 309MB/s, reaching the random write throughput. As SyncPath cannot take advantage of an I/O scheduler to merge contiguous write requests, the sequential write workload is handled in the same way as the random write workload.
0x05 Extending Device I/O Interface
SyncPath中表现出了没有合并写请求对顺序写性能的影响。现在Scatter-gather DMA I/O是一种常见的优化方式,这里提出了一种新的device IO接口,Scatter-Scatter I/O (SSIO) Interface。用于将不连续的主机内存里面的数据写入到存储设备不连续的段里面,反之同理。这利用了SSD内部的并行特性,给合并IO请求提供了额外的机会。这种方式也要求对DMA做出一些改进。
The DMA engine of the DRAM-based SSD is customized accordingly by using a set of descriptors for an I/O request. A request descriptor represents a single mapping of {host memory segment, storage address segment, data size}. The Block Control Table (BCT) maintains 1,024 request descriptors, implying that the block I/O subsystem can dispatch up to 1,024 I/O requests at a time through the SSIO interface.
0x06 STM: Synchronously Merging Discontiguous I/O Requests
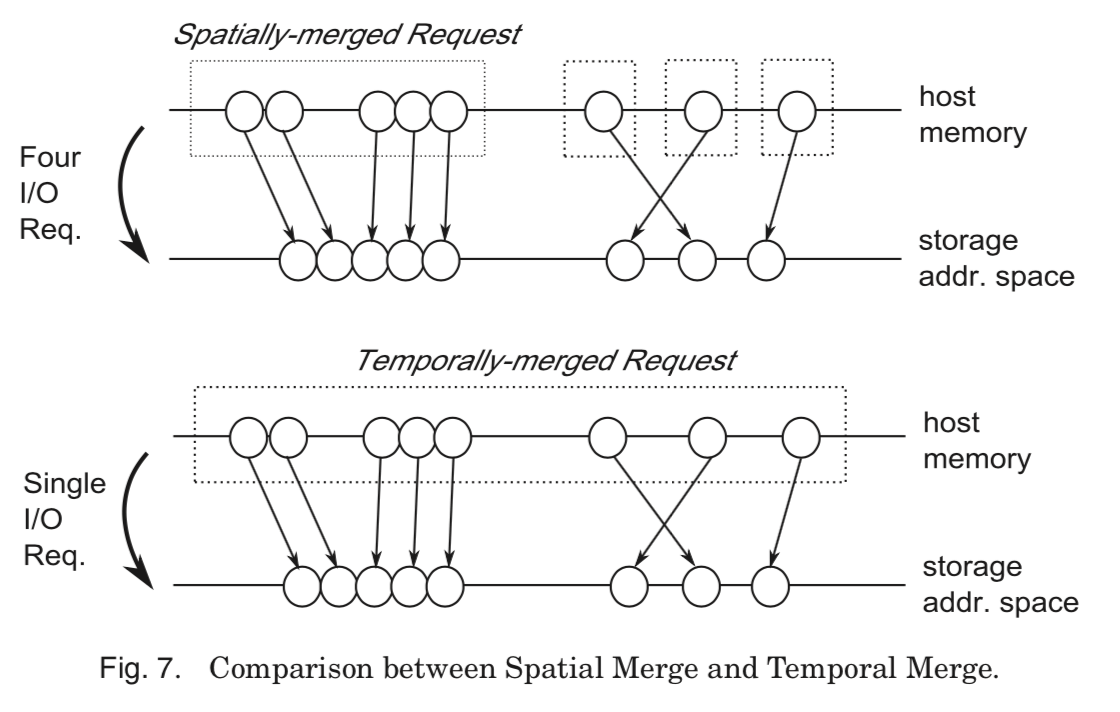
SSIO利用的是SSD的性能特点,不同于现在的Spatial Merge在空间的局部性上做合并操作,SSIO是在在时间上的局部性做合并的操作。这里就定义了Temporal Merge,即在一个时间窗口内的操作被合并到一起。利用这个特点,这里就实现了Synchronous Temporal Merge。
Figure 7 depicts the difference between Spatial Merge and Temporal Merge. When 5 contiguous and 3 discontiguous I/O requests enter the block I/O subsystem, Spatial Merge would combine them into one large I/O request and three small I/O requests, while Temporal Merge would build one I/O request with 8 request descriptors.
Synchronous Temporal Merge基于上面的O1 O2和O3。当一些IO请求并发地到达的时候,其中的一个被挑选为Winner,其它的请求则跟随Winner的操作路径。步骤如下:
(1) Choose a Winner among the CPU contexts by using an atomic operation.
(2) (Losers) Add an I/O request to the Winner’s queue and sleep in a task queue.
(3) (Winner) Perform Temporal Merge on the I/O requests in the queue.
(4) (Winner) Prepare DMA buffers, acquires an exclusive lock for a device, and dispatch the merged request through the SSIO interface.
(5) (Winner) Initiate DMA transfer and poll on the completion of the merged I/O request.
(6) (Winner) Release the resources assigned to all the requests in the merged I/O request.
(7) (Winner) Update flag variables to notify the Losers of the I/O completions.
利用时间上的局部性很好的提高了顺序写入的性能,解决了之前SyncPath存在的问题的同时了也利用好了SyncPath的优点。不过STM方式也存在缺点,一个是时间合并的在IO请求较少时难以发挥。第二个是随机读的性能明显低于随机写。
0x07 ATM: Asynchronously Merging Discontiguous I/O Requests
Asynchronous Temporal Merge可以看作是STM的一个改进版本,ATM基于上面的O1 O2和O4。不同于STM,它使用请求队列阻塞机制来积累IO请求。在将IO请求插入到IO调度队列之前,先将IO请求的kernel buffer映射到DMA buffer,这一步叫做queue bouncing。在收到一个unplugging(疏通)事件时,先Temporal Merge,然后一次性地将这些请求发送出去。在检测到IO操作完成的时候,使用每个CPU的软件中断,让之前的阻塞的CPU核心参与之后的工作。
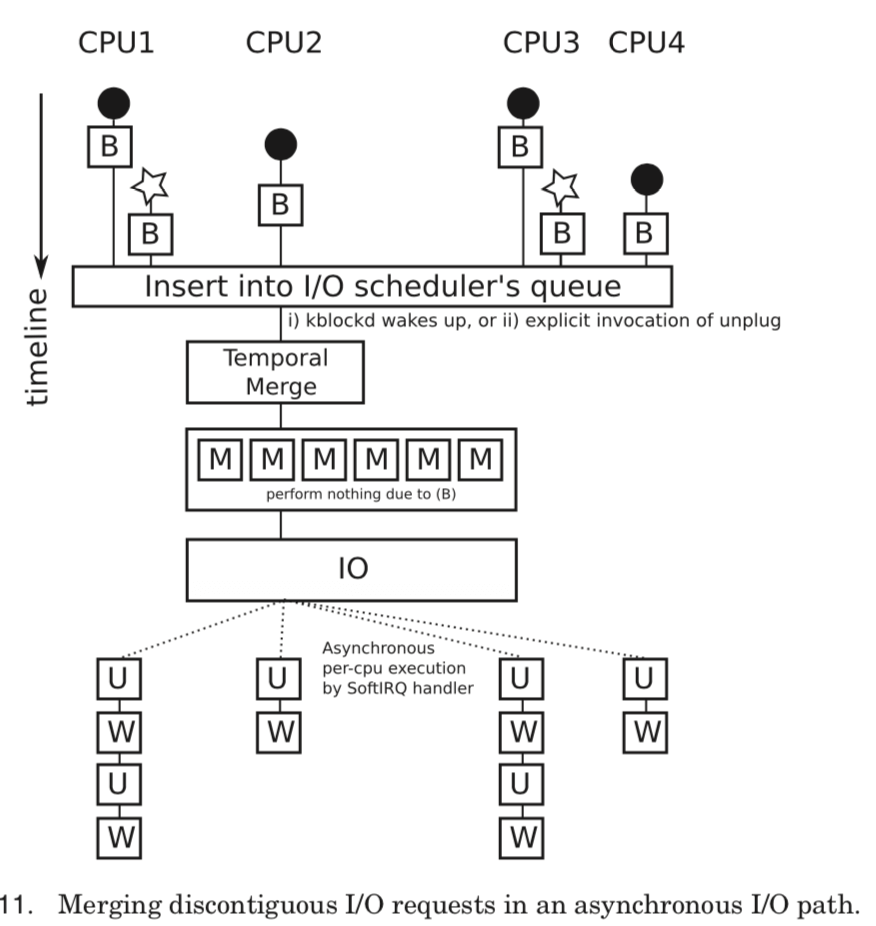
这样是不够的,还需要修改IO调度器的配置,默认的CFQ不能适应这里的情况,这里修改为NOOP之后才能发挥出来。这里涉及到2个参数的设置:unplug thresh 和 unplug delay。
ATM performs better than STM under write workloads; the improvements are 18% and 5% under the sequential write and the random write workload, respectively.
...
On the other hand, the sequential and the random read throughput by ATM are lower than those by STM, which is consistently observed across other Iozone settings. The reason is that ATM was unable to merge read requests because of the critical section design in the Linux storage stack;
ATM表现出比STM更加好的写性能,然而这里的读性能低于STM,原因在与ATM很好地合并读请求。
0x08 HTM: Hybrid Use of Synchronous and Asynchronous Temporal Merge
接下来的这种方式就是将STM和ATM组合,形成了HTM(Hybrid Temporal Merge)。STM和ATM分别对读和写友好,HTM这里就将latency-sensitive分配给STM处理, throughput-sensitive交给ATM处理。一般而言,将读请求定义为latency-sensitive,此外,将direct I/O请求也定义为latency-sensitive(不论是读还是写)。其它的就定义为throughput-sensitive。
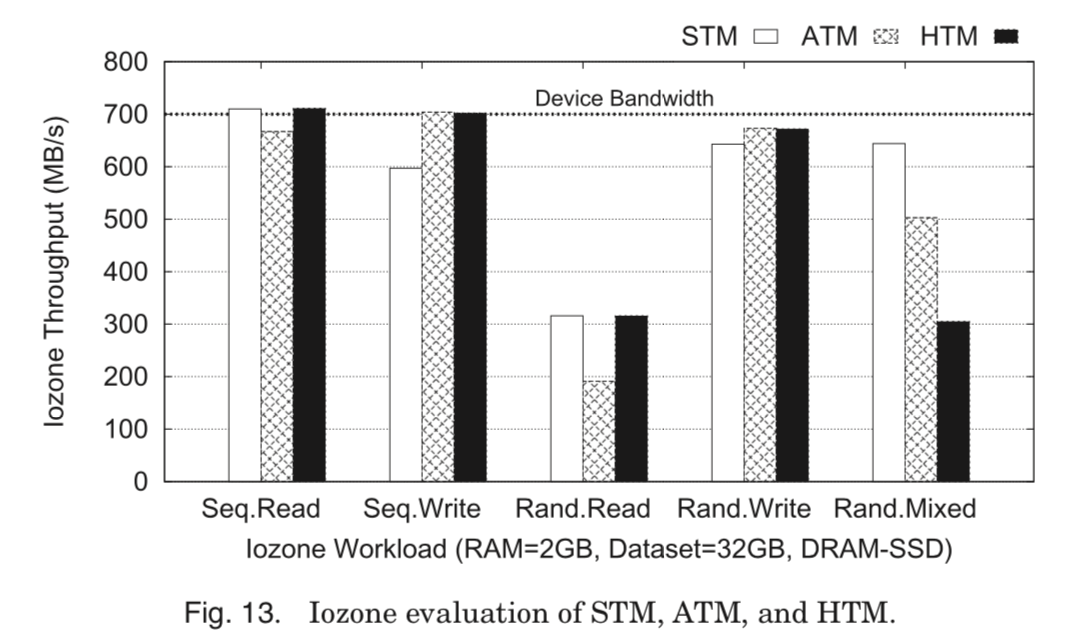
HTM achieves 100% of the device bandwidth under the sequential read and the sequential write workload, and 95% under the random write workload. Interestingly, HTM performs worse than both STM and ATM when read and write requests are mixed. Only 43% of the device bandwidth is exploited by HTM, which is comparable to the random read throughput.
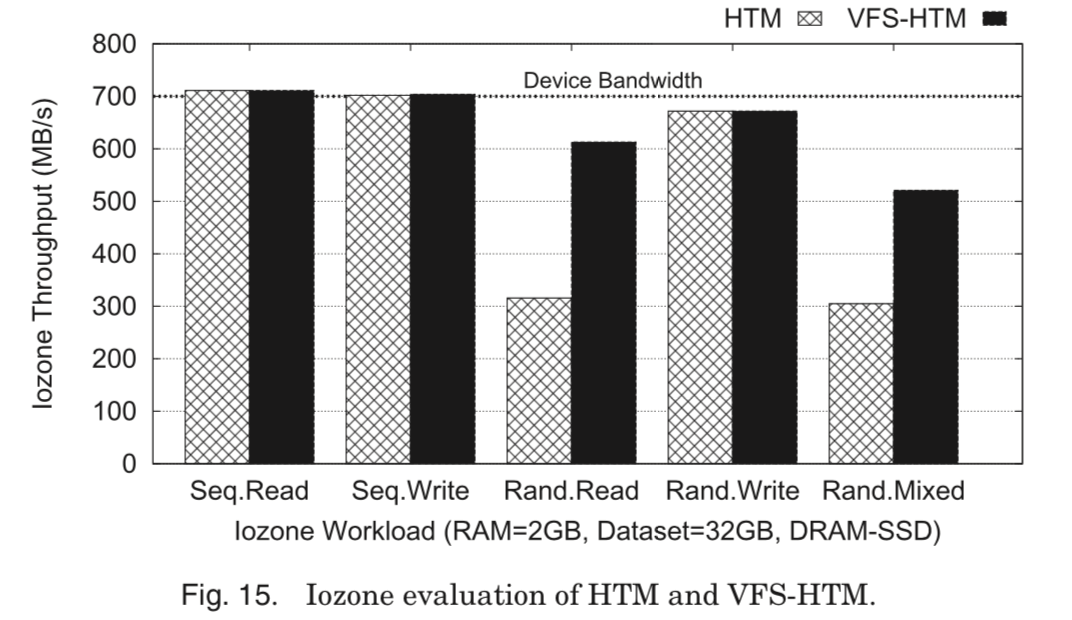
HTM对顺序读写、随机写有着非常好的性能。但是对于随机读和混合读写,性能比较差。这里认为主要是ATM和STM之间的相互干扰造成的。
0x09 VFS-HTM: Integrating the VFS Layer with HTM
在分析了上面随机读和混合读写的性能问题之后,发现问题出在Linux的VFS layer,主要原因在与不合适的预读区处理。将ra_pages(Linux 预读相关的数值,可参考相关资料)设置为0之后,产生的效果就是随机读取性能提高的,但是顺序读取性能下降了。 为了解决这个问题,这里就将VFS layer和 block I/O子系统集成,用一些策略去除不必要的操作。
It clones the I/O path in the VFS layer and directs a system call to execute the new I/O path, not requiring any modification to an OS. VFS-HTM disables the context lookup feature because block prefetching for a single-threaded sequential read workload is sufficient; even without block prefetching, Temporal Merge can build a large I/O request.
这样就很好地解决了之前的问题。
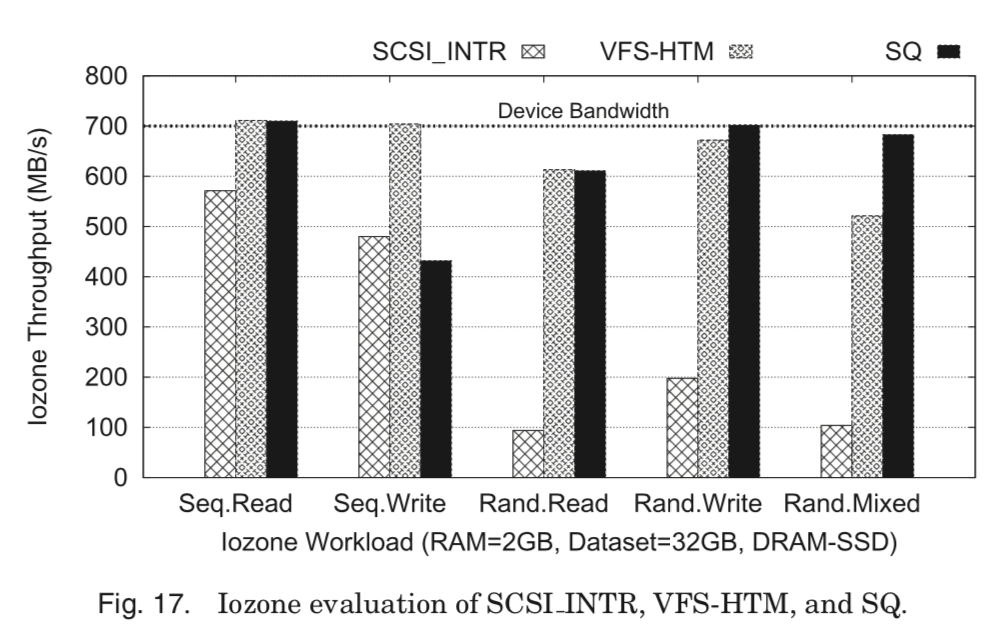
0x0A SQ: Using Double Buffering to Avoid Lock Contention
这里要解决的就是对请求队列上的竞争问题,这里加入了另外的一个队列,叫做Shadow Queue (SQ)。功能和使用方法类似于Double Buffering(所以标题就是Using Double Buffering to Avoid Lock Contention)。
The requests in the shadow queue are moved into a request queue only by a draining event. This enables the requests to remain in the request queue even when an unplugging event is triggered by the insertion of a read request. Consequently, the unplugging event ends up releasing the queuelock within 1∼2 microseconds.
这样的操作带来的优点就是随机读和混合读写的性能有所提高,但是降低了顺序写的性能。原因与文件系统(这里使用的是ext3)的日志相关。在不支持日志的文件系统如ext2上就没有见到这种情况。
In the case of ext3, the synchronous writes issued by a jour- naling thread prevent next requests from entering SQ, reducing the concurrency from which Temporal Merge benefits. Identifying such synchronous requests submitted by different file systems and minimizing the software latency of these is a remaining challenge in SQ.
这个问题没有完全解决。
0x0B 评估
总体性能:
论文中还有一大堆的其它的内容。
参考
- Yu, Y. J., Shin, D. I., Shin, W., Song, N. Y., Choi, J. W., Kim, H. S., Eom, H., Yeom, H. Y. 2014. Optimizing the block I/O subsystem for fast storage devices. ACM Trans. Comput. Syst. 32, 2, Article 6 (June 2014), 48 pages. DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.1145/2619092.
