PolarFS: An Ultra-low Latency and Failure Resilient Distributed File System for Shared Storage Cloud Database
0x00 引言
PolarFS是阿里巴巴为它推出的PolarDB设计的文件系统,作为控制面和数据面分离中的一部分。PolarFS在使用新技术时还是挺激进的,在一个商业产品上面一下子就搞这么多东西,将 network stack, IO stack都做到了user-space,使用3D XPoint ,RDMA, NVMe SSD, and SPDK 等新的技术。
0x01 基本架构
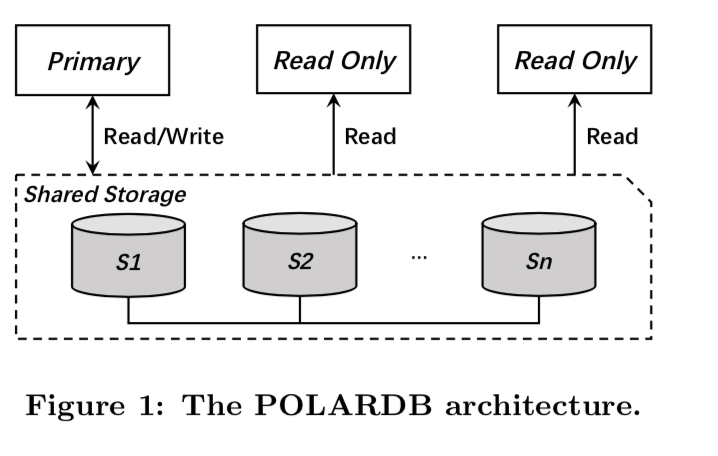
PolarFS主要分为2层,Storage Layer负责管理storage nodes的磁盘资源, 为每个数据库实例提供数据卷(volume)。File system layer 支持在这些volume上实现文件管理,同时还负责访问文件元数据时的互斥和同步。Polar的组件分为一下几个部分:
- libpfs,一个实现在用户空间的类似POSIX的文件系统接口;
- Polar-Switch,运行在计算结点上,将IO请求发送给ChunkServer;
- ChunkServers,允许在storage结点上,处理IO请求;
- PolarCtrl,PolarCtrl 时控制面,有一组master组成,同时在每一个storage结点上部署了一个agent;
0x02 组件
File System Layer

这些接口以一个libpfs 库提供给使用者。
Storage Layer
在PolarDB中一个数据库实例的大小为10GB – 100TB,这个被称为一个volmue。一个volmue被划分为chunk,发布在一组ChunkServers 上面,一个chunk只会保存在一个磁盘上面,一个chunk会被复制3份,保存在不同的ChunkServer上面。ChunkServer会使用迁移数据的形式解决一些热点的问题。 Chunk的大小被设置为了10GB,这么尺寸的Chunk显著的减小了元数据的大小,有利于其它组件处理(比如PolarSwitch)。一个chunk会被继续分为block,一个block的大小为64KB。
A 10 GB chunk contains 163,840 data blocks. The mapping table of chunk’s LBA (Logical Block Address, the linear address range from 0 to 10 GB) to blocks are stored locally in ChunkServer, together with the bitmap of free blocks on each disk. The mapping table of a single chunk occupies 640 KB memory, which is quite small and can be cached in memory of the ChunkServer.
PolarSwitch
PolarSwitch作为一个守护进程,责任就是根据数据库的IO请求,将这些请求发送给合适的ChunkServer。对于可能跨越多个chunk的请求,需要将其拆分为sub-requests。PolarSwitch通过PalrCtrl获取chunk的一些信息。所有的数据副本中,只有leader才会处理IO请求。
Leadership changes in the consensus group are also synchronized and cached in PolarSwitch’s local cache. If response timeout happens, PolarSwitch would keep retrying with exponential backoff while detecting whether leader election happens, switch to new leader and retransmit immediately if it does.
ChunkServer
ChunkServer 使用了NVMe SSD 来保存数据,负责chunk的读写等的功能,同时使用为了保证原子性和持久性,使用了WAL,这里PolarFS就直接使用了非易失性内存来加速WAL:
ChunkServer uses a piece of fixed size 3D XPoint SSD buffer as a write cache for WAL, logs are preferred to be placed in 3D XPoint buffer. If the buffer is full, ChunkServer will try to recycle dated logs. If there is still not enough space in 3D XPoint buffer, logs are written into NVMe SSD instead. Chunk blocks are always written into NVMe SSD.
ChunkServers会将这些IO请求通过使用ParallelRaft 来复制到一个 consensus group。
PolarCtrl
PolarCtrl为PolarFS的控制面,它负责结点管理, 卷管理,资源分配, 元数据同步,监控等等一大堆的功能。此外,还最近ChunkServer的负载情况,必要的时候迁移数据来尝试解决负载的问题。
As a control plane, PolarCtrl is not on the critical I/O path, its service continuity can be provided using traditional high availability techniques. Even during the short interval between PolarCtrl’s crash and recovery, I/O flows in PolarFS would not likely be affected due to the cached meta- data on PolarSwith and the self-management of ChunkServer.
0x03 I/O Execution Model
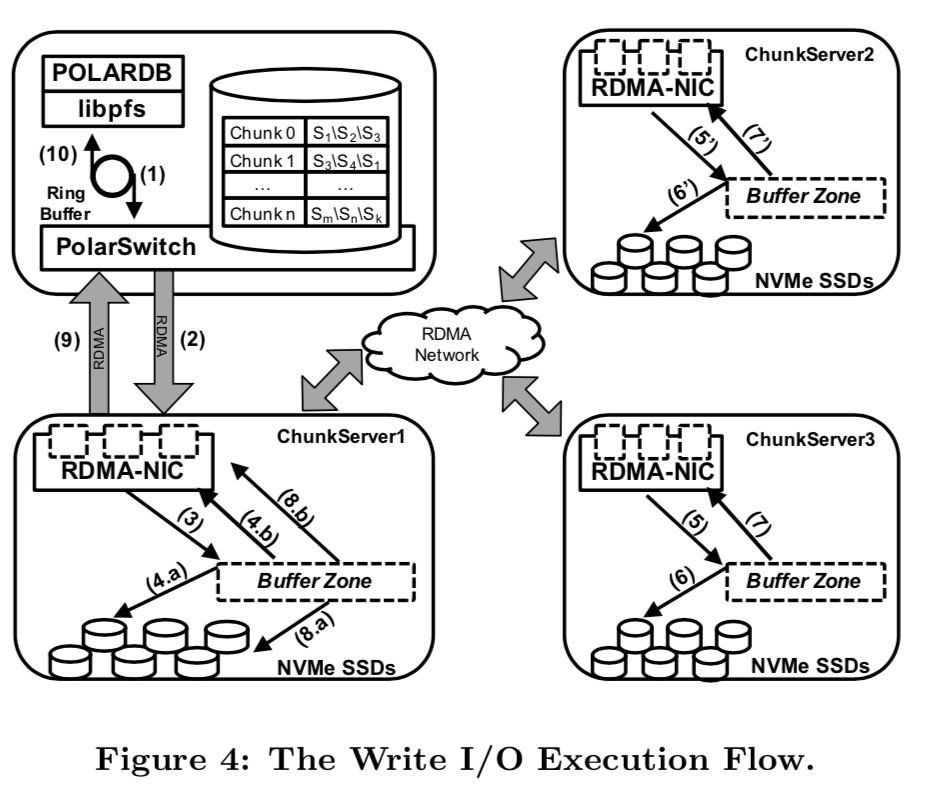
上面的图基本表示了PolarFS的写操作的流程。为了实现超低的延时和高的吞吐,这里直接使用了RDMA。RDMA有两类操作,Send/Recv 和 Read/Write,各自有不同的特点(可参考相关论文),已经有不少的key-value系统使用RDMA,并探究了Send/Recv 和 Read/Write对这些系统的性能影响。这里PolarFS混合使用了Send/Recv 和 Read/Write,对于小的请求,直接使用Send/Recv,对于大的数据的请求,先使用Send/Recv同步一些元数据,然后使用Read/Write来传输数据。
PolarFS uses a hybrid of Send/Recv and Read/Write verbs. Small payloads are transferred by Send/Recv verbs directly. For a large chunk of data or a batch of data, nodes negotiate about the destination memory address on the remote node using Send/Recv verbs, and then complete the actual data transmission over Read/Write verbs. PolarFS elimi- nates context switches by polling the CQ in user space instead of relying on interrupts.
写操作步骤分析:
- POLARDB将一个写操作的IO请求发送给PolarSwitch和libpfs的环形缓冲区;
- PolarSwitch发现这些亲戚之后,将这些请求发送给对应的chunk’s leader 结点;
- RDMA NIC在接受到一个IO请求的时候,将这些请求放入预先准备的一个buffer中,然后想请求队列里面添加一项;一个IO轮询线程发现了这些请求队列里面的项之后,立即开始处理这个请求;
- 请求被写入到通过使用SPDK写入到log里面,然后通过RDMA将发送给副本。这两部都是异步操作,真正的数据传输时同时进行的;
- 副本接受到这些请求之后,也重复类似leader的动作,最后也将这些请求放到了一个请求队列里面;
- 副本上面的IO轮询发现了请求之后,就执行写操作;
- 副本写操作完成之后,通过一个回调通知leader;
- leader在收到了超过一半的回复之后,leader执行写操作;
- leader写操作完成之后,通过RDMA通知PolarSwitch写操作完成;
- PolarSwitch记录这个写操作已经完成,同时通知client(这里就是数据库).
读操作就简单多了,leader结点处理就行。
Read I/O requests are (more simply) processed by leader alone. In ChunkServer there is a submodule named IoScheduler which is responsible to arbitrate the order of disk I/O operations issued by concurrent I/O requests to execute on the ChunkServer. IoScheduler guarantees that a read operation can always retrieve the latest committed data.
0x04 Consistency Model
Paper这一个部分将的是关于ParallelRaft的一些问题,这里就不具体讨论这个了,只关心FS本身。
0x05 FS Layer Implementation
这里讨论的就是如何实现类似文件系统结构的功能:
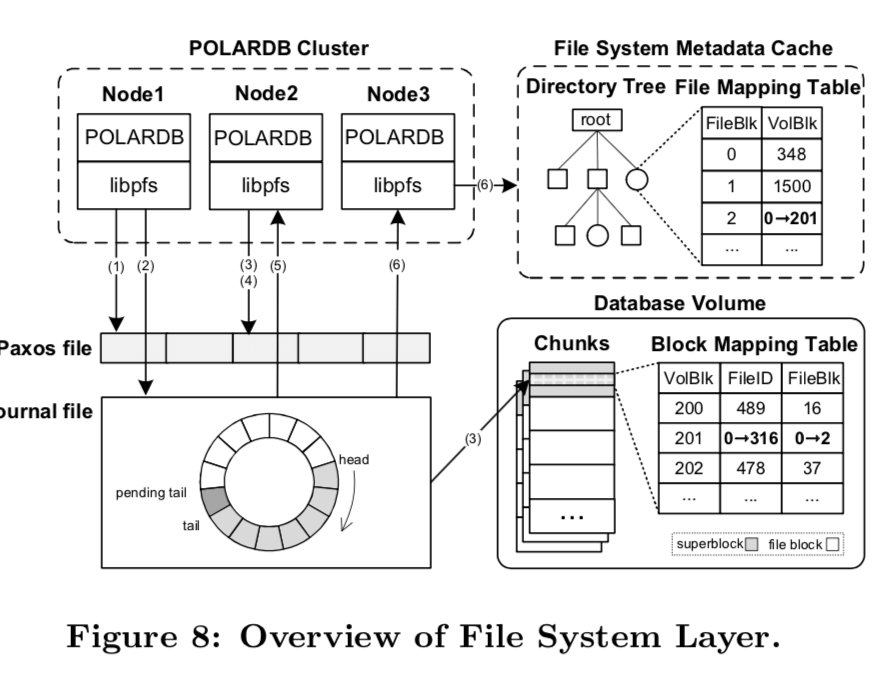
具体如何实现的参见论文。
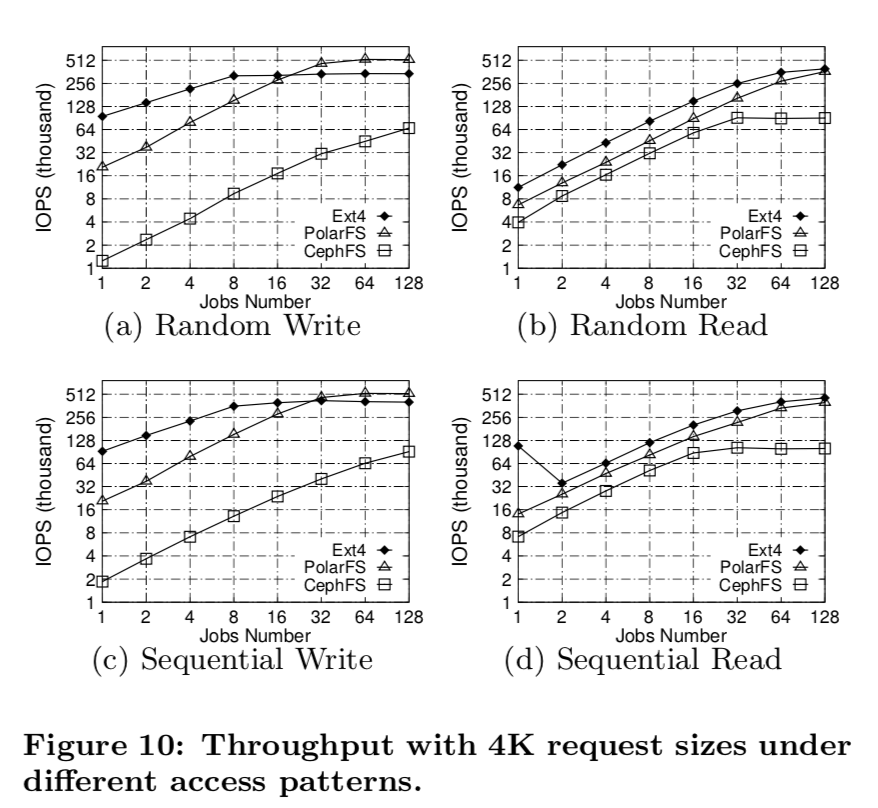
0x06 评估
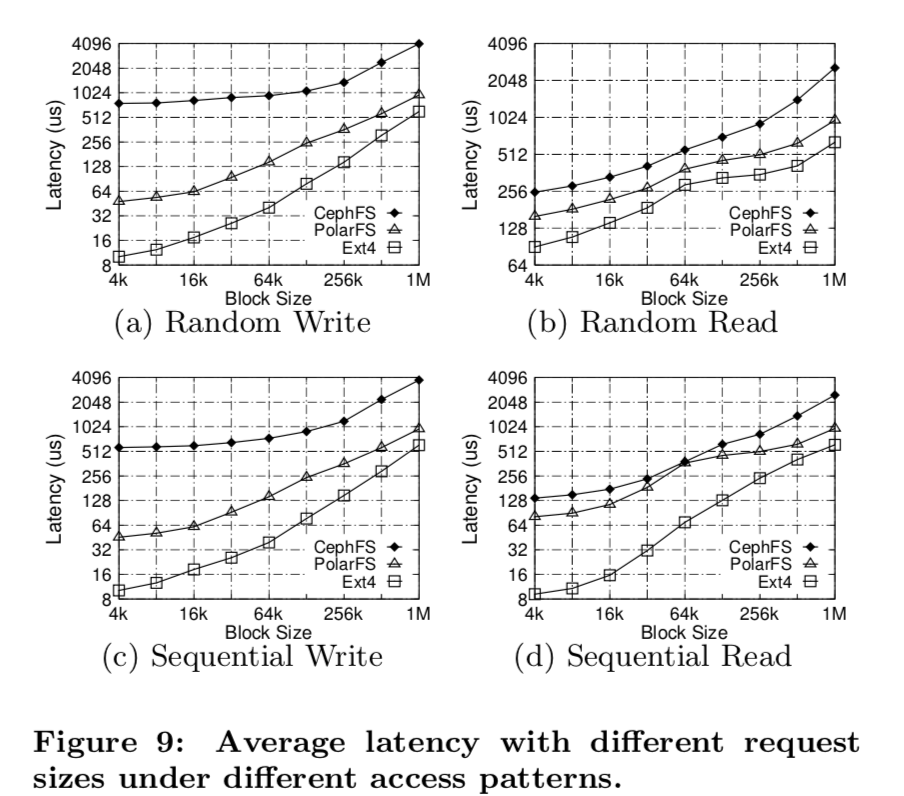
PolarFS虽然说是一个分布式的文件系统,不过由于使用了RDMA,估计还是只能在一个数据中心内部的分布式,与类似GFS的跨地域分布不同。不够他们面向的对象也不一样。文章还提了利用RDMA加速Paxos之类算法的研究,比如APUS,估计是想反正现在都用上RDMA,不如利用它再来加速一下子??瞎猜。延时:
吞吐:
参考
- Wei Cao, Zhenjun Liu, Peng Wang, Sen Chen, Caifeng Zhu, Song Zheng, Yuhui Wang, Guoqing Ma. PolarFS: An Ultra-low La- tency and Failure Resilient Distributed File System for Shared Storage Cloud Database. PVLDB, 11 (12): 1849 - 1862, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.14778/3229863.3229872
