Write-Optimized and High-Performance Hashing Index Scheme for Persistent Memory
0x00 引言
这篇OSDI 2018会议(就是今天开的, 2018-10-08)上的一篇关于Persistent Memory上hash index设计的文章[1],是Path Hashing[2]的后续,也是华科在OSDI上发表的第一篇文章???这篇论文讨论了Path Hashing没有解决的问题,其中一个就是resize如何处理。
To cost-efficiently resize this hash table, level hashing leverages an in- place resizing scheme that only needs to rehash 1/3 of buckets instead of the entire table, thus significantly reducing the number of rehashed buckets and improving the resizing performance. Experimental results demon- strate that level hashing achieves 1.4×−3.0× speedup for insertions, 1.2×−2.1× speedup for updates, and over 4.3× speedup for resizing, while maintaining high search and deletion performance, compared with state-of-the-art hashing schemes.
这里关于NVM之类的特点都不提了,可参考相关资料。这里只关注Lelvel Hasing的设计以及如何解决现在的问题。
0x01 基本思路
基本结构:
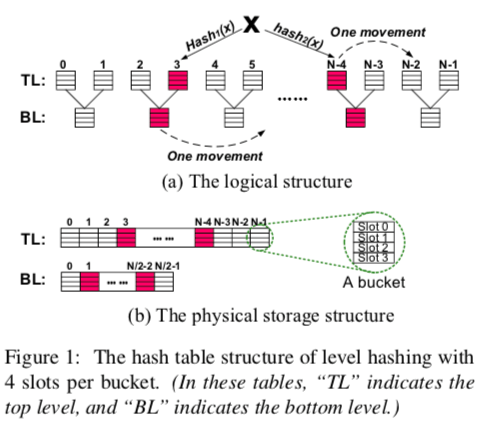
Multiple Slots per Bucket
每一个Hash table由2层组成,Top Level和Bottom Level,其中Top Level的大小是Bottom Level的2倍。每一个bucket里面有4个slot,这个做法和常见的一个cuckoo hash的设计差不多。
Two Hash Locations for Each Key
使用2个hash函数,这样一个Level里面有两个候选的buckets,加上Bottom里面的,就是4个,不过Bottom Level里面的一个bucket是被Top Level里面的2个bucket共用的。
Sharing-based Two-level Structure
Bottom Level里面的一个bucket是被top level里面的2个bucket共用的,这里的思想和Path Hashing里面的是一样的。不够这里的Bottom Level是上次rehash之前的Top Level。
At Most One Movement for Each Successful Insertion
这里选择可用的solt利用了cuckoo hash的思路,但是为了解决cuckoo hash级联的数据驱逐问题。这里最多允许最多移动一个项。选择的步骤如下:
- 利用两个hash函数计算出的2个位置,检测使用优空的slot;
- 有,则选择;没有,则检查是否通过移动一个元素就能解决;
- 能,就移动,然后选择空出来的位置;不能,则用同样的方法查看Bottom Level;
- 都不能,进行resize操作;
选择位置的计算方式:
Lt 1 = hash1 (K)%N, Lt 2 = hash2 (K)%N (1)
Lb 1 = hash1 (K)%(N/2), Lb 2 = hash2 (K)%(N/2) (2)
0x02 Cost-efficient In-place Resizing
相对于读来说,NVM写的成本比较高,为了减少resize中的写操作,这里一个创新的地方就是每次resize就创建一个新的更加大的Top Level,之前的Top Level成为新的Bottom Level,只需要移动旧的Bottom Level里面的数据就可以了,这样只要移动1/3的数据。当resize是减小size时,反过来就可以了。
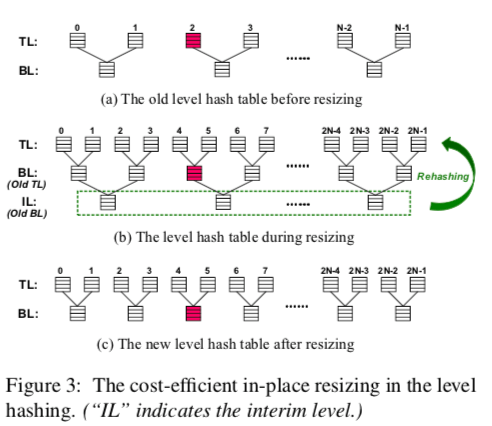
Resize这里还有2个优化:
-
为了解决2个Level数据发布不均导致的影响负载因子的问题,这里使用了一种叫做bottom-to-top movement (B2T) 的方法。具体方法是在插入操作的时候,如果所有的buckets都是满的,那么就尝试将Bottom Level两个候选的位置里面的项尝试移动到Top Level,只有在这些都不能移动的时候才resize。
By performing the B2T scheme, the items between top and bottom levels are redistributed, thus improving the maximum load factor. The red line in Figure 4 shows the load factors when the resizings occur via using the B2T scheme. -
在resize之后,由于现在的大部分数据在Bottom Level,而查找的时候总是后查找Bottom Level,这样就导致了性能的降低。这里解决方法是dynamic search scheme,通过Top Level和Bottom Level里面的项的数量来决定先查哪一个。
Thus after resizing, the items in the bottom level are more than those in the top level and hence we first probe the bottom level, thus improving the search performance.
0x03 Low-overhead Consistency Guarantee
为了标示一个slot是否为空,这里使用了一个标志位.
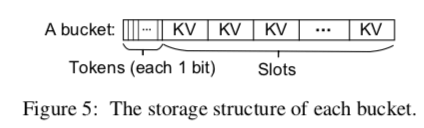
为了保证操作的一致性(关于NVM一致性的特点,可用查阅相关资料),这里提出了一种叫做log-free consistency guarantee schemes和opportunistic log-free guarantee scheme:
To reduce the overhead of guaranteeing consistency in level hashing, we propose log-free consistency guarantee schemes for deletion, insertion, and resizing operations, and an opportunistic log-free guarantee scheme for update operation, by leveraging the tokens to be performed in the atomic-write manner.
Log-free Deletion
只需要改变solt的对应的标志位即可;
since the item becomes valid until the token is set to ‘1’. If a system failure occurs during writing the item, this item may be partially written but invalid since the current token is ‘0’ and this slot is still available. Hence, the hash table is in a consistent state when system failures occur.
Log-free Insertion
没有项移动的情况下,先写入数据,然后改变标志位。然后通过MFENCE来保证数据更新到NVM上面了。在有数据项移动的情况下,先拷贝要移动的数据到可选的位置,然后将这个位置(被移动对象目前的位置)的标志位置为 1,然后将原来的位置置为0,然后执行插入操作。
If a system failure occurs after changing the token of slot-alt before changing the token of slot-cur, the hash table contains two duplicate key-value items, which however does not impact on the data consistency. It is because when searching this key-value item, the returned value is always correct whichever one of the two items is queried.
Log-free Resizing
也是基于标志位的一个操作:
we first copy the key-value item of slotold into slotnew, and then modifies the token of slotnew from ‘0’ to ‘1’ and finally modifies the token of slotold from ‘1’ to ‘0’. The ordering of the three steps is ensured via MFENCEs.
这里要处理的一个问题就是在一些crash的情况下,可能导致已经rehash的项没有被标记为删除,这里只需要检查是否已经存在相同的项即可。
Opportunistic Log-free Update
为了避免使用log保证一致性,这里使用了Opportunistic Log-free Update的方式,具体是:
- 一个bucket里面是否存在可使用的空slot,就使用类似先插入,然后同时更改标志位即可,因为同一个bucket里面的标志位在一起,可以一起修改;
- 如果没有,就使用log。
When updating an existing key-value item, if the updated item has two copies in the hash table, we first delete one and then update the other.
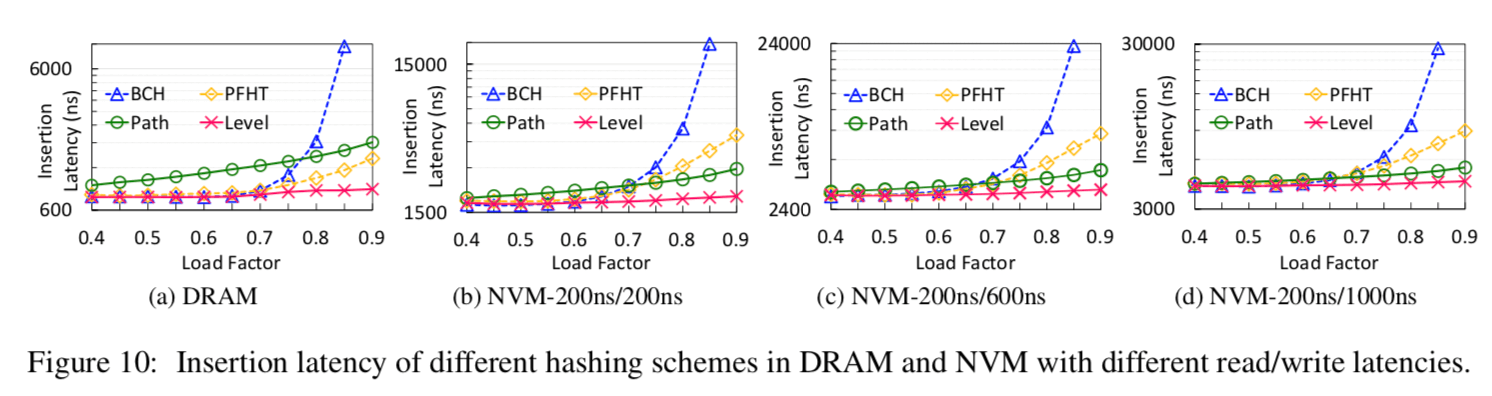
0x04 评估
详细数据查看论文.
参考
- Write-Optimized and High-Performance Hashing Index Scheme for Persistent Memory, OSDI 2018.
- A Write-Friendly and Cache-Optimized Hashing Scheme for Non-Volatile Memory Systems,TPDS 2018.
