VL2: A Scalable and Flexible Data Center Network
0x00 引言
VL2是微软设计的一个数据中心网络的架构。它的设计由下面的几个特点:
(1) flat addressing to allow service instances to be placed anywhere in the network,
(2) Valiant Load Balancing to spread traffic uniformly across network paths, and
(3) end-system based address resolution to scale to large server
0x01 分析
在讨论VL2的具体设计之前,Paper先总结了几个数据中心网络的几个特点(Paper中的观点以及数据):
-
流量分析;1. 在一个数据中心内出数据中心的流量和近数据中心的流量的比例大约为4:1;2. 尽管数据发布会跨越数据中心,但是数据密集型的计算和通信通常不会去跨越数据中心,因为长距离通信的成本;3. 数据中心内对带宽需求的增长超过了对终端的;4. 网络是计算的瓶颈。
-
流分析,这里主要讨论了数据中心内一个通信流的一些特点:
- 大部分的流传输数据的大小小于100MB,但是另外,大部分的数据都是流大小在100MB到1GB的流传输的;
- 并发的流数量,对于单台的机器,几乎没有同时由超过100个流。超过半数的时间是10条左右;
-
通信矩阵分析;两个基本特点:这些机器之间相互的通信没有什么明显的模式,也就是带有很强的随机性,没有什么规律;2. 不仅仅如此,而且一些通信模型也是很不稳定了,经常变化;
-
故障特性;大部分故障发生的规模都比较小,而且能够在短时间内得到解决,也存在一些需要很长时间才能解决的问题,
most failures are small in size (e.g., 50% of network device failures involve < 4 devices and 95% of network device failures involve < 20 devices) while large correlated failures are rare (e.g., the largest correlated failure involved 217 switches). However, downtimes can be significant: 95% of failures are resolved in 10 min, 98% in < 1 hr, 99.6% in< 1 day,but 0.09% last > 10 days.
0x02 基本架构
VL2的几个设计原则:
* Randomizing to Cope with Volatility;
* Building on proven networking technology;
* Separating names from locators;
* Embracing End Systems;
横向拓展的拓扑
这里和常见的系统也比较类型。ToR交换机和两个聚合交换机交换机相连。在Paper中的图(也就是下面这幅图)并没有表示出来。下面的图表示的是一个折叠的版本,可以理解为一个对称的图形从中间的对称轴对称之后的样子。但是诸多的中继交换机和聚合交换机的连接使得形成了大量的可行的路径。任何一个中继交换机失效只会损失1/n的双向的带宽。在VL2中,假设聚合交换机有D-A 个端口和中继交换机有DI 个端口,那么每层间的容量是 DI*DA/2 在乘以链路容量。另外,VL2利用了交换机的交换机到交换机的端口快于服务器到交换机的端口的速度,
Our current design uses 1G server links and 10G switch links, and the next design point will probably be 10G server links with 40G switch links. By leveraging this gap, we reduce the number of cables required to implement the Clos (as compared with a fat-tree), and we simplify the task of spreading load over the links
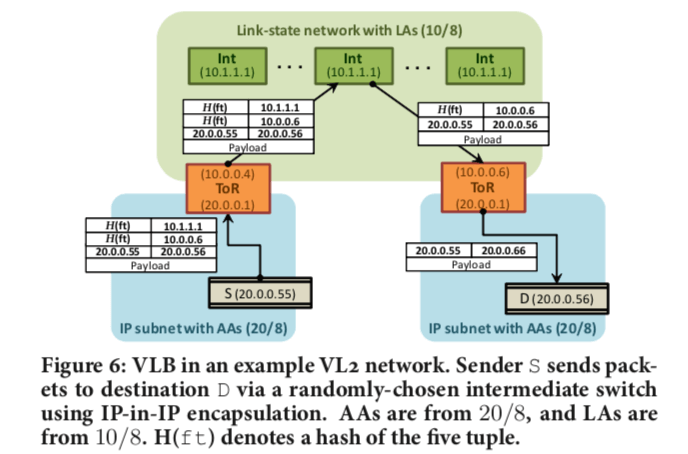
VL2的寻址和路由
-
地址解析和包转发,VL2使用两类IP地址,一类是交换机等网络的基础设施设备使用的IP地址,被称为 location-specific IP addresses (LAs),而主机使用另外类型的IP地址,被称为application-specific IP addresses (AAs)。与论文[2]中的不同,在VL2中,IP地址和主机的位置是没有什么关系的。VL使用目录系统来保存名字和位置之间映射关系。
The VL2 agent running on the host intercepts this ARP request and converts it to a unicast query to the VL2 directory system. The directory system answers the query with the LA of the ToR to which packets should be tunneled. The VL2 agent caches this mapping from AA to LA addresses, similar to a host’s ARP cache, such that subsequent communication need not entail a directory lookup. -
使用随机的路径。VL2使用Valiant Load Balancing (VLB)和ECMP两种机制来分发流量。基于流而不是包。使用随机的路径到达中继交换机之后,中继交换机使用随机的路径转发包到ToR交换机。
-
VL2 Directory System,VL2的主机的信息保存在一个VL2 Directory System中。VL2的IP和具体位置分离也主要依赖于Directory System。Directory System对性能和可靠性的要求都很高。一个基本的设计,
Our design consists of (1) a modest number (50-100 servers for 100K servers) of read-optimized, replicated directory servers that cache AA-to-LA mappings and handle queries from VL2 agents, and (2) a small number (5-10 servers) of write-optimized, asynchronous replicated state machine (RSM) servers that offer a strongly consistent, reliable store of AA-to-LA mappings.
0x03 评估
具体可以参看[1].
PortLand: A Scalable Fault-Tolerant Layer 2 Data Center Network Fabric
0x10 引言
和VL2一样,PortLand也是发表在啊SIGCOMM‘09上面关于数据中心网络的一篇Paper。PortLand也是以FlatTree为基础,认为现在的 layer 2 和 layer 3 存在诸多的问题: 缺乏可伸缩性、管理困难、通信不灵活或对虚拟机迁移的支持有限等。Paper中认为,数据中心网络的基本拓扑和增长模式一般都是可知的,基于这样的观察,Paper中提出一种 layer 2的面向数据中心网络环境的路由和转发协议PortLand,
0x11 基本思路
PortLand中引入的Fabric Manager和Positional Pseudo MAC Addresses两个概念是PortLand的两个核心内容,
-
Fabric Manager,FM是一个逻辑上中心化的管理器,维护网络的一些信息比如拓扑结构等。负责处理ARP解析、容错和多播等的功能。PortLand使用中心化的控制器是协议简单性和系统健壮性之间的一个权衡。
-
Positional Pseudo MAC Addresses,每一个主机赋予一个Pseudo MAC(PMAC),这个地址里面编码了主机在拓扑中的位置信息,例如,在同一个Pod里面的主角的PMAC地址的前缀是相同的。主机可以通过ARP请求来获取一个主机的PMAC信息,数据包的转发也是根据PMAC地址来的。出口交换机会对PMAC改写为AMAC。对一直连的主机,边缘交换机会为它们分为一个PMAC地址,格式是pod.position.port.vmid.
a 48-bit PMAC of the form pod.position.port.vmid to all directly connected hosts, where pod (16 bits) reflects the pod number of the edge switch, position (8 bits) is its position in the pod, and port (8 bits) is the switch-local view of the port number the host is connected to. We use vmid (16 bits) to multiplex multiple virtual machines on the same physical machine (or physical hosts on the other side of a bridge).下面的图是一个映射关系的实例。一个建立映射关系的例子如下:1. 当一台如空交换机观察到一个之前没有见过的MAC地址的时候,入口交换机根据规则为其分配一个PMAC地址,并将它的IP、AMAC和PMAC地址的映射关系保存,并且将这些信息发送给Fabric Manager;2. Fabric Manager接受到这些信息,保存起来,用于以后使用。这里需要对交换机的软件进行改动,以便于执行如 PMAC ↔ AMAC之类的动作。PortLand也使用了OpenFlow这样技术。与目的主机直接连接的交换机需要将 PMAC 地址重写为目的主机的 AMAC 地址,这样PMAC的机制对于主机来说就是透明的。当发生虚拟机迁移时,Fabric Manager会更新迁移后的新映射,并向虚拟机的原始连接的交换机发送更新报文。从而实现对虚拟机迁移的支持。
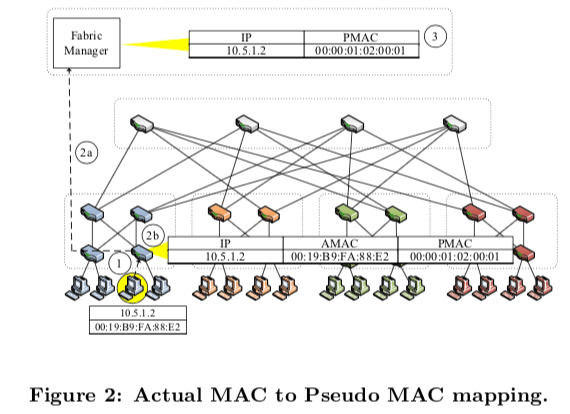
0x12 另外的几个部分
在做了上面的一些修改之后,这个网络架构还有另外的一些东西额需要改动,
-
基于代理的ARP,现在ARP的操作得依赖于Fabric Manager来完成,
-
分布式位置发现,PortLand使用拓扑相关的地址来实现转发和路由,这样可以实现高效率的操作。但是这些信息也不是固定不变了。为了应对这些原因的变化,PortLand使用了 location discovery协议,关于这个协议的具体信息可以参看[1].
-
可验证的无环路转发,简而言之就是PortLand使用的转发协议可以实现无环路的操作。
-
可容错的路由,与前面的一些控制一下样,对于一些出来故障无法正常使用的线路的路由容错页依赖与Fabric Manager来处理,
1. The detecting switch informs the fabric manager about the failure in step 2. The fabric manager maintains a logical fault matrix with per-link connectivity information for the entire topology and updates it with the new information in step 3. Finally, in step 4, the fabric manager informs all affected switches of the failure, which then individually recalculate their forwarding tables based on the new version of the topology.
0x13 评估
这里具体可以参看[3].
ElasticTree: Saving Energy in Data Center Networks
0x20 引言
这篇Paper是在[2]的基础上面的一些优化的工作,主要的优化方向就是节能。[2]中的设计好处就是提供了主机之间大量的可行的线路。但是很多时候是没有必要的。在用不到的时候可以关闭一些交换机可以达到节能的目的,在需要的时候在打开。
0x21 ElasticTree
ElasticTree本质上还是从FlatTree上面优化而来的,下面是一个ElasticTree与一般的数据中心网络架构和FlatTree的对比,
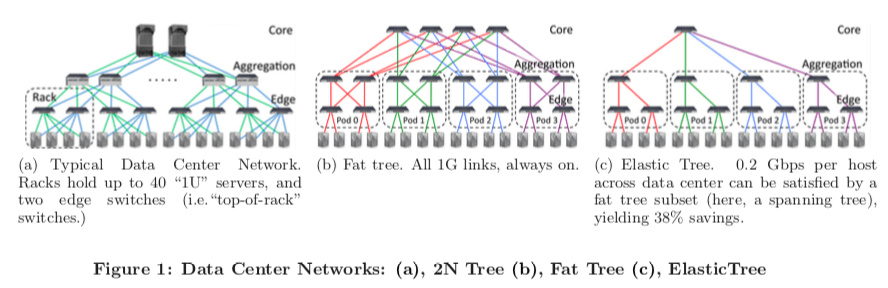
ElasticTree主要由3个部分组成:优化器,路由和电量控制。
-
优化器;优化器就是找到能够满足当前需要的一个FlatTree的一个子集,这个实际上就是一个多物网络流问题,Paper中对比使用了3中方法:
-
Formal Model,这个方法就是将问题当中是一个多物网络流问题来处理。对于多物网络流问题,使用的方法是线性规划的方法。ElasticTree使用Formal Model输出的就是原网络拓扑的一个子集,加上应采取的路由的一些信息。
-
Greedy Bin-Packing,贪心算法找出的不一定是最优的解,但是这个算法简单很多。
-
Topology-aware Heuristic,最后一种利用了启发式的方法,虽然不能使用多样的环境,但是ElasticTree本身只是面向FlatTree的优化,这里也可以满足要求。它的输入也和前面两种方法的不一样,只需要Port Counters的信息即可。它的基本思路就是从FlatTree的拓扑出发
The number of required switches in the aggregation layer is then equal to the number of links required to support the traffic of the most active source above or below (whichever is higher), assuming flows are perfectly divisible... A similar observa- tion holds between each pod and the core, and the exact subset computation is described in more detail in §5. One can think of the topology-aware heuristic as a cron job for that network, providing periodic input to any fat tree routing algorithm.
-
| Type | Quality | Scalability | Input | Topo |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Formal | Optimal | Low | Traffic Matrix | Any |
| Greedy | Good | Medium | Traffic Matrix | Any |
| Topo-Aware | OK | High | Port Counters | Fat Tree |
- 控制软件;在计算出来了结构之后,控制软件使用的是OpenFlow和NOX。作者使用OpenFlow来验证优化器给出的解决方案, 方法是直接将计算的应用程序级流路由集(application-level flow routes)推送到每个交换机, 然后生成流量,。在实时原型中, OpenFlow 还提供Traffic Matrix 、Port Counters和端口电源控制等的功能。而NOX就是一个控制平台。
0x22 节能分析和性能
这部分可以参看[4]
参考
- VL2: A Scalable and Flexible Data Center Network, SIGCOMM’09.
- A Scalable, Commodity Data Center Network Architecture, SIGCOMM’08.
- PortLand: A Scalable Fault-Tolerant Layer 2 Data Center Network Fabric, SIGCOMM’09.
- ElasticTree: Saving Energy in Data Center Networks, NSDI’10.
