There Is More Consensus in Egalitarian Parliaments
0x00 引言
这篇Paper是关于Paxos算法的一个优化策略。这篇提出了一个Paxos的一种变体EPaxos。EPaxos侧重点在消除稳定/指定的Leader/Master的设计。EPaxos的基本思路就是为每一个客户端提交的Command指定一个Leader,同时处理好这样设计的冲突和依赖的关系,并加上了一些设计和实现上面的优化,
0x01 基本设计
EPaxos的设定和一般的Paxos没有很大的区别,在副本数量为2F+1的情况下,能够容忍F个副本的故障。在EPaxos中,存在两种不同的动作,一个是Committing另外一个是Executing,且它们的顺序不一定要相同(可以乱序提交)。另外在EPaxos中的一个重要的概念是Command Interference,两个Commands存在Command Interference即当两个的顺序必须按照一定的顺序进行,负责会得到不同的结果。EPaxos可以保证存在Command Interference的两个Commands C1 C2在客户端有着怎么样的顺序关系,在每个副本上面的执行的顺序也一定会是这样的顺序关系。deps是一个副本的列表,它(们)包含了与一个Command存在Interference的Command(s),而seq则是序列号,用于打破循环依赖。
-
EPaxos中每个副本有一个唯一的ID,和常见的算法一样,为了处理新配置,EPaxos中也使用了epoch。所以在EPaxos中Ballot Number的格式是epoch.b.R,b是一个递增的自然数,R为副本ID。
-
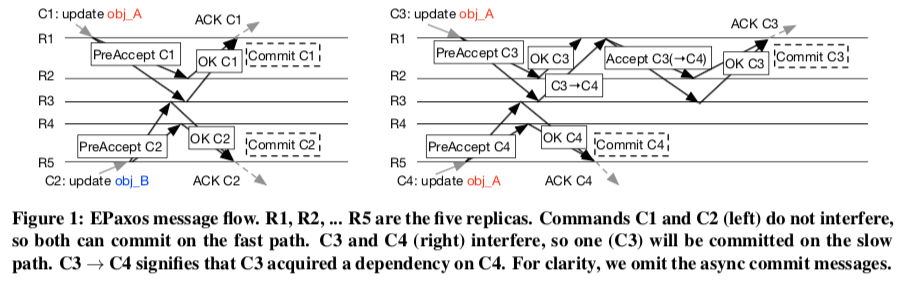
在上面的图1是一个例子。两个并发的更新操作更新不同的对象,不存在Interference,且各自选择了不同的Command Leader,按照EPaxos的Fast Path执行完毕。而两个并发的更新操作更新相同的对象,存在Interference,也选择了不同的Command Leader,则会产生冲突,则执行的是EPaxos中Slow Path。
-
基本的EPaxos中,一个Fast Path的Quorum为2F个副本,可以优化为$F + \lfloor (F+1)/2 \rfloor$。在Slow Path的处理中,一个Quorum的大小总是为F+1。
-
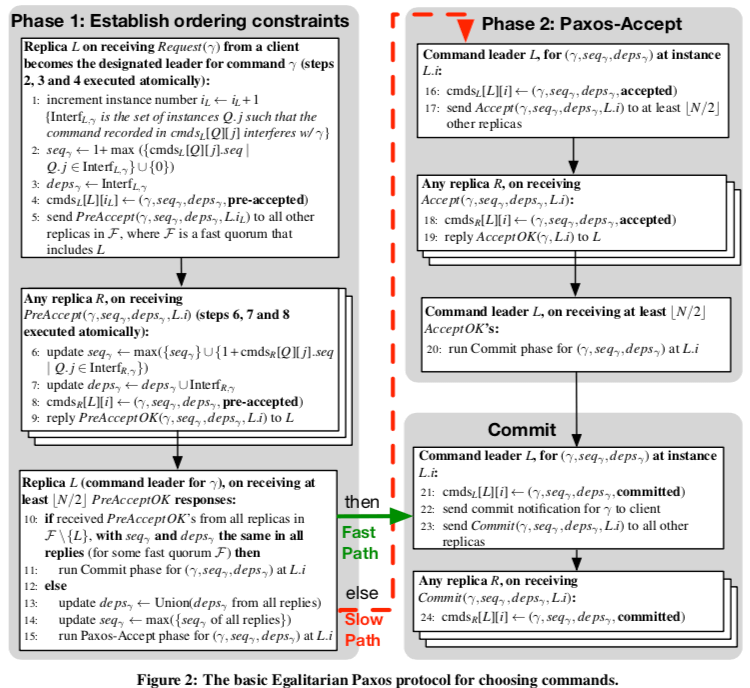
正常操作的时候一个Command Leader接受到它为Leader的操作之后,向至少为一个Fast Path的Quorum发送PreAccept消息。副本在接受到这个消息之后,更新这个Command的deps和seq属性,然后回复Command Leader。Command Leader在收到了足够数量的回复,且更新之后的属性相同(另外的副本回复的属性可能已经被更新),则可以提交这个操作。如果收到的属性存在不同,则选择一个有相同属性的多数副本的Quorum的属性,然后通知多数的副本接受这个属性,这一步操作也要等待多数副本的回复。之后Command Leader就可以回复客户端并发送异步的Commit的消息。
-
执行算法,执行的时候主要就要构建一个依赖关系拓扑,提交一个Command依赖中的没有提交的(EPaxos需要的依赖的处理在实际应用的时候估计会很困难,估计也会造成比较大的Overhead),
1. Wait for R.i to be committed(or run Explicit Prepare to force it); 2. Build γ’s dependency graph by adding γ and all commands in instances from γ’s dependency list as nodes, with directed edges from γ to these nodes, repeating this process recursively for all of γ’s dependencies (starting with step 1); 3. Find the strongly connected components, sort them topologically; 4. In inverse topological order, for each strongly conected component, do: 4.1 Sort all commands in the strongly connected component by their sequence number; 4.2 Execute every un-executed command in increasing sequence number order, marking them executed. -
EPaxos中的恢复操作的逻辑比较复杂,这里也设计到Fast Path的Quorum可以优化到$F + \lfloor (F+1)/2 \rfloor$。另外这个优化在这篇Paper中没有详细地证明,而是在另外的一篇Thesis中。

EPaxos算法中还会有很多的内容和细节。
0x02 评估
这里的具体信息可以参看[1],
SDPaxos: Building Efficient Semi-Decentralized Geo-replicated State Machines
0x10 引言
这篇Paper也是Paxos的一个优化变体。相比前面的EPaxos来说,SDPaxos(Semi-Decentralized Paxos)采用了一种更加折中的设计,而不是EPaxos使用的完全舍弃指定Leader(而是每一个Command一个Leader)的比较激进的做法。SDPaxos的基本思路就是将顺序和复制中分开,
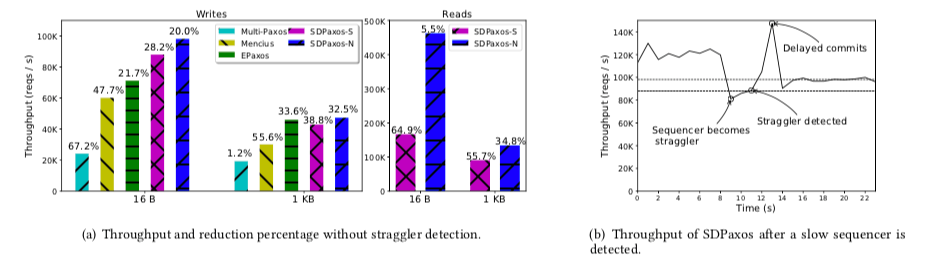
We implemented a prototype of SDPaxos, and compared its performance with typical single-leader (Multi-Paxos) and multi-leader (Mencius, EPaxos) protocols. Our experiment results demonstrate that SDPaxos achieves: (1) 1.6× the throughput of Mencius with a straggler, (2) stable performance under different contention degrees and 1.7× the throughput of EPaxos even with a low contention rate of 5%, (3) 6.1× the throughput of Multi-Paxos without straggler or contention, (4) 4.6× the throughput of writes when performing reads, and (5) up to 61% and 99% lower wide-area latency of writes and reads than other protocols.
0x11 基本设计
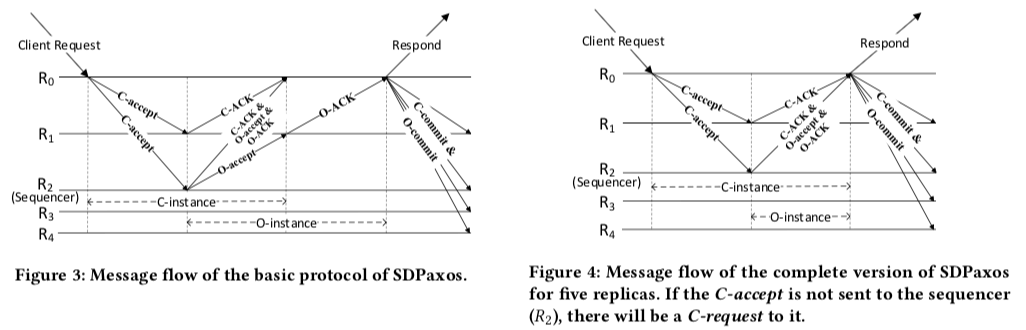
SDPaxos的基本思路是复制和定序分离,复制使用的是类似EPaxos中的方法,每次客户端的请求都是指定一个Command Leader来处理,但是处理请求顺序的是一个中心化的Sequencer节点处理。这个看起来就是一个更折中的方法。由于定序带来的开销比复制小的多,这个定序的中心节点的负载也会小于Multi-Paxos/Raft中的Leader/Master。下面的图是一个SDPaxos执行流程的示例,
-
在SDPaxos中,Instance的定义和一般的没有什么不同。不过这里它分为了C-instance和O-instance,分别对应复制和顺序。在图3中,一个副本R0在收到了一个客户端的请求之后,它就成为这个客户端的这个请求的Command Leader,选择一个C-instance,然后使用C-accept操作将这个请求复制到其它的副本。同时,R2作为Sequencer在收到了这个信息是的时候,R2提出这个请求的O-instance,然后发送O-accept给其它的副本(带有全局slot的信息)。其它的副本在收到了C-instance和O-instance之正常情况下分别回复C-ACK和O-ACK给R0,在收到了多数的副本的两个ACK回复之后,既可广播C-commit和O-commit信息。
# C-phase Replica Rn on receiving a client request for command α : sendC-accept(n,i,α,bali)to at least a majority if the C-accept is not sent to the sequencer then send C-request(n, i) to the sequencer increment the C-instance counter i Any replica R on accepting C-accept(n,i,α,bali): sendC-ACK(n,i,α,bali)toRn Rn on receiving C-ACKs from a majority of replicas: commit Cni and broadcast C-commit(n,i,α,bali) # O-phase Sequencer Rm on receiving C-accept(n,i,α,bali) or C-request(n, i) from Rn: if i ≥ number of O-instances for Rn in sequencer’s assignment log then send O-accept(j, n, balj ) to at least a majority including Rn increment the O-instance counter j Any replica R on accepting O-accept(j, n, balj ): send O-ACK(j, n, balj ) to Rn -
SDPaxos定义一个Command为ready状态指的是可以安全地回复客户端。在三个or超过五个副本的系统中,就是常用的等到多数的O-ACKs之后就可以执行提交O-instance的操作。当这个副本已经提交了这个C-instance Cni(及这个副本的第i个C-intance)且至少有i个O-instance的时候就可以返回客户端,
# Ready condition for three or more than five replicas if Rn receives O-ACKs from a majority of replicas then commit Oj and broadcast O-commit(j,n,balj) if Rn has committed Cni and at least i O-instances for Rn then respond to client在三个副本的时候,如果Command Leader和Sequencer不是同一个副本,那么它们两个就可以构成一个多数,正常情况下SDPaxos运行只要个RTT就可以Commit,因为Sequencer返回Command Leader的时候就带有O-instance的信息。而如果是多个,则多于1 RTT才能Commit。
-
SDPaxos针对5个副本的情况做了优化,使得5副本的情况下也可以在1RTT就可以Commit。这里C-instance的操作依然是没有变的,必须多数确认(C-ACKs)。而对于O-instance,从前面3副本的情况下可以看出,如果Sequencer和Command Leader不是同一个,则只能保证O-instance被2个副本确认的情况下才能满足1RTT的要求。SDPaxos的优化就是值等待Sequencer的O-accept返回,加上自己就是两个。但是如果这两个故障的时候,就可能无法恢复全部的信息,导致不能满足容错2个的要求。所以这里必须使用额外的条件,及这里要保证在O-commit的时候前面的已经提交,这里的前提是C-instance这个时候必然是在多数节点上保存了的,故障了两个节点数据不会丢,主要是要恢复顺序信息。另外还配合了SDPaxos恢复的算法。
# Ready condition for five replicas if Rn is the sequencer then commit Oj and broadcast O-commit(j, n, balj ) on receiving O-ACKs from a majority of replicas if Rn has committed Cni ∧ any Ok with k ≤ j (Oj is the ith O-instance for Rn) is accepted by a majority then respond to client else commit Oj and broadcast O-commit(j, n, balj ) on receiving the O-accept from the sequencer if Rn has committed Cni ∧ any Ok withk ≤ j (Oj is the ith O-instance for Rn ) is accepted by itself and the sequencer then respond to client
下面的图表示的节点上面的O-instance。故障两个之后中间的空洞(只会是是1个)可以根据其它节点O-instance及C-instance的信息恢复,
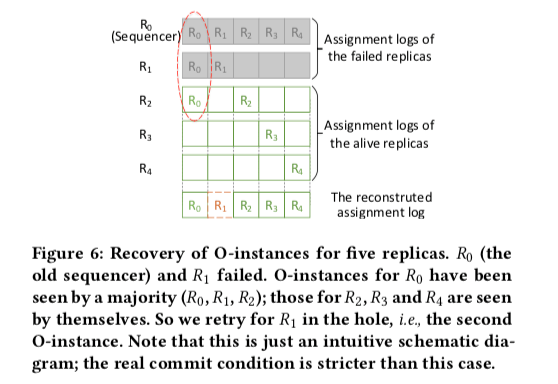
恢复
SDPaxos为了处理Sequencer的故障,通用引入了View Number(个epoch一个意思)的概念,照样会在一个选举的过程。除了5个副本的恢复外,SDPaxos的恢复过程没有特别的地方。由于SDPaxos对5个副本情况下的优化,Rm代表在这个故障中非Sequencer的那一个。恢复的过程需要从存活的版本的C-instacnes中找到Rm编号最大的一个,Sequencer找到合适O-instance,然后“补全”对应hole。
We let each voter replica report in its vote the largest-numbered C-instance of each replica it has accepted, then the new sequencer takes the maximum for Rm. C[m] implies the maximum number of Rm’s possibly ready commands, because the C-instance of any ready command of Rm must have been seen by one of the voters. Therefore, the sequencer should propose Rm’s ID in the empty O-instances until there are at least C[m] O-instances for Rm.
一个基本的伪代码,
# Recovery of O-instances
Input: C[m]: number of C-instances of Rm accepted by the majority voters;
O[m]: number of O-instances for Rm (Rm is the replica other than the old sequencer and the majority voters in five-replica groups)
if N==5 then repeat
propose Rm’s ID in the first empty O-instance
O[m] ← O[m] + 1
until O[m] ≥ C[m] ∧ there is no empty O-instance preceding the C[m]th one for Rm
foreach empty O-instance between non-empty ones do
propose no-cl
0x12 优化
SDPaxos另外的一些优化的策略,
-
消息合并,在一些情况下可以将C-instance和O-instance合并发送,减少传输包的数量;
-
掉队检测,可以Sequencer能否按序处理请求来检测Sequencer的状态,在判断Sequencer状态不是很好时可以启动ViewChang。
... in which replicas estimate the sequencer’s healthiness according to whether the sequencer can satisfy their requirements for ordering. Specifically, each replica counts the number of O-accepts for itself received from the sequencer every 500 ms. If the throughput is less than 50% of its requirement for at least 3 times, it considers the sequencer as a straggler. Then it asks others whether they make the same judgment, and if so, it will start a view change to replace the old sequencer. -
Sequencer分组,在一些具体的相同中,比如KVS相同可以根据一致性Hash来划分Sequencer。
-
O-instance批量处理,如题,
Another simple yet effective optimization is batching: a replica’s n commands can be batched in one global slot, so the number of O-instances will be divided by n. Even a small value of n like 2 or 3 can significantly reduce the load of O-instances.
0x13 评估
这里的具体信息可以参看[1],
参考
- There Is More Consensus in Egalitarian Parliaments, SOSP’13.
- SDPaxos: Building Efficient Semi-Decentralized Geo-replicated State Machines. SoCC’18.
