Write-Optimized Dynamic Hashing for Persistent Memory
0x00 引言
这篇Paper中的idea可以说是旧idea在新的环境中的一个应用。在NVM上提出了一种针对这个环境优化的Cacheline-Conscious Extendible Hashing(CCEH),它的主要的对比对象是之前的Path Hashing和Level Hashing,
CCEH effectively adapts its size as needed while guaranteeing failure-atomicity and that the tail latency of CCEH is up to 3.4× and 8× shorter than that of the state-of-the-art Level Hashing and Path Hashing, respectively.
0x01 基本思路
Extendible Hash Table
Extendible Hash Table(EHT)是一种可以实现rehashing操作为增量式的一个设计,在EHT中Hash寻址是一个两层式的。第一层为 global depth,由于寻址Directory,而第二层为local depath,用于寻址具体的Bucket。不同的Directory使用的寻址的bit数量可以是不同的,这样的话有可能不同的Direvtory是指向同样的Bucket,而rehashing操作的时候多数的时候就是某个Bucket的操作,比如图中的B2满了之后,将其中的一个的local depth变为2,如果开辟一个新的Bucket,拷贝出需要转移的数据即可。当出现locol depth大于globel depth的时候,需要处理globel depth。
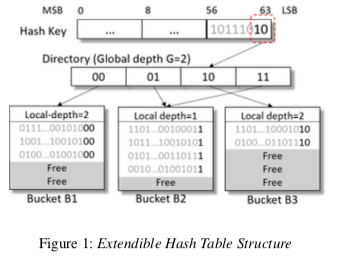
而在Cacheline-Conscious Extendible Hashing中,为了平衡Directory和Bucket的大小,以及加快在Bucket中的查找,EECH使用了一种三层的寻址方式,在之前的两层之间加入了一层的Segment。
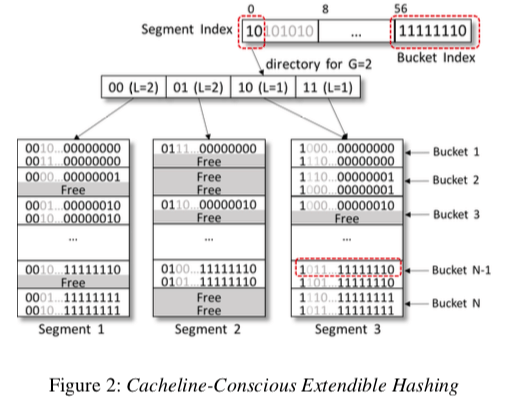
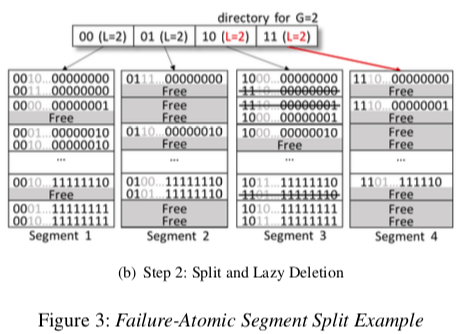
在开始的时候,可能有多个的Directory指向同一个的Segment。 CCEH接下来要处理的问题就是如果解决Segment分裂的问题。这里设计到多步的操作,要注意操作的顺序。首先是要开辟一个新的Segment,将需要转移到这个Segment的数据拷贝过来。如下图所示。下一步是对Segment 4的操作,先改变对指针和local depth,然后在是改变原来Directory中的local depth。CCEH这样的设计有可能导致一些内存的浪费,也就是说一些Segment比较满,但是另外的一些还是很“空”。这里可以采用一些类似线性探测和Cuckoo Hashing的方法,不过这些方法又可能到来一些其它的缺点,要小心使用。另外,在Segment Split之后,旧Segment里面被转移出去的数据可以使用Lazy的方式去删除。Rehashing操作不仅仅是对Hash Table的一个扩张,也可能是收缩。在EECH中收缩的操作可扩张的操作的逻辑上是一样的,只是一些操作执行的顺序是相反的。
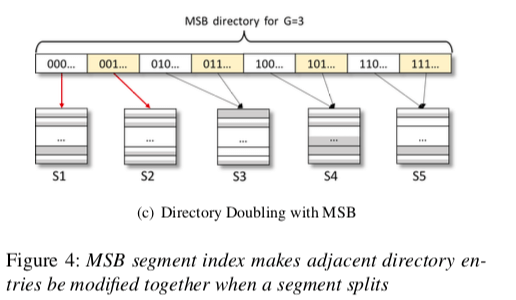
另外,在Segment的数量增长到一定程度的时候,就需要对Directory进行扩张的操作。在Directory扩张操作的时候,由于要保证数据的持久化,使用的clfush会带来不小的开销,
... overhead of clflush. Note that when we index 16 million records using 16 KByte segments, it takes 555 usec and 631 usec to double the directory when we use LSB and MSB respectively. However, clflush() takes about 2 msec (3∼4× higher). In conclusion, LSB does not help reduce the overhead of enlarging the directory size unlike the directory file on disks.
而这里使用MSB的方式寻址Segment就有利于优化这个的性能。主要源于使用MSB会使Segment相邻的特性,可以合并一些clflush的操作。
恢复
为NVM设计的数据结构一般都要考虑一个恢复的操作。恢复操作使用的一个方法是利用8bytes原子些的特性,将一个8bytes数据作为标志。对于想Segment中写入一个超过8bytes的数据,可以先写入数据,在安排一个mfence,然后写入一个8bytes的值作为提交的标志,之后在使用clflush指令即可。这样后面的恢复操作可以发现部分写入的不合格的数据,
Even if the cacheline is evicted from the CPU cache, partially written records will be ignored because the key is not valid for the segment, i.e., the MSB bits are not a valid segment index. This is the same situation as when our lazy deletion considers a slot with any invalid MSB segment index as free space.
另外的方法也利用了使用MSB寻址的方法,
When a system crashes, we visit directory entries as in binary tree traversal and check their consistency, which can be checked by making use of G and L. That is, we use the fact that, as we see in Figure 3, if G is larger than L then the directory buddies must point to the same segment, while if G and L are equal, then each must point to different segments.
并发
EECH的并发的操作主要还是留哦那个rwlock。对于Segment,也可以使用一些lock-free的方法[1].
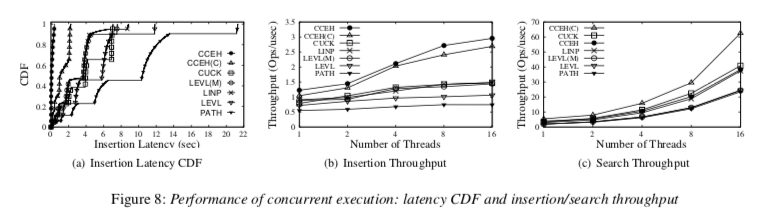
0x04 评估
这里的具体信息可以参看[1],
Reaping the performance of fast NVM storage with uDepot
0x10 引言
这篇为FAST ’19上面一篇利用NVMe等的高速存储设备设计Key-Value Store的Paper。这篇Paper主要就是两个方面的内容,第一个就是为高速IO设备设计的task run-time system,另外一个就是一个在高速IO设备上面一个优化的bitcask模型的一个实现,
... Indeed, uDepot vastly outperforms SSD-optimized stores by up to ×14.7 but also matches the performance of a DRAM-backed memcached server allowing it to be used as a Memcache replacement to dramatically reduce cost.
0x11 TRT
TRT是uDepot为高速IO设备设计的一个task run-time system。它基于目前存在的这样的一个问题:首先现在的一些处理网络请求的框架比如libevent之类的不能够很好地处理要同时处理网络和磁盘IO的环境,比如要同时处理 epoll wait,加上io getevents或者SDPK中的completion processing call。TRT就是一个类似于coroutine的一个实现。一般情况情况下,TRT开启一组线程,一般每个核心一个。其中一个任务就是作为一个类似coroutine来处理,拥有自己的栈。TRT在每个线程上面执行一个用户空间内部的调度器。TRT同样使用一般coroutine切换使用的方法。另外,TRT为了将可能地减少跨核心的通信,这里将同步原语分为了核内和核间的版本。一般情况下,一个task只会在一个核心上面运行。TRT作为一个uDept的异步IO的基础,
TRT currently supports four backends: Linux AIO, SPDK (single device and RAID-0 multi-device configurations), and Epoll, with backends for RDMA and DPDK in development. Each backend provides a low-level interface that allows tasks to issue requests and wait for results, and, built on top of that, a high-level interface for writing code resembling its syn- chronous counterpart.
0x12 uDepot
uDepot这里使用的设备空间管理的方式是将存储设备的空间分为segment,比如为1GB大小。日志式写入,配合它的垃圾回收算法,这里在另外的一篇论文里面[3].
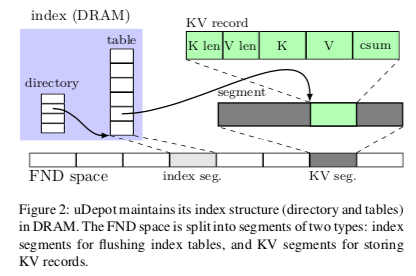
Index data structure
uDepot在整体的索引结构上面使用了一种两层式的索引结构。第一层为directory,第二层为实际的table,
uDepot使用了一种Hopscotch Hash Table的变体来实现索引结构。这里主要做了两点改进,1. 使用2的次幂个数据项,每一个Hopscotch中的组(这里称之为neighborhood)类似于一个组相连的方式,这里的思路其实和很多的Cuckoo Hash Table的设计比较像。这里的neighborhood的索引会被保存到Hash Entry中,这样也方便了在索引resize操作的。Resize的操作不需要在重新取出Key重新计算。2. 不使用一个neighborhood一个bitmap标记的设计,也不使用链表。另外,在同步的设计上面,这里使用的是常见的分段锁的方法,
... an array of locks for concurrency control. These locks protect different regions (lock regions) of the hash table, with a region being strictly larger than the neighborhood size (8192 entries by default). A lock is acquired based on the neighborhood’s region; if a neighborhood spans two regions, a second lock is acquired in order.
这里索引结构中的Hash Entry的设计也比较精细,一个Entry的大小只有64bit。分为4个部分,
struct HashEntry {
uint64 t neigh_off :5; // neighborhood offset
uint64 t key_fp_tag :8; // fingerprint MSBs
uint64 t kv_size:11; // KV size (grains)
uint64 t pba:40; // storage addr. (grains)
};
后面两者均是以grain的粒度保存数据,比如40bit的pba字段,在grain大小为4KB的时候,可以寻找4PB的空间。在neighborhood使用了5bit时候。内存中的索引使用了cityhash产生的64bit hash值的35bit(fingerprint),这个35bit被分为了两个部分,一个是27bit的index值和一个8bit的key_fp_tag。这样的话在uDepot中的一个Hash Table最多有2^27个Entry。通过在Hash Table中的索引信息,加上在neighborhood便宜的信息,加上key_fp_tag就能够得到完成的fingerprint,
... 8 bits for the tag (key fp tag), and 5 bits to allow for 32 entries in a neighborhood (neigh off). Hence, if an entry has location λ in the table, then its neighborhood index is λ−neigh off, and its fingerprint is key fp tag : (λ−neigh off).
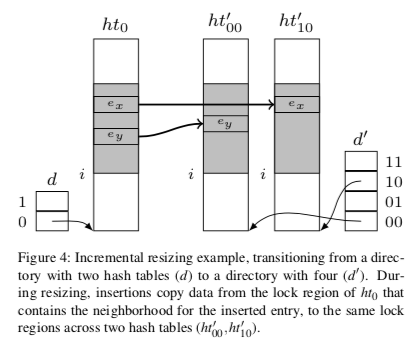
也就是,这里也和前面一些Paper使用的节约内存的方法一样,没有完整地将key保存到内存中,这样查找 or 添加操作的时候,有时候得去访问此篇确认Key是完全一致的。在Resize的操作上面,uDepot这里也是仔细优化了。如下图所示,这里的resize操作中,Directroy会被爱每次2倍增长。Resize操作的时候搬运数据采用一种增量式的方式,这个和其它很多Hash Table的设计一样。这里的索引结构的设计类似于一种简化了的Extensible Hash Table的设计。这里索引结构的设计第二层的大小这样的设计在数据量比较小的时候会存在一些浪费。同样地,uDepot这样也会讲索引结构周期性的将索引结构持久化到硬盘上面,这里和一般的Bitcask的做法没有很大的区别。
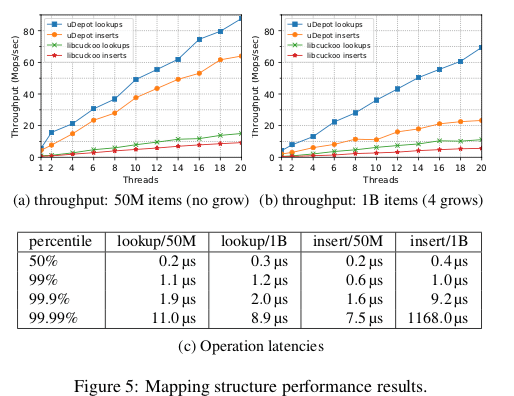
0x13 评估
这里的详细信息可以参看[2]。uDepot在一个有26个NVMe设备的机器上面跑出的性能很惊人,
参考
- Write-Optimized Dynamic Hashing for Persistent Memory, FAST ‘19.
- Reaping the performance of fast NVM storage with uDepot, FAST ‘19.
- Elevating commodity storage with the SALSA host translation layer, arXiv.
