Accordion: Better Memory Organization for LSM Key-Value Stores
0x00 基本思路
Accordion对LSM-Tree的改进思路与前面的[2]的思路很相似,也是将内存中主要的数据结构分为可变的部分和不可变的部分,可变的部分和一般的LSM-Tree的实现没有什么不同。在一般的LSM-Tree中,一个Memtable转变为immutable的时候不会对这个memtable的结构做什么样的变化,而在Accordion中,会将其转变为一种更加节省内存的结构,称之为flat segemnt。一个Active Segment在达到一定的大小之后转变为Flat Segment,这个操作称之为in-memory flush。内存中的Flat Segment也会做合并的操作,称之为in-memory compaction。这个思路应用到Rocksdb上面也可能是一个很好的优化。
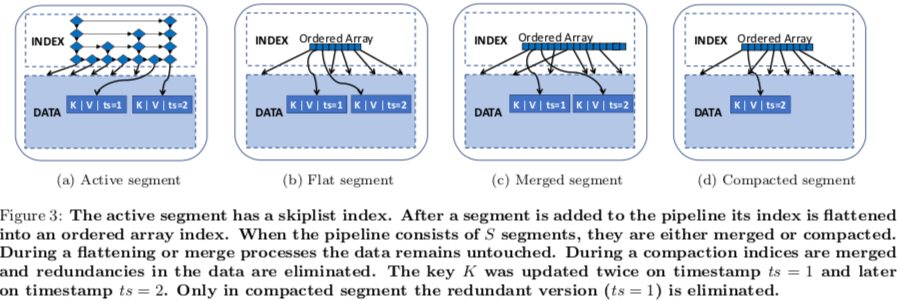
这个的in-memory的合并操作也和常见的LSM-Tree Compaction操作一样,Basic操作不会去除冗余的数据,比如一个Key的旧的版本的数据,Overhead比较低,而Eager合并则会去除器中的冗余的数据,Overhead比较高。 Accordion使用自适应的方法,会根据系统的情况选择合适的合并方式。
Splaying LSM-Tree
0x10 基本思路
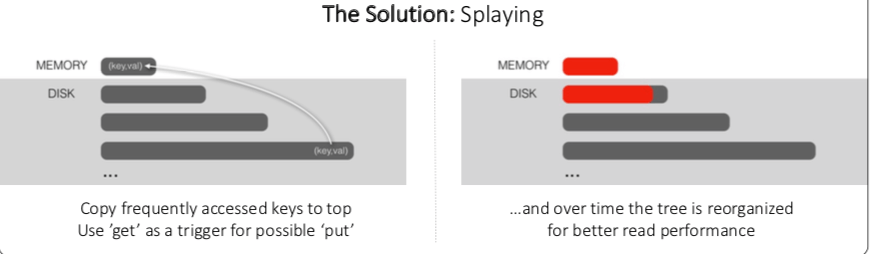
Splaying LSM-Tree的基本思路是将下层的Key-Value通过一定机制可以转移到上层中来,处理的问题是一个下层中的Key-Value变得比较Hot,这个时候处理这个Key-Value旧不如将其直接放入到内存中的L0中。可以通过类似Count Sketch的数据结构统计Key的热度,在合适的时候重新执行统计操作即可。
0x11 另外一个
Splaying LSM-Tree的思路可以很简单地拓展一下,当一个memtable被flush到磁盘上面的时候,其中如果存在比较Hot的Key-Value,这个操作是对处理这个Key-Value不利的。这个时候旧可以将这些Key-Value Pairs不要Flush到磁盘上去,而是继续保留到memtable中。这里以及上面Splaying的做法也会带来一些Overehad,只在一些情况下有比较好的效果。
SlimDB: A Space-Efficient Key-Value Storage Engine For Semi-Sorted Data
0x20 引言
SlimDB也是基于LSM-Tree的一个设计,它的设计有两个特点:
-
数据在Block中是不完全排序的,结合使用ECT压缩数据,还结合使用Three-level Block索引;
SlimDB only needs to support semi-sorted keys that consist of a prefix and a suffix. This means that the keys in a SlimDB SSTable only need to be sorted by their prefixes. This enables us to use entropy-coded tries (ECT)to compress prefixes and suffixes separately in the index block. ECT can efficiently index a sorted list of fixed-sized hash keys using only 2.5 bits per entry on average. -
使用Multi-level Cuckoo Filter,不仅仅是对于和SST文件的Filter,Multi-level Cuckoo Filter可以
0x21 Space-efficiency of an SSTable Index
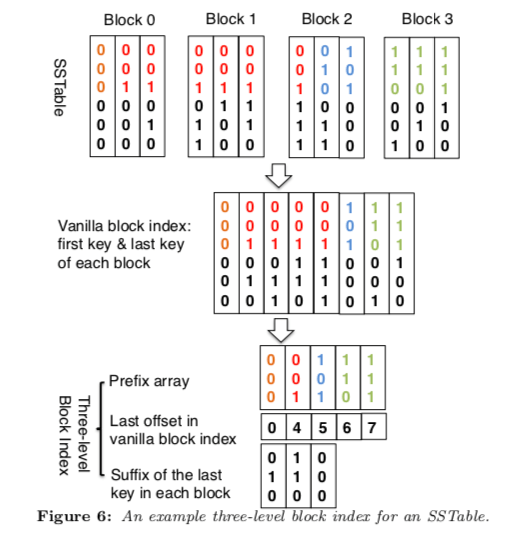
SlimDB的Block里面的数据不是完全排序的,而是根据前缀来排序。而一个Block里面可能存在不同Prefix的数据。根据前缀来既是First-Level的索引。这样的话保存到有同样的Key Prefix的时候数据不同拍下,另外就是Key不必要保存这个Pefix,在另外的一个地方保存一份即可。这样在一些情况下,可以省略很多的冗余的数据。第2个Level的是为快速找到有同样的Prefix的Key存在的Blocks的范围,它记录了这个Prefix的Key最后一个Block的Offset的信息。第3层的所以来自Suffix,例如查找001000,前缀可能存在0到2的Block中,虽然索引第1条的Prefix为000,但是还是可能存在001的数据,
To locate its block, we use its suffix “000” to complete a binary search among the array of suffixes (“010”, “110”) that differentiate the three candidate block groups. Since “000” is smaller than “010”, “001000” can only be stored in Block 0.
0x22 Multi-Level Cuckoo Filter
Cuckoo Filter是一种功能类似Bloom Filter的数据结构[4]。这里的Multi-Level Cuckoo Filter针对LSM-Tree的情况做了一些修改。Multi-Level Cuckoo Filter分为两个主要的Table,Primary Table保存来fingerprint和key所在的Level,这样就可以直接找的所在Level。Secondary Table是为了处理多个Key有同样的fingerprint的情况,在Secondary Table中会保存完整的Key,
When searching for an entry, first search the secondary table to see if there is any matching full key. If found, the level number of this entry can be retrieved from the secondary table; otherwise, continue to check the primary table of the multi-level cuckoo filter. With the secondary table in memory, the worst case lookup performs at most one disk read since it is guaranteed that there is only one copy of each fingerprint in the primary table.
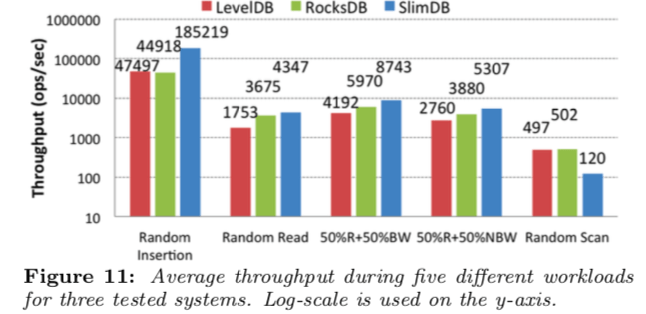
0x23 评估
这里具体的信息可以参看[3].
Redesigning LSMs for Nonvolatile Memory with NoveLSM
0x30 引言
NoveLSM的主要出发点是优化LSM-Tree在NVM上面的表现。主要就是利用NVM可以byte寻址、可持久化保存数据来减少序列化、反序列化带来的开销,利用NVM可直接访问来减少Compaction、Logging的开销,利用NVM高带宽、低延迟的特性支持并发读取。
Our analysis with popular benchmarks and real-world workload reveal up to a 3.8x and 2x reduction in write and read access latency compared to LevelDB. Storing all the data in a persistent skip list and avoiding block I/O provides more than 5x and 1.9x higher write throughput over LevelDB and RocksDB.
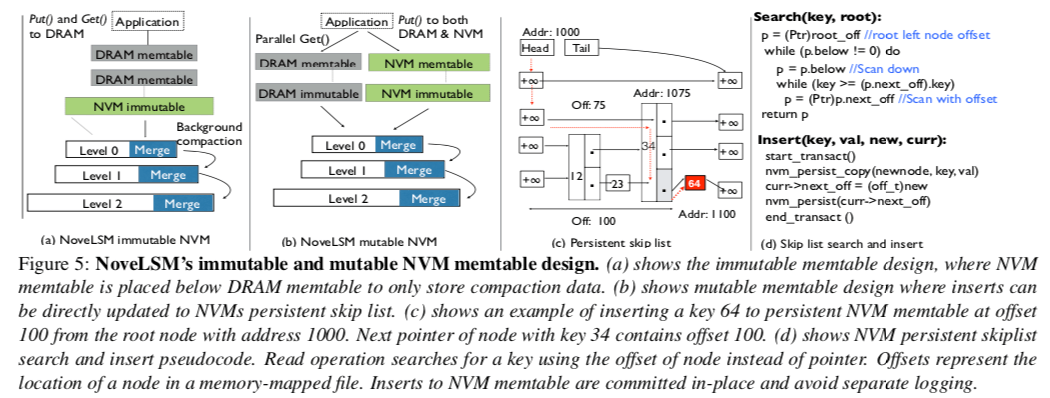
0x31 基本思路
减少序列化、反序列化开销
NoveLSM使用了一种可以直接持久化保存到NVM上面的Skip List。在内存中的memtable中Flush到NVM上面的时候,直接使用memcpy 拷贝到NVM上面,不用序列化。这个Skip List的节点从一段mmap的NVM中分配,节点使用到root节点的offset来寻找。在恢复的时候的时候,重新映射这个区域,其它的节点也可以直接根据root的位置来恢复。 这里个人感觉完全是一个多余的设计。完全可以将内存中的memtable遍历一下,作为一个有序的数组拷贝到NVM上面。不仅仅可以减少很多冗余的结构,后面的查找操作就可以直接使用二分,速度更快。整体的逻辑也更加简单。 NVM保存的Level完全可以不用磁盘上面的SST文件的复杂的结构。(这里完全还可以有更多的优化方式)。
减少Compaction开销 & 减少Logging开销
这里的主要思路就是如前面图中的(b)。内存中memtable中达到一定的大小的时候,会将其flush到NVM上面。这个时候如果写入速度太快,就转为使用NVM中的mutable的memtable,
When the DRAM memtable is full, it is made immutable, and the background compaction thread is notified to move data to the SSTable. Instead of stalling for compaction to complete, NoveLSM makes NVM memtable active (mutable) and keys are directly added to mutable NVM memtable.
写入到NVM的mutable memtable的时候,就可以不同WAL来保证持久化。而写入到内存中的时候还是需要写入WAL。这里会带来另外一个问题,也就是不一定是内存中的数据更新,也可能是NVM中的memtable中的数据更新,这里NovelLSM使用一个版本好来解决这个问题。
支持并发读取
按照通常的处理流程,一个读取操作最大的延迟为Tread ≈ TmemDRAM + TmemNVM + Timm + TSST。而Novel可以使用同时读取内存中和NVM中的数据,这样就有Tread-parallel ≈max(TmemDRAM +TmemNVM,Timm,TSST)+C。这里的一个问题就是如果是Level比较大的数据先返回,还是要等待Level较小的返回。 这里就是的思路就是用更高的(计算)资源消耗来降低前面几个Level查不到数据的时候的延迟。
0x32 评估
这里的具体信息可以参看[5],
参考
- Accordion: Better Memory Organization for LSM Key-Value Stores, VLDB ‘18.
- Reducing the Storage Overhead of Main-Memory OLTP Databases with Hybrid Indexes , SIGMOD ‘16.
- SlimDB: A Space-Efficient Key-Value Storage Engine For Semi-Sorted Data, VLDB ‘17.
- Cuckoo Filter: Practically Better Than Bloom, CoNEXT’14.
- Redesigning LSMs for Nonvolatile Memory with NoveLSM, ATC ‘18.
