The eXpress Data Path: Fast Programmable Packet Processing in the Operating System Kernel
0x00 引言
eXpress Data Path(XDP)是Linux的一个新功能。现在一些类似于netmap、DPDK之类框架得到了大量的使用。类似于DPDK这样的bypass内核的方式在提高了性能的同时也带来的另外的一些问题,比如隔离性、安全机制,还有就是可移植性等。XDP就是直接在Linux内核中实现的一个可编程的包处理机制。XDP也提高了很高的性能,而且可以弥补之前bypass内核的一些系统存在的问题。现在Facebook已经有一个利用XDP做负载均衡的项目开源了,XDP之后的应用前景应该会很好,
XDP achieves single-core packet processing performance as high as 24 million packets per second, and illustrate the flexibility of the programming model through three example use cases: layer-3 routing, inline DDoS protection and layer-4 load balancing.
0x01 基本架构
XDP是一个包处理的框架,不是一个完整的网络栈。在可以在数据包进入Linux内核网络栈之前(ingress)or出网络栈之后对数据包进行处理(outgress)。在下面的图中,表示来在收到数据包的时候,早构建sk_buff之前就可以对其进行处理,可以对其操作转发到Contrainer 和 虚拟机中,实现一些Contrainer网络、Open vSwitch的功能。另外Linux提供来一个新类型的Socket:AF_XDP,可以直接将这些数据包交给用户程序来处理。另外的TC BPF中,可以执行一些用户定义的eBPF的程序逻辑,这里可以用来处理一些不支持XDP模式的网卡驱动情况。
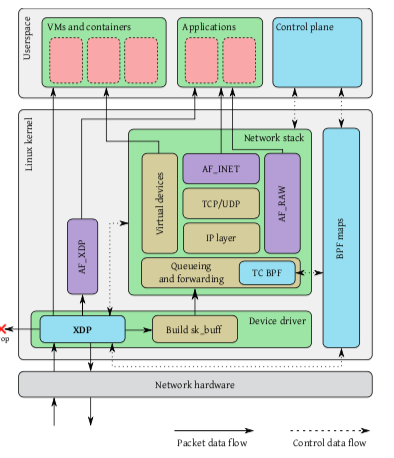
XDP基本的一个架构如下图,它包含了这样的几个部分,
-
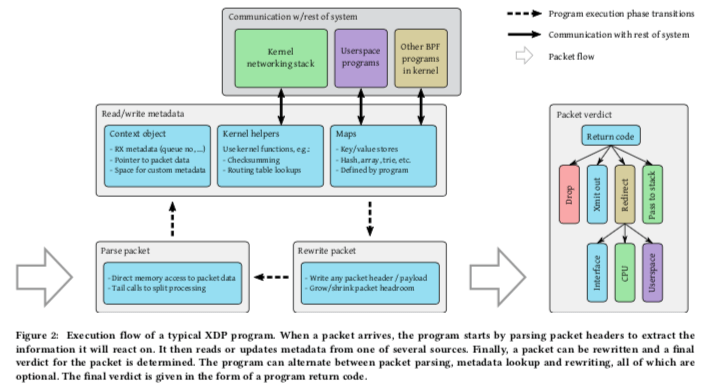
XDP Driver Hook,在设备驱动中的一个“钩子”用于网卡在收到数据包的数据执行一个XDP程序。和netmap之类的系统一样,XDP也要在驱动上做一些改进。这个XDP程序可以获取数据包的元数据和数据。这个程序一般都是以解析数据包的一些Header开始,了解包类型等的信息。根据这些信息可以来决定对包的一些数据方式,另外这个程序也可以直接对包的一些数据进行改写,对包进行封装 or 解封。另外可以对包进行重定向处理。基本的逻辑图下面的图,
The redirect functionality can be used (1) to transmit the raw packet out a different network interface (including virtual interfaces connected to virtual machines), (2) to pass it to a different CPU for further processing, or (3) to pass it directly to a special userspace socket address family (AF_XDP). -
eBPF虚拟机,执行XDP程序的字节码,这里还会使用JIT的方式来提高性能。Linux中的eBPF最近做了很多强化。这里的JIT利用了LLVM来实现。
-
BPF maps,一个Key-Value的结构。由于XDP程序是每一个数据包触发执行一次,为例和系统其它部分进行数据交互 or 保存一些数据,需要用到这个功能;
-
eBPF verifier,在装载XDP程序之前验证它的安全性;
0x02 例子
Paper中谈到了用XDP使用LVS(IPVS)的功能,在这个来看不会很复杂。下面是一个在Github上面找到的做Layer4负载均衡的例子[2],
// SPDX-License-Identifier: (GPL-2.0 OR BSD-2-Clause)
// Copyright (c) 2018 Netronome Systems, Inc.
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stddef.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <linux/bpf.h>
#include <linux/icmp.h>
#include <linux/if_ether.h>
#include <linux/if_vlan.h>
#include <linux/in.h>
#include <linux/ip.h>
#include <linux/tcp.h>
#include <linux/udp.h>
#include "bpf_endian.h"
#include "bpf_helpers.h"
#include "jhash.h"
#define MAX_SERVERS 512
/* 0x3FFF mask to check for fragment offset field */
#define IP_FRAGMENTED 65343
struct pkt_meta {
__be32 src;
__be32 dst;
union {
__u32 ports;
__u16 port16[2];
};
};
struct dest_info {
__u32 saddr;
__u32 daddr;
__u64 bytes;
__u64 pkts;
__u8 dmac[6];
};
struct bpf_map_def SEC("maps") servers = {
.type = BPF_MAP_TYPE_HASH,
.key_size = sizeof(__u32),
.value_size = sizeof(struct dest_info),
.max_entries = MAX_SERVERS,
};
static __always_inline struct dest_info *hash_get_dest(struct pkt_meta *pkt)n{
__u32 key;
struct dest_info *tnl;
/* hash packet source ip with both ports to obtain a destination */
key = jhash_2words(pkt->src, pkt->ports, MAX_SERVERS) % MAX_SERVERS;
/* get destination's network details from map */
tnl = bpf_map_lookup_elem(&servers, &key);
if (!tnl) {
/* if entry does not exist, fallback to key 0 */
key = 0;
tnl = bpf_map_lookup_elem(&servers, &key);
}
return tnl;
}
static __always_inline bool parse_udp(void *data, __u64 off, void *data_end,
struct pkt_meta *pkt){
struct udphdr *udp;
udp = data + off;
if (udp + 1 > data_end)
return false;
pkt->port16[0] = udp->source;
pkt->port16[1] = udp->dest;
return true;
}
static __always_inline bool parse_tcp(void *data, __u64 off, void *data_end,
struct pkt_meta *pkt) {
struct tcphdr *tcp;
tcp = data + off;
if (tcp + 1 > data_end)
return false;
pkt->port16[0] = tcp->source;
pkt->port16[1] = tcp->dest;
return true;
}
static __always_inline void set_ethhdr(struct ethhdr *new_eth,
const struct ethhdr *old_eth,
const struct dest_info *tnl,
__be16 h_proto) {
memcpy(new_eth->h_source, old_eth->h_dest, sizeof(new_eth->h_source));
memcpy(new_eth->h_dest, tnl->dmac, sizeof(new_eth->h_dest));
new_eth->h_proto = h_proto;
}
static __always_inline int process_packet(struct xdp_md *ctx, __u64 off) {
void *data_end = (void *)(long)ctx->data_end;
void *data = (void *)(long)ctx->data;
struct pkt_meta pkt = {};
struct ethhdr *new_eth;
struct ethhdr *old_eth;
struct dest_info *tnl;
struct iphdr iph_tnl;
struct iphdr *iph;
__u16 *next_iph_u16;
__u16 pkt_size;
__u16 payload_len;
__u8 protocol;
u32 csum = 0;
iph = data + off;
if (iph + 1 > data_end)
return XDP_DROP;
if (iph->ihl != 5)
return XDP_DROP;
protocol = iph->protocol;
payload_len = bpf_ntohs(iph->tot_len);
off += sizeof(struct iphdr);
// 这里先处理包的元数据
/* do not support fragmented packets as L4 headers may be missing */
if (iph->frag_off & IP_FRAGMENTED)
return XDP_DROP;
pkt.src = iph->saddr;
pkt.dst = iph->daddr;
/* obtain port numbers for UDP and TCP traffic */
if (protocol == IPPROTO_TCP) {
if (!parse_tcp(data, off, data_end, &pkt))
return XDP_DROP;
} else if (protocol == IPPROTO_UDP) {
if (!parse_udp(data, off, data_end, &pkt))
return XDP_DROP;
} else {
return XDP_PASS;
}
// 计算hash值
/* allocate a destination using packet hash and map lookup */
tnl = hash_get_dest(&pkt);
if (!tnl)
return XDP_DROP;
// 然后对包进行处理
/* extend the packet for ip header encapsulation */
if (bpf_xdp_adjust_head(ctx, 0 - (int)sizeof(struct iphdr)))
return XDP_DROP;
data = (void *)(long)ctx->data;
data_end = (void *)(long)ctx->data_end;
/* relocate ethernet header to start of packet and set MACs */
new_eth = data;
old_eth = data + sizeof(*iph);
if (new_eth + 1 > data_end || old_eth + 1 > data_end ||
iph + 1 > data_end)
return XDP_DROP;
set_ethhdr(new_eth, old_eth, tnl, bpf_htons(ETH_P_IP));
/* create an additional ip header for encapsulation */
iph_tnl.version = 4;
iph_tnl.ihl = sizeof(*iph) >> 2;
iph_tnl.frag_off = 0;
iph_tnl.protocol = IPPROTO_IPIP;
iph_tnl.check = 0;
iph_tnl.id = 0;
iph_tnl.tos = 0;
iph_tnl.tot_len = bpf_htons(payload_len + sizeof(*iph));
iph_tnl.daddr = tnl->daddr;
iph_tnl.saddr = tnl->saddr;
iph_tnl.ttl = 8;
/* calculate ip header checksum */
next_iph_u16 = (__u16 *)&iph_tnl;
#pragma clang loop unroll(full)
for (int i = 0; i < (int)sizeof(*iph) >> 1; i++)
csum += *next_iph_u16++;
iph_tnl.check = ~((csum & 0xffff) + (csum >> 16));
iph = data + sizeof(*new_eth);
*iph = iph_tnl;
/* increment map counters */
pkt_size = (__u16)(data_end - data); /* payload size excl L2 crc */
__sync_fetch_and_add(&tnl->pkts, 1);
__sync_fetch_and_add(&tnl->bytes, pkt_size);
return XDP_TX;
}
SEC("xdp")
int loadbal(struct xdp_md *ctx)
{
void *data_end = (void *)(long)ctx->data_end;
void *data = (void *)(long)ctx->data;
struct ethhdr *eth = data;
__u32 eth_proto;
__u32 nh_off;
nh_off = sizeof(struct ethhdr);
if (data + nh_off > data_end)
return XDP_DROP;
eth_proto = eth->h_proto;
/* demo program only accepts ipv4 packets */
if (eth_proto == bpf_htons(ETH_P_IP))
return process_packet(ctx, nh_off);
else
return XDP_PASS;
}
0x03 评估
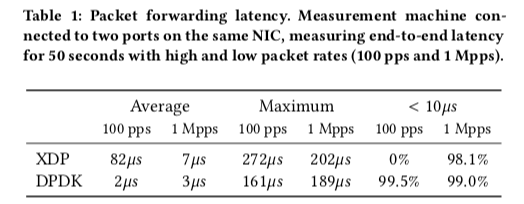
这里具体的信息可以参看[1]。和DPDL比,XDP性能不一定占有,在Paper中的一些数据中,CPU消耗方面XDP好不少,
参考
- The eXpress Data Path: Fast Programmable Packet Processing in the Operating System Kernel, CoNEXT ’18.
- https://github.com/Netronome/bpf-samples/blob/master/l4lb/l4lb_xdp.c
