Split-Ordered Lists: Lock-Free Extensible Hash Tables
0x00 基本结构
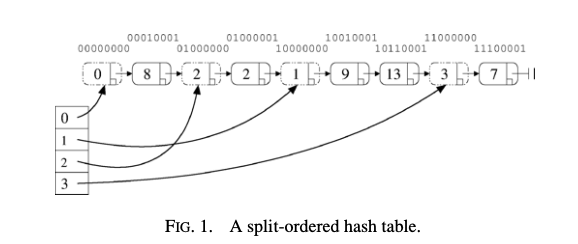
Split-ordered是一种Extensible Hash Table。这种hash table包含两个主要的结构,一个是一个linked list,保存数据项,另外一个类似于一个索引结构,保存的是一个逻辑上面的bucket。初始化的时候,一般选择初始化长度为2,后面每次size超过size x L的时候,就进行扩容的操作。这个L就是hash table的load factor。初始的时候,每个bucket是一个uninitialized状态,而index 0初始的时候指向的是一个empty list。一般的hash table rehash操作的时候,需要对数据进行移动 or 逻辑上面的移动。但是这里可以避免数据的移动。在table的size为2^i的时候,一个bucket b包含所有的keys其 k mod 2^i = b的key。在size变为2^(i+1)的时候,这个bucket被分裂为2个bucket,对于k mod 2^(i+1) = b + 2^i的keys,被转移到第b + 2^i个bucket。为了避免一个bucket分裂的时候需要对数据进行重新整理的操作,最好就是一个bucket的分裂点处于这个bucket数据项的中间的一个值,前面的是还是在bucket b,后面的分裂之后成为b + 2^i的bucket的数据。所以这里最好就是在推进的时候就根据其hash进行一定的顺序整理。另外,为了处理删除由bucket指向的item的问题,这里引入了dummy node的方式,
... it is nontrivial to manage deletion of nodes pointed to by bucket pointers. Our solution is to add an auxiliary dummy node per bucket, preceding the first item of the bucket, and to have the bucket pointer point to this dummy node. The dummy nodes are not deleted, which helps keep things simple.
Paper中还附带了一个简单的代码实现。
Horton Tables: Fast Hash Tables for In-Memory Data-Intensive Computing
0x10 基本结构
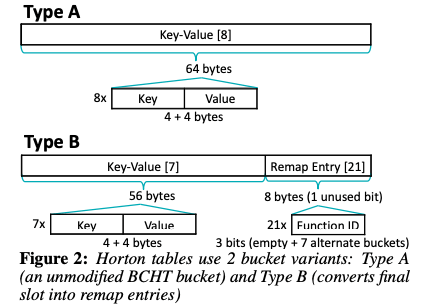
Horton Table是bucketized cuckoo hash tables (BCHTs)的一个优化。BCHT是最近hash table研究的一个热门的地方。BCHT在查询不存在的key的时候比在查询存在的key的时候,需要查询key的位置要不少,造成更大的cache miss,性能损失。Horton Table的思路是引入了两种不同的bucket,Type A就是普通的bucket,而Type B包含了额外的元信息。一般情况下,Horton Table使用primary hash function来决定使用哪个Type A的bucket,这个bucket称之为primary bucket。在primary 添加不了的情况下,会使用Type B的secondary bucket,通过secondary hash functions计算的hash值来寻址。到这里其实和一般的BCHT没有啥区别。Horton Table的一个改进是Type B的结构,其最后一个Pair改成了remap entry array结构,其中的 remap entries记录了 secondary hash的function ID,即使用了哪个 secondary hash,
Remap entries can take on one of 2^k different values, 0 for encoding an un- used remap entry, and 1 to 2^k − 1 for encoding which of the secondary hash functions R_1 to R_2^k−1 was used to remap the items.
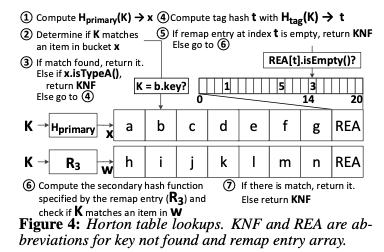
在这种结构下面,Horton Table中查找操作的逻辑如下,先计算primary hash的hash值,寻址到bucket x。如果在x中发现了,直接返回。如果没有发现且x为Type A的bucket,直接返回Key Not Found,否则根据根据对于tag hash计算使用的那一个remap entry t,如果t是empty,返回Key Not Found,否则根据remap entry指示的secondary hash计算hash值,在第二个bucket中进行查找操作。查找操作中,一些操作可以借用SIMD来优化。
添加操作。为了保证性能等方面的原因,Horton Table在添加的时候使用下面的一些guidelines,
1. Secondary items never displace primary items.
2. Primary items may displace both primary and secondary items.
3. When inserting into a full Type A bucket, only convert it to Type B if a secondary item in it cannot be
这样的话会尽量的将bucket维持在Type A,避免第二次查找。添加操作的时候:1. 根据primary hash的hash值找到primary bucket,如果这个bucket可以添加到话,直接添加。如果bucket是满的,一般情况下的操作逻辑如下图,会尝试使用多个其它的secondary hash function添加到其它的bucket,如果添加成功的话,在对应remap entry中记录下使用的secondary hash function的id。但是这里还有其它的一些情况需要处理。
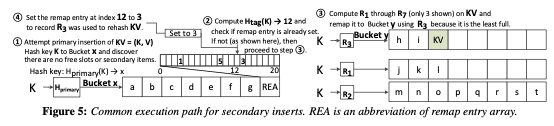
添加Type A or B Bucket满了的时候,Horton都会先尝试踢出一个secondary的元素,即不是使用primary hash来保存到这个位置的元素。如果没有这样的元素,且开始添加的时候是一个Type A的bucket,就不能使用上面的直接使用remap entry array,需要将这个Type A的bucket转化为Type B的bucket。如下图所示,这样会remap entry array需要使用h占用的空间,这样需要将其先保存到其它的地方,即使用secndary hash functions定位其它的bucket,另外需要在转换之后的bucket x中的remap entries中记录下使用的hash ID,之后的添加执行和上面一般情况下的添加类似。
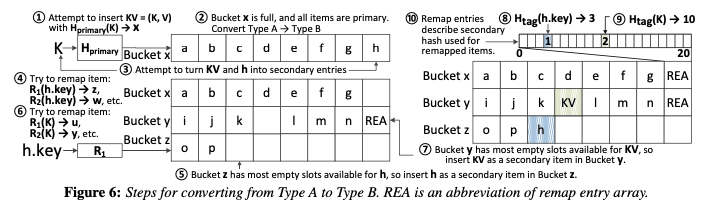
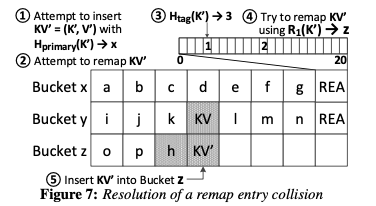
这里要处理的一个比较麻烦的问题是remap entries的冲突问题。Horton Table的第一个尝试是减少这样的冲突,这里在hash的方式上面做了一些优化[2]。不过最主要的还是处理在冲突的时候如果寻址bucket,需要使用对于remap entry的hash函数来作为secondary hash函数,否则的话查找会出问题。这样添加的逻辑如下: 1. 如下图,添加的时候primary bucket x满了,会尝试从x中踢出来一个secondary item;2. 不能的话尝试使用remap entry,如果对应的entry已经设置的情况下,使用对应的信息计算出hash寻址到bucket z,如果有free solt直接添加。如果不在free solt的时候,执行递归的踢出操作,这个操作和一般的Cuckoo Hash添加的时候出现冲突的处理方式类似,不过选择第二个hash函数的时候要利用remap entry。
Horton Table在删除的时候也有一些问题需要处理:1. 先根据primary hash函数寻址到primary bucket,存在的话直接删除即可;2. 如果不存在且这个bucket是Type B类型的,会先检查对应的remap entry,如果已经设置了,根据这个来计算第二个hash值,寻址secondary bucket,在这个bucket尝试删除操作;3. 有时候可以移除remap entry,这里,
To determine whether we can delete the remap entry, we check to see if additional elements in the secondary bucket have the same primary bucket as the deleted element. If none do, we remove the remap entry.
这里还可以的优化是在可以的时候将Type B的bucket变成Type A,Paper中将这部分的工作作为未来的内容,没有具体说明。
Hopscotch Hashing
0x20 基本结构
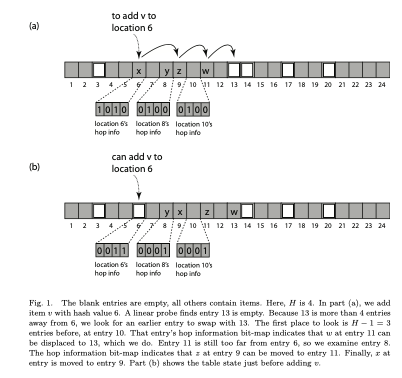
Hopscotch Hashing可以看作是线性探查方式和Cuckoo Hashing的一种结合,其基本思路是在线性探查的基础之上,设置一个探查的距离/数量限制。这个限制这里使用H表示,Paper中使用H=32。在添加的时候,根据hash函数定位到一个位置i,这个i及后面的H-1个位置就是一个虚拟的bucket。如果这个bucket有添加的空间,增添加进去数据,如果没有,则将这个bucket可以踢出的一些元素踢出,重复操作。可能需要递归操作,在必要的时候就rehash,
Here is how to add item x where h(x) = i:
—Starting at i, use linear probing to find an empty entry at index j.
—If the empty entry’s index j is within H − 1 of i, place x there and return.
—Otherwise, j is too far from i. To create an empty entry closer to i, find an item y whose hash value lies between i and j, but within H − 1 of j, and whose entry lies below j. Displacing y to j creates a new empty slot closer to i. Repeat. If no such item exists, or if the bucket already i contains H items, resize and rehash the table.
查找和删除操作的时候,由于元素在位置i后面能够保存的位置是有限的,只要在这些有限的位置查找即可,删除的话找到并将其删除。
参考
- Split-Ordered Lists: Lock-Free Extensible Hash Tables,
- Horton Tables: Fast Hash Tables for In-Memory Data-Intensive Computing, ATC ‘16.
- Hopscotch Hashing, http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1432291.1432316
