Resumable Online Index Rebuild in SQL Server
0x10 引言
这篇Paper关注的是数据库论文中很少涉及到的一个内容,是一篇工程性质的论文。主要的内容是关于数据索引重建,一般在某些操作之后进行索引重建的工作可以提供性能,减少占用的磁盘空间等。这里主要关注在在云环境的情况下,如何处理在索引重建工程中的failure问题,从而提出了Resumable Online Index Rebuild的思路,即索引重建可以从系统failure之前的位置重新开始。另外的一些race condition的处理也比较有意思,相关的心Index创建的问题在92年的一篇Paper中有讨论, 提出了两种基本的方法,这里使用的方法类似于其中描述的NSF,No Side File的方法。索引重建工作一般分为三种步骤:
- Preparation Phase,这一部分先建立一个新的空索引。在这一部分的时候它先先获取一个表上的S LOCK,用于等待这个表上面的更新操作完成,以及阻塞后面的更新操作。更新元数据之后,就释放这个S LOCK,所以不会有影响。这样做的目的是更新元数据,以便让后面的更新操作知道有这个重建过程中的索引,而进行更新添加到这个索引中;
- Build Phase,这一部分操作会扫描原来的索引,在需要的时候对数据进行排序,然后重新添加到新的索引中。在这个过程中,对表的更新操作要同时更新所有存在的索引,包括创建中的索引。
- Final Phase,在新的索引创建完成之后,索引创建进程/过程会请求一个table的X LOCK,一个原因是等待现在的操作完成,同时Block后面的操作。请求到X LOCK之后,更新元数据,更新完成释放LOCK。后面的操作使用元数据更新完成之后table的情况进行处理。
在前面的基本操作流程之上,还有一些额外的race condition需要处理,1. 比如一个删除操作删除一行数据的时候,这行数据以及被Index Builder读取到了,但是还没有添加到新的数据中。这种情况下,这个删除操作可能删除新index的数据的时候没有看到这行数据,但是之后有被重新添加进去。2. 一个添加操作需要添加到原来的index和新的index,Index Builder读取的数据的时候,和添加新数据的操作之后操作原index和新index的顺序相关,可能导致一个duplicate key的错误。3. 一个并发的DML操作可能在任何时刻进行回滚操作,Index Builder操作需要保证操作完成的时候只会包含一句提交的数据。SQL Server这里使用如下的方法来解决这样的一些问题,
-
这里没有使用某些特殊类型的lock or logging方式来保证新 index中值包含以及被提交的数据,而是使用扫描的时候扫描一个snapshot。Index Builder扫描原index的时候不需要获取LOCK(s),而在讲数据添加到新index的时候,想要获取exclusive row locks,来同步并发的在新index的更新操作。这里还使用批量出来的方式来提高性能。
-
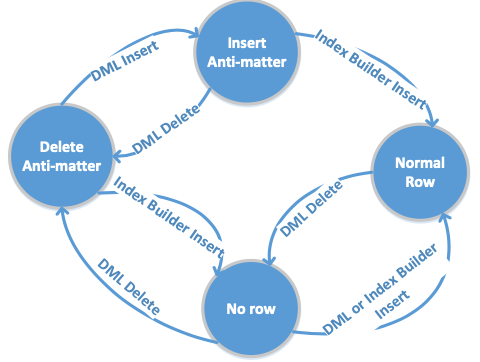
为了解决前面提到的删除的问题,这里使用了一个deleta anti-matter的方式。一个删除操作在新index中没有发现对应行的数据的时候,会在新index中添加一个对应key为deleta anti-matter的数据。Index Builder添加数据的时候,发现这样的一行记录的时候需要讲这行数据删除,需要讲对应行的数据删除。Index Builder扫描的是一个snapshot的数据,能保证deleta anti-matter的数据在最后都会被删除。
-
Index Builder使用snapshot scan的时候不会看到扫描开始之后被添加的数据,所以要求更新操作也必须讲更新添加到新index中。但是这里可能的一个问题是Index Builder取添加一行数据的时候,发现已经被更新操作添加了一个更加新的版本的数据。处理这种问题的一种方式是Index Builder会忽略duplicate的行。而这里还使用了额外的一种insert anti-matter的思路,用于区分falst duplicate和real duplicate。insert anti-matter的状态会被在这行数据被标记了delete anti-matter的时候添加,
The “insert anti-matter” state is used whenever an insert occurs on top of a row that was earlier marked as “delete anti0matter” to indicate that this row already existed when the index build operation started and, therefore, can be safely ignored. Updates are also treated as a delete followed by an insert and will also introduce an “insert anti-matter”. New row insertions, on the other side, will insert regular rows, not marked as “insert anti-matter”.也就是说新添加的行不会被标记这个,新添加的行不会被snapshot scan看到,只是会被更新操作添加而已,和Index Builder的操作互不不影响。而Index Builder添加行到新index的时候,会将这个标记清除。如果看到了一个同样的没有标记的行,一位这这里有一个unique key violation,操作会失败。同样地,这个insert anti-matter也之后添加到扫描的snapshot中已经存在的数据,所以这些insert anti-matter最终会被删除。行的一个state转换入下图,
0x11 基本设计
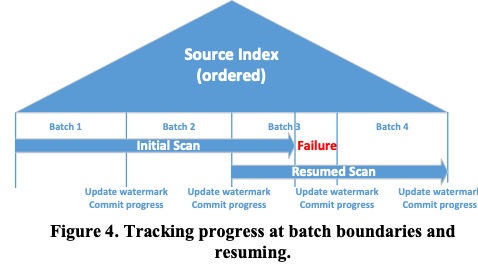
为了支持Resumable Online Index Rebuild,也就是索引重建的过程可以中断之后重新开始。这里使用的基本思路是讲整个工作拆分为若干个更小的工作单元,周期性地提交操作的结构,并将索引操作的状态信息持久化,以便于在中断时候重新开始操作。 操作的基本思路表现如下图。
* Split the overall operation into incremental units of work so that each unit can be completed within a small amount of time.
* Periodically commit the progress of the operation, using internal transactions, to harden the work completed so far.
* Persist the state that is required for the operation to resume from this point in case of failure.
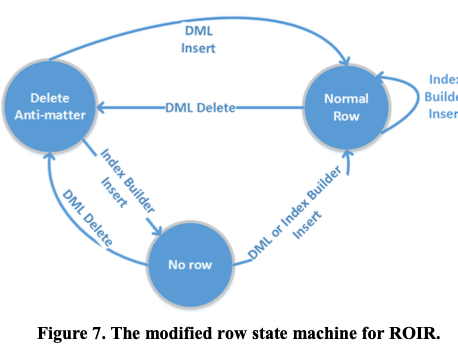
在这样的基本思路之上,需要解决的一些问题:1. 并行化操作的问题。使用的思路是Range分区的方式。基于数据库的一些统计信息,将数据分为range,每个线程处理一个分配好的range。每个线程处理记录自己的进度状态信息;2. 并行的DML操作处理的问题,想要在前面的算法的基础上你进行修改;3. Schema更新的问题,通过使用一个schema lock来避免这个操作过程中的shema变更;4. Log Management,目前的Index Rebuild操作作为一个大的transaction存在,这样的一个问题就是在ARIES风格的WAL算法下,这个事物没有操作完成,对于的Log就不能进行回收处理,这样的长transaction可能带不小的隐患,ROIR想要优化这里,通过使用更“小”的transaction来实现Rebuild;5. Statistics,在Rebuild过程中更新统计信息是一个很好的idea;6. Checkpointing,RIOR持久化进度状态信息等带来的开销。7. No Side-File vs. Side-File的问题,即使用[2]中描述的方法的哪一种,RIOR选择了NSF方法,一位这种方法在SQL Server已经使用了一段时间。RIOR操作相关状态改变如下图,和上面的对比少了一个insert anti-matter的状态。
-
由于索引重建的操作可能在故障之后重新开始,这里就没有使用scan一个snapshot的方法。可能是故障之后相关的一些信息会丢失。
-
删除操作和前面的类似。无论删除的key在新index的存在与否,都是会讲这行的数据变为delete anti-matter的状态。但是insert操作不会在区添加一个insert anti-matter,而是使用直接添加一个普通行的方式,如果之前这行数据被标记为delete anti-matter,则将其变更为正常的状态。Index Builder的操作记录如下,
* If the row was deleted by a concurrent DML operation, the Index Builder will find a “delete anti-matter” and the row can be removed completely. * If the row was inserted by a concurrent DML operation, the index builder will find a regular row and can safely ignore it since the version that has been inserted by the DML operation is guaranteed to be the newest version of the row.Index Buider扫描数据的时候也只会扫描已经提交的数据。为了提高操作的并发性,也是使用scan一个snapshot数据的方式,但是这里不会要求一直是一个consistent snapshot。这个snapshot只会在读已经提交的数据时候使用,在操作重启之后会使用一个新的snapshot。
-
前面的算法中,加入insert anti-matter主要是为了处理unque index创建的问题。原来的方法在这里不适用了。这里将会使用额外的结构来处理这个问题。
To achieve this, however, the original algorithm also depended on having a consistent snapshot to guarantee that any concurrent updates will not be visible to the Index Builder. Given that this capability is not available for ROIR, this state is no longer useful and can be eliminated for simplicity. -
这里还有另外一个细节上面的不同:就是在Index Rebuild操作完成之后,不能保证所有的delete anti-matter记录都被删除了。因为现在的delete anti-matter添加可能在Index Builder操作完成之后加上了的,这样的话这些delete anti-matter标记就清楚不了了。这里需要讲这样的数据行视为ghosts来处理。为什么原来的不会发生这样情况呢,原来的处理方式是:when a delete operation does not find the corresponding row in the new index, it will insert a row with the same key and the “delete anti-matter” state set。而现在的处理方式是:any deletion in the new index will insert a “delete anti-matter” row for this key。为什么要这么处理呢?因为这里Index Builder Scan老的Index的时候,不是一个consistent snapshot,可能中间重启过了。
正确性证明在Paper中有详细地论述,还有一个开源的TLA+ Verification。
0x12 评估
这里的具体信息可以参看[1].
参考
- Resumable Online Index Rebuild in SQL Server, VLDB ‘17.
- Algorithms for Creating Indexes for Very Large Tables Without Quiescing Updates, SIGMOD ‘92.
