Swift: Delay is Simple and Effective for Congestion Control in the Datacenter
0x00 基本内容
Swift是Google提出的一个为数据中心内通信使用的基于延迟的拥塞控制算法。Swift的设计是基于target delay的,即一个目标的延迟,而不是类似的一些算法的delay的变化情况。这就意味着Swift需要对系统中正常的延迟有一个了解,更加适合于情况较为明了的地方。这个算法实现在Google自己的一个网络栈Snap中,Paper中提到这个算法已经使用了数年的时间。Swift将延迟分为了两个部分,一个是NIC-to-NIC (fabric) delay以及 endpoint delay两个部分。Paper中分析了通信过程中的delay的来源,
- Local NIC Tx Delay,write操作到NIC Tx Queue发动packet的延迟。Paper中提到在使用pull模式的情况下,host在NIC准备好发送的时候才移交packet,这种情况下这个延迟是很小的;
- Forward Fabric Delay,即packet传输过程中serialization, propagation and queuing delays等等带来的delay,NIC的serialization delay也包括在内;
- Remote NIC Rx Delay,packet在remote的NIC queue中到被remote的网络栈拿走处理的delay。在远端的host处理能力到达一个瓶颈的时候,这个delay会显著增大。
- Remote Processing Delay,remote的网络栈处理的delay,从remote的网络栈开始处理packet到产生和这个packet相关的ACK的过程的delay;
- Remote NIC Tx Delay,和Local NIC Tx Delay是一样的,这里指的是ACK Packet;
- Reverse Fabric Delay,和Forward Fabric Delay,这里指的是ACK Packet;
- Local NIC Rx Delay,local的网络栈开始处理这个ACK packet到确定ACK的过程;
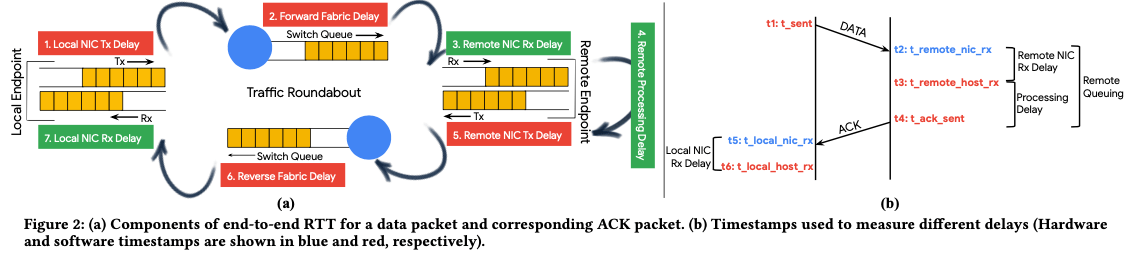
基本的示意图如上图。测量延迟的时候,利用现代的NIC可以使用的hardware times-tamps的功能,处理的过程中有多个点测量了timestamp,表示上面提到了几个delay。
0x01 基本算法
Swift还是沿用了Congestion Control算法中的AIMD原则,将endpoint-delay定义为sum of remote-queuing (echoed in the ACK) 和 Local NIC Rx Delay (given by t6 − t5),fabric-delay定义为RTT减去endpoint-delay。针对这两个delay,使用两个congestion windows,fcwnd处理fabric congestion,处理endpoint congestion。两个部分对应不同的delay target,分别称之为fabric-delay-target 和 endpoint-delay-target,两个窗口分别表示为fcwnd和ecwnd。但是两个部分使用的控制算法是一样的。在delay小于target delay的时候,使用加性增加的方式,在delay大于target delay的时候,使用乘性减少的方式。在使用这些delay的时候,Swift使用 Exponentially Weighted Moving Average (EWMA) 的方式来过滤一些偏差太大的delay数值,来降低这些噪音数据多算法的影响。最终的congestion window使用fcwnd和ecwnd中较小的一个。
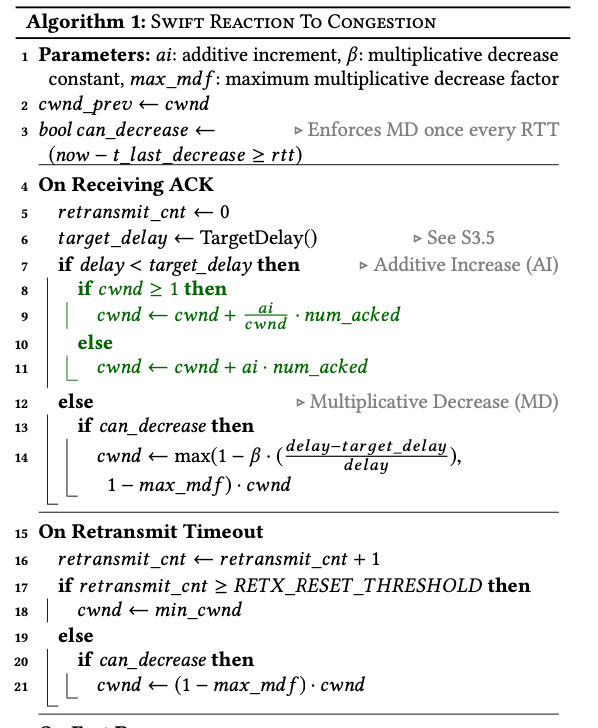
这里提到的另外一个问题就是incase的问题,实际部署的时候经常遇到很大量的流的目的是一个host。这种情况下一个一般方法很难去避免网络的overload,这里使用的测量时允许cwnd为一个很小的值,
... In this scenario, when number of flows exceed the path BDP, even a congestion window of one is too high to prevent overload. To handle such cases, we augmented Swift to allow the congestion window to fall below one packet down to a minimum of 0.001 packets.
为此,在算法1的Lines 29–32实现了一个inter-packet delay的功能。这样的效果时是,以cwnd为0.5为例,会导致发发送了一个packet之后,会delay of 2 × RTT在发送下一个。算法中的can decrease也和这里的逻辑相关?
前面讨论的情况是target delay是一个固定的值,Paper中还讨论了这么动态地处理这个target delay。Target delay在Swift中分别固定的一部分和动态的一部分,如下图所示,
The base portion of target delay consists of delays incurred for a single hop network with a small number of flows: propagation delay, serialization delay in NIC and switch (which depends on link speed), queuing delay for a small number of flows, measurement errors from software and hardware timestamps, as well as any unaccounted delays in network...
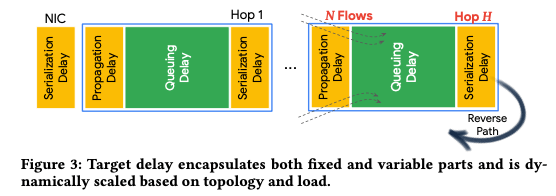
Target delay scaling包括这样的一些部分,
- Topology-based Scaling,和网络的拓扑相关,互联网中测量路径延迟是比较麻烦的,但是在数据中心内,拓扑是比较固定的。这里的delay就使用fixed base delay 加上 a fixed per-hop delay的方式来计算。IP Packet中的IP TTL (Time-To-Live)可以获取到hop数量的信息;
- Flow-based Scaling,这里根据有竞争关系的flow数量条调整delay。根据其它的一些研究,一条链路上面有n个流,每个的开始的时间随机, average queue length成流数量的平方根级别增长,即O(√N)的关系。这里cwnd和流数量存在一个反比的关系,这里跳过target delay就根据 1/√cwnd的比例来调整。 target delay增大,cwnd减小。结合着两个部分,得出总体的调整方式,
其中:
* base_target is the minimum target delay required to provide 100% utilization in a one hop network with a small number of flows.
* fs_tange specifies the additional target on top of base that is progressively reduced over the cwnd range [fs_min_cwnd, fs_max_cwnd]. h is the per-hop scaling factor.
丢包的处理和一般TCP协议也是基于两个基本的方式:第一个selective acknowledgements (SACK)用于fast recovery。这里使用一个sequence number bitmap来处理SACK,发现这个bitmap有hole时候,执行retransmit的操作,congestion window乘性减小。另外一个就是retransmission timeout (RTO)。在ACK方面,Swift协议不使用显示地使用延迟确认的方式,但是一些ACK可以合并的时候还是会合并处理。另外Swift也考虑了QoS,
Switches have ∼10 QoS queues per port that can share the buffer space across ports based on usage. We reserve a subset of QoS queues for Swift traffic and give them a share of the link capacity via weighted-fair-queuing. By using larger scheduler weights for higher priority traffic, we are able to handle tenants with different traffic classes.
0x02 评估
这里的具体内容可以参看[1].
参考
- Swift: Delay is Simple and Effective for Congestion Control in the Datacenter, SIGCOMM ‘20.
