Can Applications Recover from fsync Failures?
0x00 基本内容
PostgreSQL之前有过一个丢失数据的BUG,这个BUG和fsync的错误相关。PostgreSQL使用来错误的方式处理fsync返回错误时的情况。Linux上面某些文件系统在fsync错误的时候可能会直接丢弃内存中的错误,这个时候重试操作可能是错误的方式。fsync的运作可能产生一些错误,一般的系统也会有一些处理fsync的逻辑,POSIX对fsync发生错误的时候,具体的语义并没有明确的定义。是这篇Paper考察的几个开源的存储系统,认为它们的处理方式都存在一些缺陷。fysnc syscall可能返回多种类似的错误,不同的FS还存在一些细节的差别。一些errno比如ENOSPC、 EDQUOT、EBADF、EINVAL和EIO等。Paper中先测试了一些FS在Single Block Update、Multi Block Append两种workload发生一些错误的情况下,FS的一些行为。这里的错误是使用工具注入的。
Single Block Update:
open, lseek(4K), write(4K), fsync, fsync, sleep(40), close.
Multi Block Append:
write(4K), fsync, sleep(40), write(4K), fsync, sleep(40), close.
对于上面的测试,这里关系这样的一些问题:
Basics of fsync Failures:
Q1 Which block (data, metadata, journal) failures lead to fsync failures?
Q2 Is metadata persisted if a data block fails?
Q3 Does the file system retry failed block writes?
Q4 Are failed data blocks marked clean or dirty in memory? Q5 Does in-memory page content match what is on disk?
Failure Reporting:
Q6 Which future fsync will report a write failure?
Q7 Is a write failure logged in the syslog?
After Effects of fsync Failure:
Q8 Which block failures lead to file-system unavailability?
Q9 How does unavailability manifest? Does the file system shutdown, crash, or remount in read-only mode?
Q10 Does the file suffer from holes or block overwrite failures? If so, in which parts of a file can they occur?
Recovery:
Q11 If there is any inconsistency introduced due to fsync failure, can fsck detect and fix it?
0x01 实例
对于上面的问题,Paper中测试了几个常见的FS,发现这样的一些东西,总结到了下面的表格中,
-
对于ext4的ordered模式下面。Single Block Update的操作,写入的一个block先写到了page cache中。第一个fsync导致的写data block故障了不会导致更新metadata的日志写入到日志中,但是写入的block会被标记为clean。但是前面的write操作实际上将这个block写脏了。虽然这里metadata更新的操作不会被写入日志,但是后面的fsync和其它的操作会导致关于更新时间的却写入到日志中。这样的结果就是一个不一致,系统这个时候去读取会获取到新写入的数据,但是重启之后读取到旧的数据。当fsync失败是写一个 journal block失败的时候,会导致fs进入readonly的状态,后面的写入操作会失败。
-
ext4下面的Multi Block Append,写入一个data block失败时候同样会导致page cache中对应的block标记为clean。FS在执行metadata checkpoint操作的时候,会将inode table 和 block bitmap的更新写入到磁盘。即使是数据没有被实际写入,元数据也会引用到这些blocks。后面的write操作也会看到之前的错误,但是后面的操作会正常。这样读取的时候可能读取到一个block之前的数据而不是这次写入的数据。对于journal block写入的失败同样会导致fs进入readonly模式。ext4提供一些挂载参数来处理一些错误,paper中发现这些并没有什么用,
... to abort the journal if an error occurs in a file data buffer (mount option data_err=abort) and remount the file system in read-only mode on an error (mount option errors=remount-ro). However, we observe that the results are identical with and without the mount options. -
在data模式下面,ext4 fsync的一些错误处理和ordered下面类似,但是有一个区别。data模式下面数据也先写入日志,这样写data block错误的情况下也可能写入是成功的,这样对于上面的Single Block Update操作,可能是第二个fsync返回错误,而不是第一个。
-
在XFS下面的一些错误和ext4 ordered模式下面类似,也会有写入data block失败但是page cache中的dirty block被标记为clean的问题。XFS中写入journal block失败会导致fsync失败,但是写入metadata block失败则不会导致fsync失败。XFS的一些问题的处理上也和ext4有一些不同,比如写journal block故障之后,不是进入readonly模式而是任何的操作都会失败,即shutdown。另外写metadata block故障的时候,可以设置重试操作,超过设置的次数之后,也会使得fs shutdown。
-
XFS的Multi Block Append操作,第一个data block写入失败之后,后面的fsync操作就会失败,metadata也不会被写入到日志中。后面继续写入数据的时候,也会造成引用到一个前面失败写入操作的non-overwritten block。但是在XFS,最后面的一些写入失败不会和ext4中的问题,这里不会更新metdata。最后一个失败的append操作不会导致文件的size变化,但是可能其它的元数据字段变化,
Thus, while in ext4 a failed write always causes a non-overwritten block, in XFS, non-overwritten blocks cannot exist at the end of a file. However, for either file system, if the failed blocks remain in the page cache, applications can read those blocks regardless of whether they are in the middle or the end of a file. -
Btrfs在data block写入失败的时候,不会有ext4和XFS存在的问题,Btrfs可以恢复到之前的状态。在写入log tree故障的时候会导致fsync故障,而写入metadata故障会导致FS进入readonly模式,但是前面的fsync会成功。在Multi Block Append操作下面,第一个append操作失败之后,Btrefs会恢复到之前的状态,但是后面继续append操作时候,会导致这个文件出现一个hole。而且这里Btrfs deterministic block allocator 会下次分配的时候还是分配到这个block,如果这个写入故障时暂时的,结果就是产生了一个hole,否则的话后面的写入操作会继续失败。
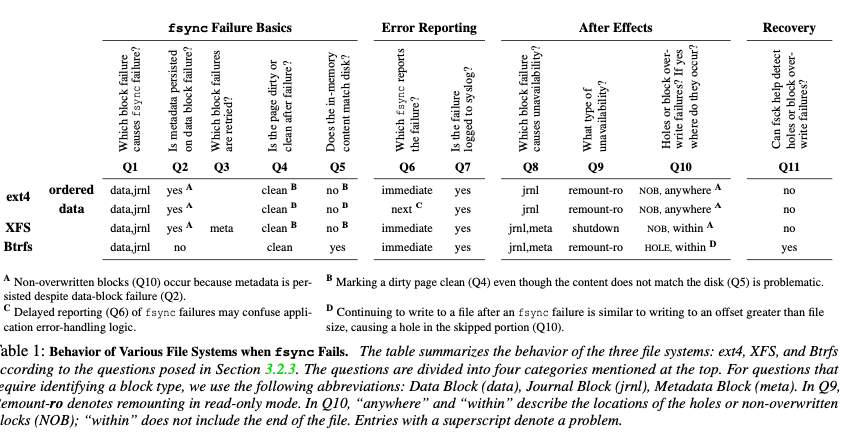
这里FS都会有写入data block时候导致将page cache中标记为clean的问题。可能和一些认为不同,这个并不是VFS层造成的,而是错误的clear_page_dirty_for_io使用方式。
0x02 Application Study
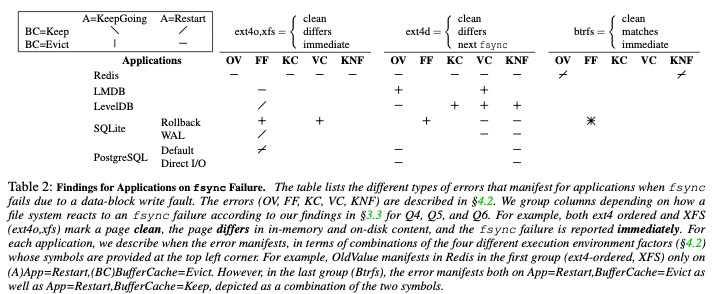
除了文件系统之前,这里还测试了几个存储系统(Redis (v5.0.7), LMDB (v0.9.24), LevelDB (v1.22), SQLite (v3.30.1), and PostgreSQL (v12.0))在处理fsync的策略,这里使用的是加入了错误注入的一个机遇FUSE的FS,称之为CuttleFS。这里的测试有Key-Value Store,也有关系型数据库。测试的时候都是当做KVS来使用,在诸如来多次错误注入之后,dump出来所有的key value pair,测试这里的数据。从这个测试中发现了这样的一些问题,
• OldValue (OV): The system returns the new value for a while but then reverts to an old value, or the system conveys a successful response but returns the old value later on.
• FalseFailure (FF): The system informs the user that the operation failed but returns the new value in the future.
• KeyCorruptions (KC) and ValueCorruptions (VC): Corrupted keys or values are obliviously returned.
• KeyNotFound (KNF): The system informs the user that it has successfully inserted a key but it cannot be found later on, or the system fails to update a key to a new value but the old key-value pair disappears as well.
在错误注入之后,app的错误处理策略一般有这样的一些,
App=KeepGoing: The application continues without restarting.
App=Restart: The application restarts either after a crash or a graceful shutdown. This forces the application to rebuild in-memory state from disk.
BufferCache=Keep: No evictions take place.
BufferCache=Evict: One or more clean pages are evicted.
对于不同的app,发现了这样的一些行为,
- Redis,Redis没有处理fsync失败的问题,认为下层的存储是可靠的。Redis中各种错误都可能发生;
- LMDB,LMDB使用一些CoW的策略,处理得比Redis好。可能发生一些ValueCorruptions的错误( ValueCorruptions and OldValue errors occur on BufferCache=Evict, regardless of whether the application restarts or not)。
- LevelDB,可能有FalseFailures错误(only on App=Restart with BufferCache=Keep)。FalseFailures错误是因为写入log entry失败的时候给用户返回错误,重启的时候,log entry还在page cache中,LevelDB会从这些entries中创建SST文件,而导致。在log file有问题的时候,可能有KeyNotFound 和 OldVersion 错误(BufferCache=Evict and App=Restart, LevelDB rejects the corrupted log entry and returns the old value for future read operations)。
- SQLite,在rollback journal模式和SQLite WAL模式下面都可能发生错误,WAL模式下面表现更好一些;
- PostgreSQL,在下面的table中看来,PostgreSQL是表现得最好的。在default模式即WAL使用page cache的情况下,可能有FalseFailure的问题。 和前面的app一样,OldVersion 和 KeyNotFound Error其实一般由同样的原因导致,错误不同看key之前存在与否。在使用DirectIO模式下面,WAL不使用page cache,不会有FalseFailures的错误。
0x03 Discussion
根据上面的一些测试,Paper在最后给出了一些关于如何处理fsync错误的一些discussion,
-
Existing file systems do not handle fsync failures uniformly,现在的文件系统都没有很好地处理fsync错误,每个文件系统都有些区别,不同的模式下面的也有区别;
-
Copy-on-Write file systems such as Btrfs handle fsync failures better than existing journaling file systems like ext4 and XFS,CoW的文件系统处理这些问题更好一些,上面的table也显示了在Btrfs下面app发生错误的可能是最少的;
-
Ext4 data mode provides a false sense of durability,ext4提供的一致只是对于fs本身而言的,应用不能知道从fsync中接受到的错误是前面那一次操作导致的;
-
Existing file-system fault-injection tests are devoid of workloads that continue to run post failure,
We believe that file-system developers should also test workloads that continue to run post failure, and see if the effects are as intended. -
Application developers write OS-specific code, but are not aware of all OS-differences,
We hope that the Linux file-system maintainers will adopt a similar approach in an effort to han- dle fsync failures uniformly across file systems. Note that it is also important to think about when to classify whether a device has been removed. -
Application developers do not target specific file systems;
-
Applications employ a variety of strategies when fsync fails, but none are sufficient,这些app处理fsync错误的策略都有一些问题;
-
Applications run recovery logic that accesses incorrect data in the page cache,恢复操作的时候最好避免从page cache中读取数据,而是读磁盘上面的内容;
-
Application recovery logic is not tested with low level block faults。
参考
- Can Applications Recover from fsync Failures?, ATC ‘20.
